 Local Disorder Impacts a Quantum Material’s Electronic States February 24, 2026 - Machine learning tools and experiments at the ALS enabled the identification of defect-rich regions in single-crystalline Co3Sn2S2 that link to how surface electrons move. Atom-level understanding of how the surface electronic properties of a magnetic semimetal can be tuned could guide its use in advanced technologies like spintronics and catalysis. Read more »
Local Disorder Impacts a Quantum Material’s Electronic States February 24, 2026 - Machine learning tools and experiments at the ALS enabled the identification of defect-rich regions in single-crystalline Co3Sn2S2 that link to how surface electrons move. Atom-level understanding of how the surface electronic properties of a magnetic semimetal can be tuned could guide its use in advanced technologies like spintronics and catalysis. Read more » Aerosol Chemistry Offers Clues to the Arctic’s Future February 24, 2026 - Researchers used scanning transmission x-ray microscopy to analyze Arctic aerosols, which strongly influence cloud formation and overall climate. Understanding what these particles are and how they change as they travel could help improve climate models and yield more accurate predictions of the changing Arctic environment’s global impact. Read more »
Aerosol Chemistry Offers Clues to the Arctic’s Future February 24, 2026 - Researchers used scanning transmission x-ray microscopy to analyze Arctic aerosols, which strongly influence cloud formation and overall climate. Understanding what these particles are and how they change as they travel could help improve climate models and yield more accurate predictions of the changing Arctic environment’s global impact. Read more »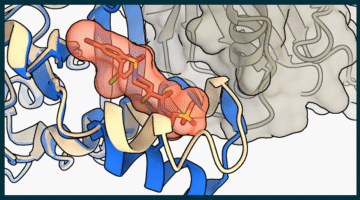 Disrupting Cancer’s Broken Molecular Switch February 24, 2026 - Researchers identified a compound that disrupts a hard-to-target tumor growth pathway in breast, lung, and other cancers and used the ALS to characterize the chemical interactions critical to its potency. This work contributed to the development of a similar compound currently undergoing clinical trials in cancer patients, and informs hypotheses for designing better drug candidates. Read more »
Disrupting Cancer’s Broken Molecular Switch February 24, 2026 - Researchers identified a compound that disrupts a hard-to-target tumor growth pathway in breast, lung, and other cancers and used the ALS to characterize the chemical interactions critical to its potency. This work contributed to the development of a similar compound currently undergoing clinical trials in cancer patients, and informs hypotheses for designing better drug candidates. Read more »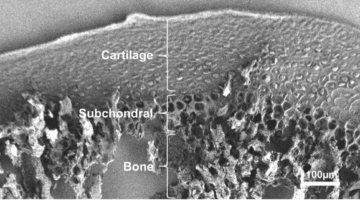 How Zinc Alters Mineral Structure in Early Arthritis February 24, 2026 - Using high-resolution x-ray techniques, researchers from UCSF, the ALS, and SSRL uncovered structural evidence that zinc subtly alters bone mineral in vulnerable joint regions, revealing early changes that may explain how arthritis begins and progresses. Read more »
How Zinc Alters Mineral Structure in Early Arthritis February 24, 2026 - Using high-resolution x-ray techniques, researchers from UCSF, the ALS, and SSRL uncovered structural evidence that zinc subtly alters bone mineral in vulnerable joint regions, revealing early changes that may explain how arthritis begins and progresses. Read more »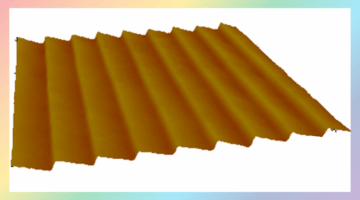 Thin-Film Coating Boosts X-Ray Instrument Performance January 27, 2026 - Optimized thin films doubled the efficiency of gratings in x-ray experiments at the ALS. The atoms-thick copper and gold layers let the grooved surfaces deliver energy that had previously been lost to absorption in the diffraction gratings, which are key elements in x-ray spectroscopy. Read more »
