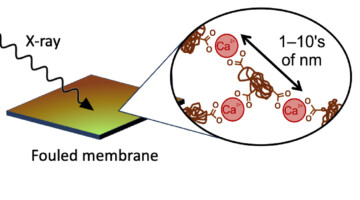
Membrane filtration offers a cost-effective, energy-efficient approach to purify and desalinate water, but fouling limits the performance of these devices. A new study explored the new experimental design that allows one to study the dynamic fouling process in real time to improve the field’s understanding of how materials deposit, accumulate, and/or crystallize on the membrane’s surface. Read more »![]()
![]()
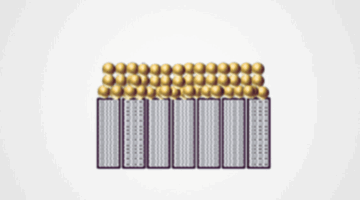
Advancing high-temperature electrostatic energy storage via linker engineering of metal–organic frameworks in polymer nanocomposites
High-performance, thermally resilient polymer dielectrics are essential for film capacitors used in advanced electronic devices and renewable energy systems, particularly at elevated temperatures where conventional polymers fail to perform. Herein, we unravel the untapped potential of UiO-66 metal–organic framework (MOF) derivatives as exceptional nanofillers for tuning the properties of the widely used polyetherimide (PEI). Read more »
Two-dimensional perovskite templates for durable, efficient formamidinium perovskite solar cells
When the lattice-matched 2D perovskite BA2FAPb2I7 (red) is incorporated into a yellow-phase FAPbI3 matrix (yellow), the 2D crystallites present a perovskite-like surface, which serves as a template for the FAPbI3 to convert to its photoactive phase (black). The resulting phase-stabilized FAPbI3 shows substantially improved optoelectronic properties and exceptional stability under 85°C and sunlight. Read more »
How Bulky Molecules Improve Next-Generation Solar Cells
Adding “bulky” organic molecules earlier in solar-film synthesis slows crystal growth, leading to the formation of a protective surface layer that improves durability and efficiency. These next-gen materials could revolutionize solar-cell technology, offering increased efficiency, lower cost, lighter weight, and flexible solar modules. Read more »![]()
![]()
An Organic Transistor That Can Sense, Process, and Remember
Traditional AI hardware employs physically separated information sensing, processing, and memory architecture, a configuration that suffers from large energy and time overhead. Now, researchers have fabricated an organic transistor device that can simultaneously act as the sensor and processing core of a streamlined AI hardware system. Read more »
Keeping Water-Treatment Membranes from Fouling Out
When you use a membrane for water treatment, junk builds up on the membrane surface—a process called fouling—which makes the treatment less efficient. In this work, researchers studied how membranes are fouled by interactions between natural organic matter and positively charged ions commonly found in water. Read more »
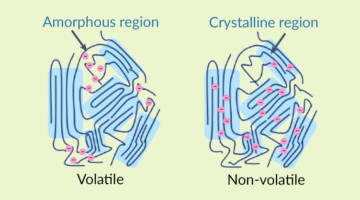
Electric Vehicle Batteries Could Get Big Boost With New Polymer Coating
Scientists have developed a conductive polymer coating—called HOS-PFM—that conducts both electrons and ions at the same time. This ensures battery stability and high charge/discharge rates while enhancing battery life. The coating also shows promise as a battery adhesive that could extend the lifetime of a lithium-ion battery from an average of 10 years to about 15 years. Read more »
Surface Charge and Nanoparticle Chromophore Coupling to Achieve Fast Exciton Quenching and Efficient Charge Separation in Photoacoustic Imaging (PAI) and Photothermal therapy (PTT)
Organic semiconductor nanoparticles (OSNs) convert absorbed light into heat, and are commonly used in photothermal therapy and photoacoustic imaging. Here, the OAN, Y6, is shown to form strong intermolecular packing, manipulated by surface charge under restrained sizes, yielding new pi-pi stacking and fast exciton quenching. The temperature of the tumor area can rise to more than 70 degrees under NIR irradiation, which can effectively ablate a tumor. Read more »
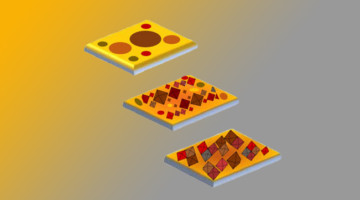
Versatile Sequential Casting Processing for Highly Efficient and Stable Binary Organic Photovoltaics
Ideal bulk heterojunction morphology is critical in organic solar cells (OSCs). Here, researchers show how sequential casting improves device performance in both fullerene- and nonfullerene-based systems, in which the donor and acceptor are deposited sequentially. The film spin-coating method is analogous to the traditional Chinese pancake-making process. Read more »
A Split-Screen View of Solar-Cell Crystallization
Researchers simultaneously monitored both the structure and function of a photovoltaic material as it crystallized from solution. The work raises the prospect of rationally tuning materials for optimal performance in photovoltaics and other light-manipulating devices, including light-emitting diodes, detectors, and lasers. Read more »![]()
![]()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- Next Page »