The User Office is accepting new General User Proposals (GUPs) from scientists who wish to conduct research at the ALS in the August-December 2017 cycle. The deadline for submission is March 1, 2017. Read more »
All News & Updates
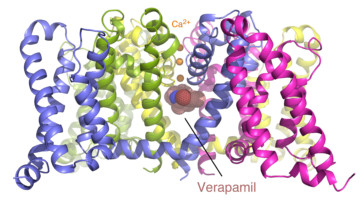
Two Basic Mechanisms of Cardiovascular Drugs
The structures of proteins controlling calcium-ion transport through cell membranes have been revealed, bound to two drugs known as calcium channel blockers. The discovery might accelerate the development of safer and more effective drugs for treating cardiovascular disorders such as high blood pressure, chest pain, and irregular heartbeat. Read more »![]()
![]()
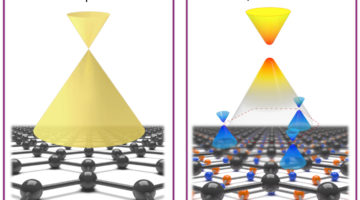
Altered States in Graphene Heterostructures
ARPES directly reveals for the first time how electronic states are altered when epitaxial graphene is deposited on a substrate of hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN). The interaction between the materials in this heterostructure greatly improves its suitability for advanced, ultralow-power device applications. Read more »![]()
![]()
Magnetism Emerges at Wonky Interfaces
Researchers have found a new way to control magnetism at the atomic level that will serve as a model for studying emergent phenomena in other systems. The ability to engineer and tune properties on such small length scales can (eventually) enable us to design exciting new magnetic devices. Read more »
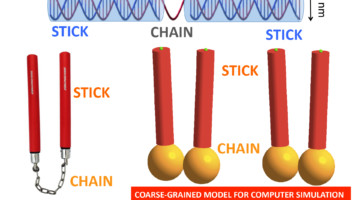
The Smectic Phase of DNA “Nano-Nunchaku”
Researchers designed DNA sequences that self-assemble into a nanoparticle about 50 nm long, composed of two double-stranded DNA duplexes linked together by a single-stranded DNA filament. The nanoparticle resembles nunchaku—a traditional weapon of several martial arts—but 30 million times smaller. Read more »
Chemistry on the Edge: Study Pinpoints Most Active Areas of Reactions on Nanoscale Particles
Experiments confirm that structural defects at the periphery are key in catalyst function. The SINS study is an important step in chronicling how the atomic structure of nanoparticles impacts their function as catalysts in chemical reactions. Read more »
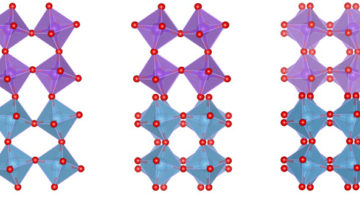
New Multiferroic Material for Ultralow-Power Electronics
Scientists paired ferroelectric and ferrimagnetic materials so that their alignment can be controlled with a small electric field at near room temperatures, a major step in the development of ultralow-power microprocessors, storage devices, and next-generation electronics. Read more »![]()
![]()
Exploring the Structure of Aqueous Solutions with SALSA
Researchers have published a series of papers that open up the possibility of probing hydrogen bonds in aqueous solutions by combining x-ray emission spectroscopy and resonant inelastic soft x-ray scattering, using the specialized Solid and Liquid Spectroscopic Analysis (SALSA) endstation at Beamline 8.0.1. Read more »
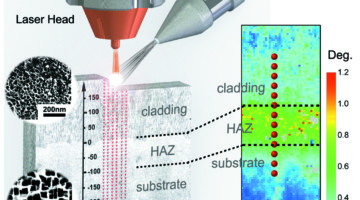
X-Rays Help Evaluate Quality of 3D-Printed Repairs
Laser 3D printing is a promising way to repair machine parts (such as jet-engine turbine blades) made of single-crystal superalloys. But microstructural inhomogeneities created by the high-power laser are a major reliability concern, so researchers employed x-ray Laue microdiffraction to probe the microstructure. Read more »
Fernando Sannibale, Division Deputy for Accelerator Operations and Development
Fernando Sannibale, previously the principal investigator of the Advanced Photoinjector Experiment (APEX) at LBNL, has recently taken on a new role as leader of the ongoing ALS Accelerator Physics program in the Accelerator Technology and Applied Physics Division and will also serve as the ALS Division Deputy for Accelerator Operations and Development. We recently sat down with Sannibale to talk about his years at the ALS and what he hopes to accomplish in his new role. Read more »
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- …
- 139
- Next Page »