Researchers use the ALS to confirm the structure of an engineered immune protein that could open new opportunities to treat inflammatory bowel disease. Read more »
ALS Work Using Protein Crystallography
Protein crystallography is used for determining the molecular structure of proteins. Crystallized protein molecules cause a beam of incident x-rays to scatter in many directions, with constructive and destructive interference generating a diffraction pattern. By analyzing these patterns, a crystallographer can produce a three-dimensional picture of the density of electrons within the crystal and thus determine the protein's structure.
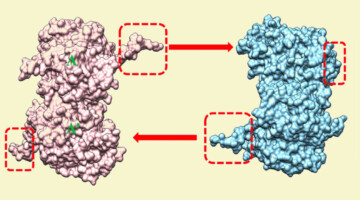
Deep-Dive Inspection of a Molecular Assembly Line
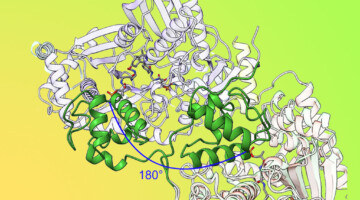
By locking down certain movable parts of a modular drug-building protein, researchers learned new details about how carrier proteins transfer the product protein between modules. The results offer insights that could enable scientists to design and create new and improved medicines, such as antibiotics, using synthetic biology. Read more »![]()
![]()
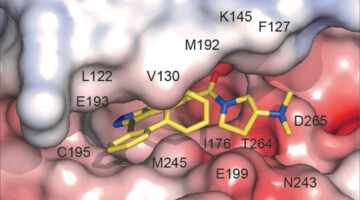
Identification of Structurally Novel KRASG12C Inhibitors through Covalent DNA-Encoded Library Screening
DNA-encoded library (DEL) technology was used to prepare a ~1.6 × 107-compound cysteine-reactive library (representative component shown at bottom, cysteine-reactive site indicated). Screening this library against the KRASG12C oncoprotein identified multiple structurally novel inhibitors of this challenging-to-drug target (e.g., frontmost green compound in the X-ray structure at right, covalent bond to KRASG12C indicated). Read more »
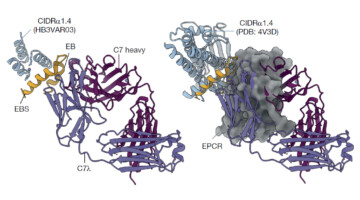
Identification and Structural Characterization of Antibodies for Severe Malaria
Researchers used x-ray crystallography at the ALS to characterize how two newly discovered antibodies prevent the protein interactions responsible for severe malaria. Understanding this mechanism offers novel insights for vaccine development. Read more »![]()
![]()
Structure of the human autophagy factor EPG5 and the molecular basis of its conserved mode of interaction with Atg8-family proteins
The study reports the first structure of human EPG5 (HsEPG5) determined by cryo-EM and AlphaFold2 modeling. Read more »
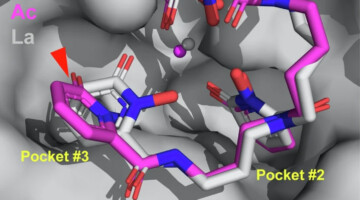
A Macromolecular Scaffold for Probing Actinium Chemistry
By encapsulating actinium atoms within a macromolecular complex for analysis using protein crystallography, researchers discovered that actinium has a unique solid-state bonding configuration. A better understanding of actinium behavior could help improve a promising cancer treatment known as targeted alpha therapy. Read more »![]()
![]()
Protein Pioneer: Enabling Scientists to Design Novel Proteins for the Future
The 2024 Nobel Prize in Chemistry was awarded to David Baker, Demis Hassabis, and John M. Jumper for the development of protein structure prediction and design. At the ALS, Baker leveraged high-throughput small-angle x-ray scattering (SAXS) and protein crystallography capabilities to design novel proteins and pave a new pathway for science, technology, and the environment. Read more »
A Promising Compound for Reversible Male Contraception
Researchers found that a small-molecule protein inhibitor—screened from billions of compounds and analyzed using structural insights from protein crystallography—reversibly suppresses male fertility in mice. The work addresses the pressing need for more contraceptive options that enable all individuals to control their own fertility. Read more »![]()
![]()
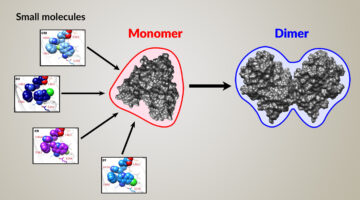
Time-Resolved SAXS Screen of Small-Molecule Drug Candidates
Time-resolved, high-throughput, small-angle x-ray scattering improved the screening of small-molecule drug candidates, providing insight into how they stimulate structural transitions in protein targets. The work will speed the discovery of treatments designed to activate biomolecular dynamics associated with desired therapeutic outcomes. Read more »![]()
![]()
Mechanistic Insight into a Viral-Factory Component
Recent protein-structure studies conducted at the ALS provided mechanistic insights into the function of a protein (σNS) involved in viral replication. Understanding these mechanisms will foster the development of therapeutic strategies against viruses that use σNS-like proteins to replicate. Read more »
- 1
- 2
- 3
- …
- 15
- Next Page »