Thin-Film Coating Boosts X-Ray Instrument Performance January 27, 2026 - Optimized thin films doubled the efficiency of gratings in x-ray experiments at the ALS. The atoms-thick copper and gold layers let the grooved surfaces deliver energy that had previously been lost to absorption in the diffraction gratings, which are key elements in x-ray spectroscopy. Read more »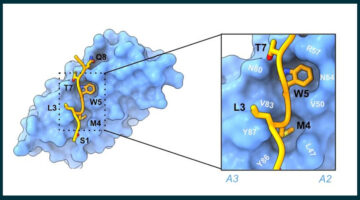 AI Delivers Rapid, Precise Design of Tumor-Targeting Protein January 27, 2026 - A new protein designed using AI can precisely recognize a key therapeutic target for cancer. X-ray crystallography data collected at the ALS confirmed the new protein’s specificity for its target, demonstrating a configurable and scalable approach to cancer therapy. Read more »
AI Delivers Rapid, Precise Design of Tumor-Targeting Protein January 27, 2026 - A new protein designed using AI can precisely recognize a key therapeutic target for cancer. X-ray crystallography data collected at the ALS confirmed the new protein’s specificity for its target, demonstrating a configurable and scalable approach to cancer therapy. Read more »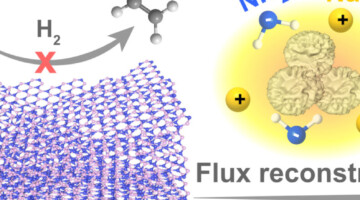 The Goldilocks of Ethylene Purification January 27, 2026 - Researchers engineered defects in boron nitride to develop a metal-free route for purifying ethylene to remove acetylene. The ALS shed light on how the engineered defects were responsible for exceptional selectivity. Read more »
The Goldilocks of Ethylene Purification January 27, 2026 - Researchers engineered defects in boron nitride to develop a metal-free route for purifying ethylene to remove acetylene. The ALS shed light on how the engineered defects were responsible for exceptional selectivity. Read more »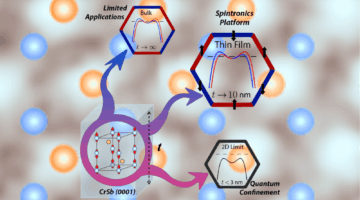 Altermagnetism All the Way Down January 27, 2026 - Altermagnets are an emerging class of magnetic materials that offer the potential for energy-efficient, high-density memory chips. Researchers at Penn State, UC Santa Barbara, and the ALS demonstrated that characteristic altermagnetic band splitting in chromium antimonide is evident in thin films relevant for real-world device application. Read more »
Altermagnetism All the Way Down January 27, 2026 - Altermagnets are an emerging class of magnetic materials that offer the potential for energy-efficient, high-density memory chips. Researchers at Penn State, UC Santa Barbara, and the ALS demonstrated that characteristic altermagnetic band splitting in chromium antimonide is evident in thin films relevant for real-world device application. Read more »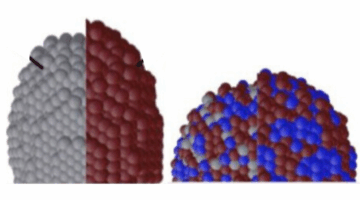 Dynamic Surface Restructuring in Ag–Cu Boosts CO2 Conversion December 10, 2025 - Multimodal in situ x-ray experiments at the ALS revealed how copper–silver nanoparticle catalysts evolve during CO2 photoreduction. The findings, which demonstrate dynamic catalyst restructuring at the atomic level, provide crucial insights for enhancing the selectivity and efficiency of CO2 conversion into high-value chemicals. Read more »
Dynamic Surface Restructuring in Ag–Cu Boosts CO2 Conversion December 10, 2025 - Multimodal in situ x-ray experiments at the ALS revealed how copper–silver nanoparticle catalysts evolve during CO2 photoreduction. The findings, which demonstrate dynamic catalyst restructuring at the atomic level, provide crucial insights for enhancing the selectivity and efficiency of CO2 conversion into high-value chemicals. Read more » Ancient Asteroid Provides Evidence of Amino Acid Precursors December 10, 2025 - Researchers identified nitrogen-rich compounds in samples from the asteroid Bennu, returned to Earth by NASA’s OSIRIS-REx mission. The results support the idea that asteroids like Bennu may have delivered the essential chemical building blocks of life to Earth in the distant past. Read more »
Ancient Asteroid Provides Evidence of Amino Acid Precursors December 10, 2025 - Researchers identified nitrogen-rich compounds in samples from the asteroid Bennu, returned to Earth by NASA’s OSIRIS-REx mission. The results support the idea that asteroids like Bennu may have delivered the essential chemical building blocks of life to Earth in the distant past. Read more »