A small amount of compressive strain turns a nonmetallic form of tin into a 3D topological Dirac semimetal—a kind of “supermetal” with very high electron mobility. With its rich topological phase diagram, the material shows promise for both novel physics and eventual device applications. Read more »![]()
![]()
All News & Updates
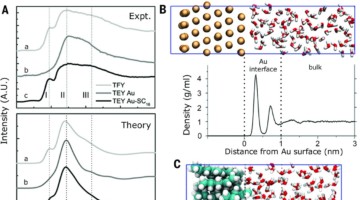
Electronic Phase Separation and Dramatic Inverse Band Renormalization in the Mixed-Valence Cuprate LiCu2O2
Angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy was used to measure the electronic structure of LiCu2O2, a mixed-valence cuprate where planes of Cu(I) (3d10) ions are sandwiched between layers containing one-dimensional edge-sharing Cu(II) (3d9) chains. Read more »
ALS User Forum Returns on Thursdays
The User Forum, also known as “Cookie Time,” has returned to the ALS. Every other Thursday at 3 p.m., ALS users and staff are invited to mix and mingle in the downstairs lobby over cookies and coffee. The ALS operating schedule lists specific dates for the events. Read more »
Modulating Infrared Light with 2D Black Phosphorus
Two-dimensional materials represent a promising new frontier in the field of optoelectronics. Most progress so far, however, has been in the visible-light range. Now, at the ALS, researchers have measured the infrared transmission spectra of ultrathin samples of black phosphorus under an applied electric field. Read more »![]()
![]()
ALS Workshop Brings Together Theory and Experiment
On April 13 the ALS convened a workshop entitled “Soft X-Ray Spectroscopy: Theory and Experiment, Hand-in-Hand.” The event brought together soft x-ray experimentalists and materials theorists to discuss potential collaborations and areas of soft x-ray spectroscopy that would benefit from more robust theory. Read more »
New Insights into Nanoscale Deformation
A group of scientists used Laue x-ray microdiffraction at the ALS to probe plastic deformation mechanisms at the nanoscale. Their findings may overturn conventional theory and reshape our understanding of the mechanical behavior of a host of nanocrystalline metals. Read more »
Ingrid Hallsteinsen, Magnetic Spectroscoper
Ingrid Hallsteinsen is a postdoctoral researcher at ALS Beamline 4.0.2, the magnetic spectroscopy and scattering beamline, where she is currently studying magnetism in oxide thin films. Read more »
Tribute to E.O. Lawrence Moves into ALS Lobby
There’s some new artwork gracing the ALS lobby—a stately portrait of Berkeley Lab founder Ernest Orlando Lawrence. The painting has a deep connection to the Lab, and so does the artist. He was a longtime Berkeley Lab employee and the father of Berkeley Lab Mechanical Technician Jim Dougherty, who frequently works on the undulators at the ALS. Read more »
COSMIC Achieves First Light
On Wednesday, March 29, the COherent Scattering and MICroscopy (COSMIC) Beamline (7.0.1) achieved first light, a significant milestone in the ALS’s plans to capitalize on recent gains in soft x-ray coherence provided by modern storage-ring light sources. Read more »
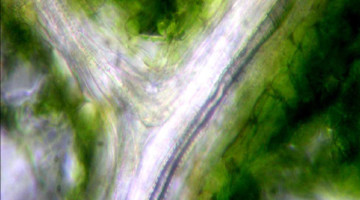
3D Visualization of Leaves during Drought
The veins of living leaves at increasing levels of drought stress were visualized using x-ray microtomography. The results expand our view of leaf drought responses, beyond the traditional embolism-centric view, to a broader focus on the role of the surrounding living tissues in water movement during drought. Read more »
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- …
- 140
- Next Page »