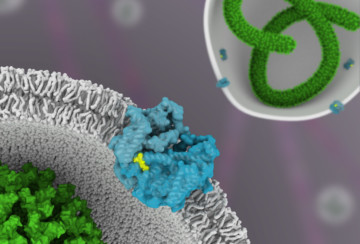
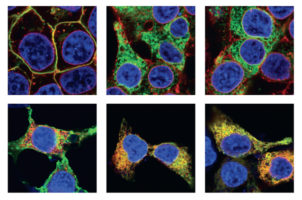
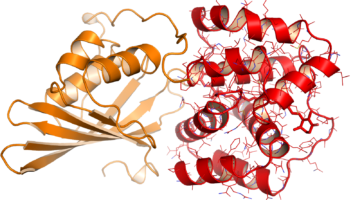
Researchers have used protein crystallography at the ALS to understand how a drug molecule that has shown some efficacy against Ebola in mice inactivates a membrane protein, called TPC1, used by viruses to infect host cells. Read more »![]()
![]()
Exploring the Repeat-Protein Universe
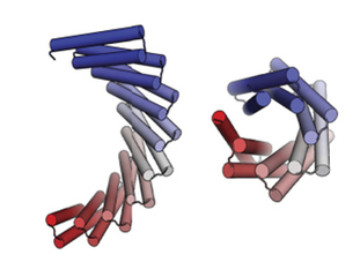
Researchers have published a landmark study that used both crystallography and SAXS to validate computationally designed structures of novel proteins with repeated motifs. The results show that the protein-folding universe is far larger than realized, opening up a wide array of new possibilities for biomolecular engineering. Read more »![]()
![]()
Improving Anti-Influenza Medications
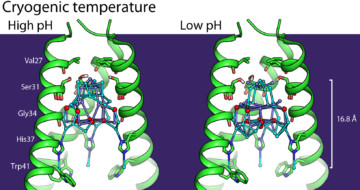
Protein crystallography at ALS Beamline 8.3.1 helped scientists understand the M2 proton-channel structure from the influenza A virus, an understanding that is needed to design better anti-influenza medications. Read more »
Improving Meningococcal Vaccines
Scientists have found a way to improve the stability of an essential antigenic protein to develop vaccines with higher efficacy for prevention of bacterial meningitis. Read more »
New Hope for Retinitis Pigmentosa Patients
Using FTIR microspectroscopy at the NSLS in Brookhaven and at ALS Beamline 1.4.3, scientists got a first glimpse into the structural changes that result from point mutations in opsin, one of the causes of retinitis pigmentosa. Read more »![]()
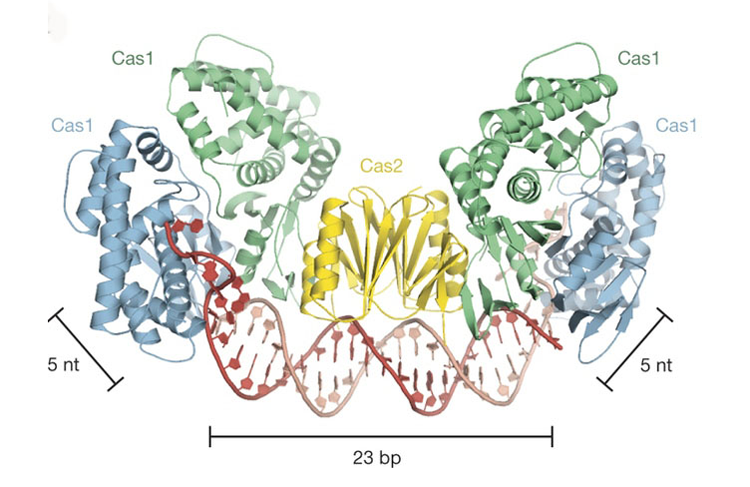
Foreign DNA Capture during CRISPR–Cas Adaptive Immunity
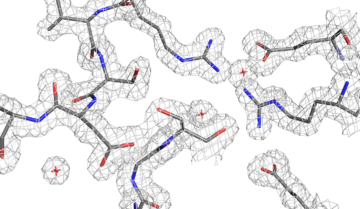
Using macromolecular crystallography at Beamline 8.3.1 at the ALS, Berkeley researchers discovered how CRISPR/Cas captures foreign DNA for the bacterial immune system. Read more »
A New Pathway for Radionuclide Uptake
Scientists have reported a major advance in understanding the biological chemistry of radioactive metals, opening up new avenues of research into strategies for remedial action in the event of possible human exposure to nuclear contaminants. Read more »![]()
![]()
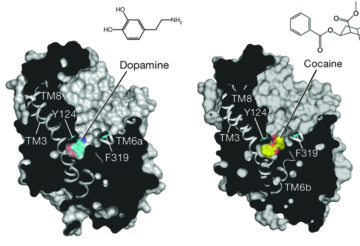
Binding Behavior of Dopamine Transporter Key to Understanding Chemical Reactions in the Brain
Scientists working at the ALS recently solved the crystallographic structures of several amine transporters in an effort to better understand why the human brain responds to chemicals like dopamine and serotonin. What they found will help in the design of drugs to treat many neurological diseases, and may also lead to a better understanding of how addiction to abused drugs such as cocaine can be managed. Read more »![]()
![]()
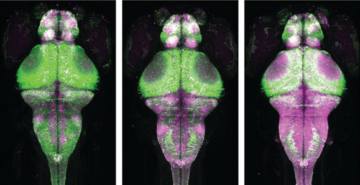
A Designed Protein Maps Brain Activity
A team of scientists designed and validated via x-ray crystallographic studies a fluorescent protein (CaMPARI) that allows the permanent marking of active brain cells. The protein was then used to study live changes via fluorescence in the active nerve cells in brains of fruit flies, zebrafish, and mice. Read more »![]()
![]()
Carotenoid Pigment Is the Key to Photoprotection
A technique newly available at the ALS has enabled the discovery of a surprising key event in photosynthetic systems. A protein shifting from an “orange” light-absorbing state to a “red” photoprotective state turns out to be an unanticipated molecular priming event in photoprotection. Read more »![]()