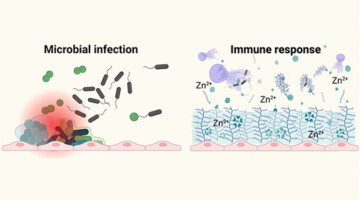
Matrix stones are an unusual type of soft kidney stone closely associated with the presence of bacteria from unchecked urinary tract infections. Researchers conducted a comprehensive study of surgically extracted matrix stones, work that highlights how host defense mechanisms against microbes can simultaneously encourage harmful stone formation. Read more »
Organic Matrix Derived from Host–Microbe Interplay Contributes to Pathological Renal Biomineralization
A composite image of a rare form of kidney stone, illustrating extensive organic filamentous networks abundant with immune response-related proteins such as calprotectin (displayed in red), myeloperoxidase (in yellow), and DNA molecules (in blue). Originating from intricate host-microbe interplay, these organic networks promote the heterogeneous nucleation and precipitation of inorganic particulates. Read more »
Decoupling the metal–insulator transition temperature and hysteresis of VO2 using Ge alloying and oxygen vacancies
The VO2 metal–insulator transition underpins applications in thermochromics, neuromorphic computing, and infrared vision. Ge alloying is shown to expand the stability of the monoclinic phase to higher temperatures, and by suppressing the propensity for oxygen vacancy formation, renders the hysteresis of the transition exquisitely sensitive to oxygen stoichiometry. Read more »
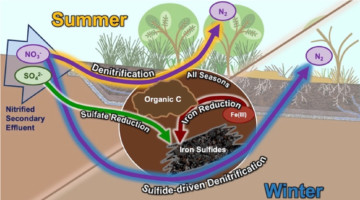
Removing Nitrogen from Wastewater using Horizontal Levees
Treated municipal wastewater often contains nitrogen, which has been linked to algal blooms that can devastate coastal ecosystems. In a recent study, researchers characterized the primary nitrogen-removal pathways in a horizontal levee, an engineered subsurface water-treatment system consisting of a gently sloping strip of land adjacent to storm-control levees. Read more »
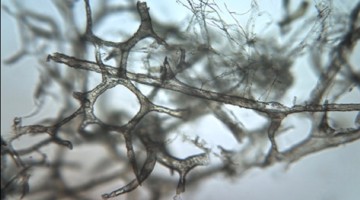
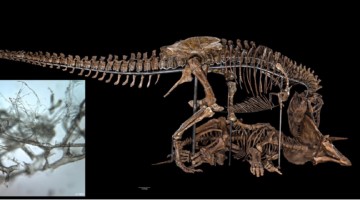
Survival of T. rex Microvascular Structures from Deep Time
Researchers used several analytical techniques at the ALS to demonstrate how soft-tissue structures may be preserved in dinosaur bones, countering long-standing scientific dogma that protein-based body parts cannot survive more than one million years. Read more »
Berkeley Lab Helps Reveal How Dinosaur Blood Vessels Can Preserve Through the Ages
A team of scientists used infrared and x-ray imaging performed at the Advanced Light Source to determine the chemical mechanisms that allow soft tissue structures to persist in dinosaur bones—countering the long-standing scientific dogma that protein-based body parts can’t survive more than 1 million years. Read more »
Molecular Framework Imparts Stability to Reactive Catalyst
Researchers have shown that a rigid metal–organic framework (MOF) can be used to stabilize core regions of a reactive catalyst that has potential for use in artificial photosynthesis. The framework immobilizes and preserves key reactive intermediates and affords a clearer view of how the catalyst’s structure correlates with function. Read more »
Catalyst Improves Cycling Life of Magnesium/Sulfur Batteries
Magnesium/sulfur batteries hold promise as a safer, energy-dense advancement, but previous iterations have suffered from extremely limited recharging capabilities. Studies at the ALS provided electrochemical insights into battery polarization and revealed how a titanium catalyst activates magnesium/sulfur compounds to improve battery performance. Read more »
Here Comes the Sun: A New Framework for Artificial Photosynthesis
Scientists have long sought to mimic the process by which plants make their own fuel using sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water through artificial photosynthesis devices, but exactly how catalysts work to generate renewable fuel remains a mystery. Now, a study has uncovered new insight into how to better control cobalt oxide, one of the most promising catalysts for artificial photosynthesis. Read more »
A facile route for the synthesis of heterogeneous crystal structures in hierarchical architectures with vacancy-driven defects via the oriented attachment growth mechanism
TiO2 nanorod arrays based on substrates with heterogeneous crystal structures and remarkable crystalline stability have potential as promising photocatalysts. Researchers synthesized a 1D anatase/rutile heterogeneous TiO2 crystal structure in a hierarchical architecture by forming hybrid organic–inorganic interfaces in a solution-based environment. Read more »