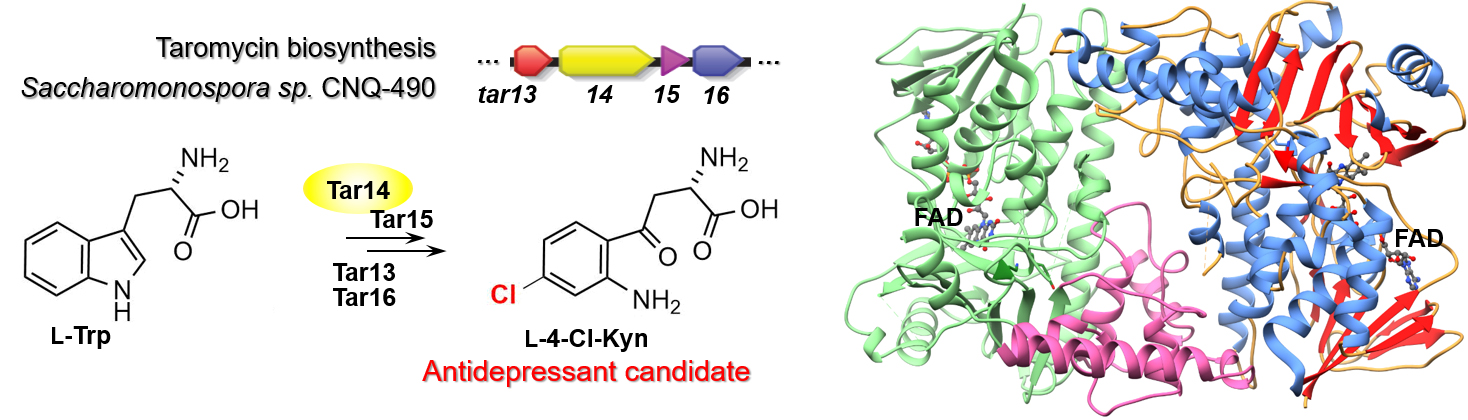
Beyond the 20 amino acids commonly found in proteins, there are hundreds of other (“non-proteinogenic”) amino acids in nature, representing an untapped resource for chemical diversity and drug design. For example, a non-proteinogenic amino acid, ʟ-4-chlorokynurenine, is in clinical trials for the treatment of major depressive disorder and suicidal ideation. It also shows promise in the treatment of neuropathic pain, epilepsy, Parkinson’s and Huntington’s diseases.
To date, antibiotics taromycin A and B from the marine bacterium Saccharomonospora sp. remain the only characterized natural chemicals that contain ʟ-4-chlorokynurenine. Recently, a group of researchers discovered four genes from the taromycin biosynthetic gene cluster that encode the biosynthesis of ʟ-4-chlorokynurenine. Using genetic, biochemical, structural, and chemical analyses, the researchers replicated the natural three-step conversion of ʟ-tryptophan to ʟ-4-chlorokynurenine. The ultimate goal is the scalable bioproduction of ʟ-4-chlorokynurenine either through bacterial fermentation or chemoenzymatic synthesis—more efficient and sustainable processes than chemical synthesis. This work also opens up opportunities for treating neurological disorders through the engineering of a probiotic strain capable of controllable production of ʟ-4-chlorokynurenine within the gut.
Of particular interest was Tar14, a tryptophan flavin-dependent halogenase (TFH) that catalyzes the chlorination of ʟ-tryptophan. This type of enzyme is under development for industrial halogenation of small aromatic molecules. Another interesting aspect of Tar14 was its generous substrate promiscuity and ability to generate dihalogenated tryptophans. The researchers solved the structure of Tar14 in complex with its cofactor FAD using protein crystallography at ALS Beamline 8.2.1. Structural comparisons with related enzymes highlighted conserved features of the putative active site and FAD binding and revealed the existence of two structural subtypes of C6 TFHs.
H. Luhavaya, R. Sigrist, J.R. Chekan, S.M.K. McKinnie, and B.S. Moore, “Biosynthesis of ʟ‐4‐Chlorokynurenine, an Antidepressant Prodrug and a Non‐Proteinogenic Amino Acid Found in Lipopeptide Antibiotics,” Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 58, 8394 (2019), doi:10.1002/anie.201901571.