ALS research has shown that manganese reduction-oxidation (redox) reactions are an important factor in controlling the rate of plant debris decomposition. Understanding the role of manganese will help build better models to predict how litter decomposition rates—and thus nutrient cycling and the ecosystem carbon balance—may behave in future climate scenarios. Read more »![]()
![]()
New Hope for Retinitis Pigmentosa Patients
Using FTIR microspectroscopy at the NSLS in Brookhaven and at ALS Beamline 1.4.3, scientists got a first glimpse into the structural changes that result from point mutations in opsin, one of the causes of retinitis pigmentosa. Read more »![]()
Space Dust Analysis Could Provide Clues to Solar System Origins
New studies of space dust captured by NASA’s Stardust Interstellar Dust Collector have shown that interstellar particles may be much more complex in structure and composition than previously thought. Read more »![]()
![]()
Infrared Mapping Helps Optimize Catalytic Reactions
A pathway to more effective and efficient synthesis of pharmaceuticals and other flow-reactor chemical products has been opened by a study in which, for the first time, the catalytic reactivity inside a microreactor was mapped in high resolution from start to finish. Read more »![]()
![]()
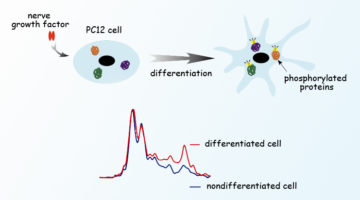
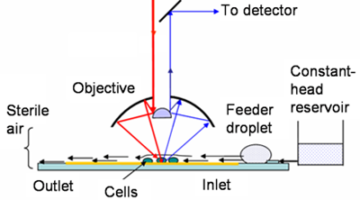
Tracking Living Cells as They Differentiate in Real Time
Berkeley Lab and University of California researchers have developed a new technique for monitoring protein phosphorylation inside single living cells, enabling them to follow live cellular chemical changes without bias and without harming the cells. Read more »![]()
![]()
Molecular Measurements of the Deep-Sea Oil Plume in the Gulf of Mexico
To study the effects of oil spilled from the Deepwater Horizon blowout, researchers collected deep-water samples from across the Gulf of Mexico and analyzied their physical, chemical, and microbiological properties using a variety of techniques, including SR-FTIR. Read more »![]()
![]()
Real-Time Chemical Imaging of Bacterial Biofilm Development
Almost all bacteria can form biofilms—dynamic communities of cells enclosed in self-produced matrices of polymers. Researchers have developed a robust and label-free method to probe the chemical underpinnings of developing bacterial biofilms. Read more »![]()
![]()
Extracellular Proteins Promote Zinc Sulfide Aggregation
Researchers from the ALS, Berkeley Lab’s National Center for Electron Microscopy (NCEM), and Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory analyzed biofilm samples rich in zinc sulfide and dominated by sulfate-reducing bacteria, which were collected from lead–zinc mine waters.
Read more »![]()
![]()
Particles from Comet 81P/Wild 2 Viewed by ALS Microscopes
NASA’s $200-million, seven-year-long Stardust mission returned to Earth thousands of tiny particles snagged from the coma of comet 81P/Wild 2. Four ALS beamlines and the researchers using them were among the hundreds of scientists and dozens of experimental techniques in facilities around the world that contributed to the preliminary examination of the first samples.
Read more »![]()
![]()