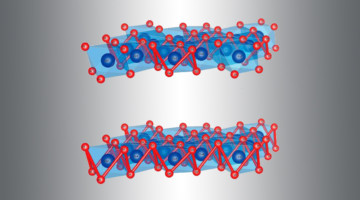
Fluoride ions show promise as charge carriers in batteries but have limited cyclability. Here we show the reversible and homogeneous topochemical insertion/deinsertion and bulk diffusion of F ions within the one-dimensional tunnels of submicrometer-sized FeSb2O4 particles at room temperature. Read more »
2020 Shirley Award to Honor Miquel Salmeron
By taking surface studies from ultrahigh vacuum to near-ambient pressure, Miquel Salmeron’s work at the ALS has had deep impact on a broad range of scientific questions, revealing the chemical, electronic, and mechanical properties of surfaces and interfaces on the nanometer (and often atomic) scale. Read more »
Seeing ‘Under the Hood’ in Batteries
To push battery performance, researchers want to learn how the individual ingredients of battery materials behave beneath the surface. But many techniques only scratch the surface of what’s at work inside batteries. A high-sensitivity x-ray technique is attracting a growing group of scientists because it provides a deeper, more precise dive into battery chemistry. Read more »
Full Energy Range Resonant Inelastic X-ray Scattering of O2 and CO2: Direct Comparison with Oxygen Redox State in Batteries
The evolving oxygen state plays key roles in the performance and stability of high-energy batteries involving oxygen redox reactions. Comparison of the mRIXS profiles of four different oxygen states reveals that oxygen redox states in batteries have distinct widths and positions along the excitation energy. Read more »
How a New Electrocatalyst Enables Ultrafast Reactions
With key data from the ALS, researchers discovered how a new, low-cost electrocatalyst enables an important oxygen reaction to proceed at an ultrafast rate. The work provides rational guidance for the development of better electrocatalysts for applications such as hydrogen-fuel production and long-range batteries for electric vehicles. Read more »![]()
![]()
Fingerprint Oxygen Redox Reactions in Batteries through High-Efficiency Mapping of Resonant Inelastic X-ray Scattering
We provide a comprehensive analysis and an explicit interpretation of the five evolving components of O-K mRIXS of the typical battery electrode that involves lattice oxygen redox reactions upon cycling. This work is the first benchmark for a complete assignment of all the important mRIXS features collected from battery materials, and thus delivers guidelines for future studies of oxygen redox reactions. Read more »
Reversible Lattice-Oxygen Reactions in Batteries
Researchers quantified a strong, beneficial, and reversible (over hundreds of cycles) chemical reaction involving oxygen ions in the crystal lattice of battery electrode materials. The results open up new ways to explore how to pack more energy into batteries with electrodes made out of low-cost, common materials. Read more »![]()
![]()
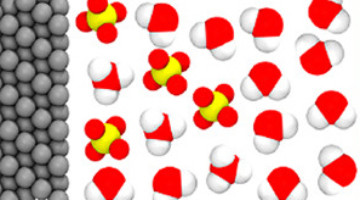
Plumbing the Depths of Interfaces and Finding Buried Treasure
Understanding the interfaces where solids and liquids meet is key to controlling a wide range of energy-relevant processes, from how batteries store energy to how metals corrode, and more. Now researchers have explored such interfaces and found what they describe as a treasure trove of unexpected results that expands our understanding of working interfaces and how to probe them. Read more »
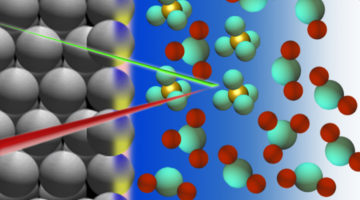
Getting to the Bottom of a Metal/Acid Interface
Researchers identified the molecules that collect at the interface between a platinum electrode and an acidic electrolyte under an applied voltage. Knowledge of the structure and composition of such nanometer-thin interface regions is key to understanding topics such as corrosion, geochemistry, electrocatalysis, and energy storage. Read more »![]()
![]()
New Manganese Materials Bolster Cathode Capacity
The most expensive component of a battery, the cathode, requires rare transition metals like cobalt. Previous attempts to replace cobalt with inexpensive and non-toxic manganese delivered insufficient performance. Now, researchers have optimized the composition of high-energy-density, high-capacity manganese-based cathodes. Read more »