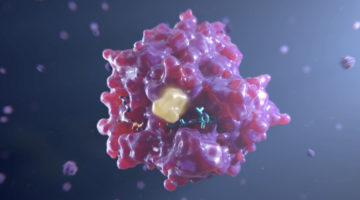
In the fight against SARS-CoV-2, scientists have been working on identifying neutralizing antibodies that could be used in preventative treatments or as post-exposure therapies. The latest findings, which include data from the ALS, indicate that antibodies from SARS survivors could potently block entry of SARS-CoV-2 into host cells. Read more »![]()
Study Leads to Firmer Grasp of Biochemical “Reactive Handle”
Protein crystallography provided new insight into a functional group of molecules that, if added to bacterial enzymes, could enable a variety of alterations to the bacteria’s polymer output. Tweaking enzymes to produce these “reactive handles” is a first step toward biosynthesizing diverse polymers with tailored properties. Read more »
Assembly Lines for Designer Bioactive Compounds
Researchers successfully bioengineered changes to a molecular “assembly line” for bioactive compounds, based in part on insights gained from small-angle x-ray scattering at the ALS. The ability to re-engineer these assembly lines could improve their performance and facilitate the synthesis of new medically useful compounds. Read more »![]()
![]()
Staff at Berkeley Lab’s X-Ray Facility Mobilize to Support COVID-19-Related Research
X-rays allow researchers to map out the 3D structure of proteins relevant to diseases at the scale of molecules and atoms, and the ALS has been recalled to action to support research related to COVID-19, the coronavirus disease that has already infected about 2 million people around the world. Read more »
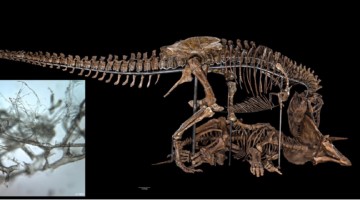
Survival of T. rex Microvascular Structures from Deep Time
Researchers used several analytical techniques at the ALS to demonstrate how soft-tissue structures may be preserved in dinosaur bones, countering long-standing scientific dogma that protein-based body parts cannot survive more than one million years. Read more »
X-ray Crystal Structures of the Influenza M2 Proton Channel Drug-Resistant V27A Mutant Bound to a Spiro-Adamantyl Amine Inhibitor Reveal the Mechanism of Adamantane Resistance
The M2 proton channel, shown with front and back monomer helices removed, is an anti-influenza drug target. Here, a bound inhibitor blocks the transport of protons through the V27A mutant channel. Read more »
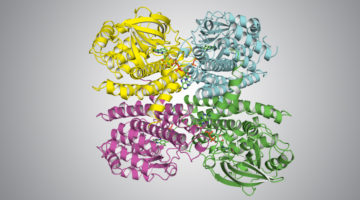
ALS Reveals Vulnerability in Cancer-Causing Protein
A promising anticancer drug, AMG 510, was developed by Amgen Inc. with the help of novel structural insights gained from protein structures solved at the ALS. AMG 510, which is currently in phase II clinical trials for efficacy, targets tumors caused by mutations in the KRAS protein, one of the most common causes of cancer. Read more »![]()
![]()
Berkeley Lab Helps Reveal How Dinosaur Blood Vessels Can Preserve Through the Ages
A team of scientists used infrared and x-ray imaging performed at the Advanced Light Source to determine the chemical mechanisms that allow soft tissue structures to persist in dinosaur bones—countering the long-standing scientific dogma that protein-based body parts can’t survive more than 1 million years. Read more »
X-Ray Technology Sheds New Light on Antibiotic Synthesis
Atomic-scale structural analyses performed at the ALS are helping scientists understand the inner workings of the enzyme “assembly lines” that microbes use to produce an important class of compounds, many of which have uses as antibiotics, antifungals, and immunosuppressants. Read more »
77Se NMR Probes the Protein Environment of Selenomethionine
Sulfur is critical for protein structure and function but lacks a sensitive isotope for nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) experiments. This can be circumvented by substituting sulfur with selenium, which has an NMR-compatible isotope (77Se). To enable interpretation of the NMR data, the structures of five of protein variants were solved by x-ray crystallography to a resolution of 1.2 Å. Read more »
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- …
- 24
- Next Page »