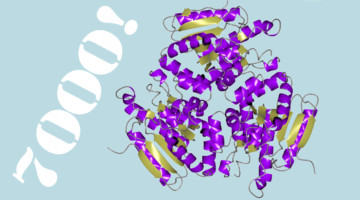
The eight structural biology beamlines at the ALS have now collectively deposited over 7000 proteins into the Protein Data Bank (PDB), a worldwide, open-access repository of protein structures. The 7000th ALS protein (entry no. 6C7C) is an enzyme from Mycobacterium ulcerans (strain Agy99), solved with data from Beamline 5.0.2. Read more »
Genentech Advances Research Toward Better Medicines to Lower Cholesterol
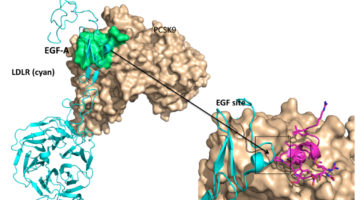
Genentech has been working in collaboration with the ALS for years with the goal of identifying a better cholesterol treatment mechanism that targets a cholesterol-regulating protein in the body known as PCSK9. Recent advances in understanding PCSK9’s structure have put them closer to that goal. Read more »![]()
NIH Grant Will Enhance Structural Biology Research Experience for ALS Users
A recently awarded National Institutes of Health (NIH) grant will help integrate existing structural biology resources at the ALS to better serve users. The funds will help establish a centralized collaborative mechanism, called ALS-ENABLE, that will guide users through the most appropriate routes for answering their biological questions. Read more »
A Bacterial Jigsaw Puzzle Is Solved
Bacterial microcompartments (BMCs) are hollow protein shells that encapsulate enzymes involved in bacterial metabolism. Crystallography studies have provided atomic-resolution views of a fully assembled BMC, revealing basic principles of shell construction for fighting pathogens or bioengineering applications. Read more »![]()
![]()
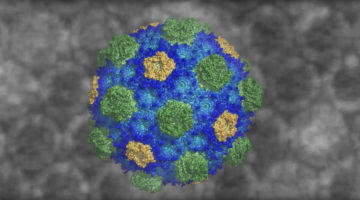
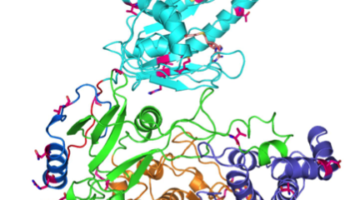
Structure of a Key Protein from the Zika Virus
The Zika virus (ZIKV) is a mosquito-borne pathogen recently linked to birth defects in infants. At the ALS, researchers have resolved the structure of a key ZIKV protein to 3.0 Å, an important step toward the rational design of drugs capable of disrupting viral functions and halting the spread of the disease. Read more »![]()
![]()
Study Sheds Light on How Bacterial Organelles Assemble
Scientists are providing the clearest view yet of an intact bacterial microcompartment (BMC), revealing the polyhedral structure and assembly of this organelle’s protein shell. Having the full structure can help provide important information in fighting pathogens or bioengineering bacterial organelles for beneficial purposes. Read more »
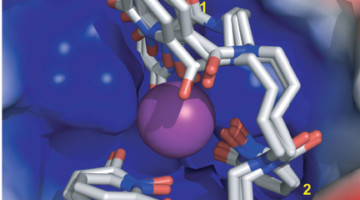
Protein Complex Shows Promise for Berkelium Separation
Scientists found that the element berkelium breaks form with its heavy-element peers by taking on an extra positive charge when bound to a synthetic organic molecule. This property could help scientists develop better methods for handling and purifying nuclear materials. Read more »
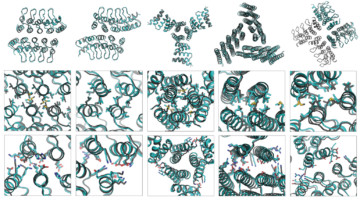
A Systematic Approach to Customizing Cyclic Proteins
Proteins consisting of identical subunits arranged symmetrically around a central axis (cyclic homo-oligomers) play key roles in many biological processes. Researchers have now developed a systematic approach to their design and demonstrated its accuracy using protein crystallography and small-angle x-ray scattering. Read more »
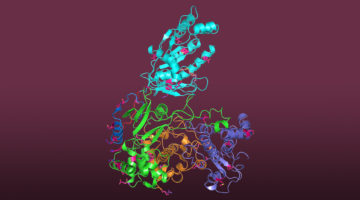
Researchers Gain Insight into Protein Critical to Zika Virus Reproduction
Zika virus is a mosquito-borne infectious disease linked to certain birth defects in infants. Scientists have mapped a key viral protein called NS5, which contains two enzymes: one reduces the body’s ability to mount an immune response against infection and the other helps start the genetic replication process. Read more »
How Berkelium Stands Out in a Heavy Metal Crowd
Using several spectroscopic techniques, scientists found that the element berkelium breaks form with its heavy-element peers by taking on an extra positive charge when bound to a synthetic organic molecule. This property could help scientists develop better methods for handling and purifying nuclear materials. Read more »
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- Next Page »