Scientists have discovered a novel chemical state of the element manganese. This chemical state, first proposed about 90 years ago, enables a high-performance, low-cost sodium-ion battery that could quickly and efficiently store and distribute energy produced by solar panels and wind turbines across the electrical grid. Read more »
A Path to a Game-Changing Battery Electrode
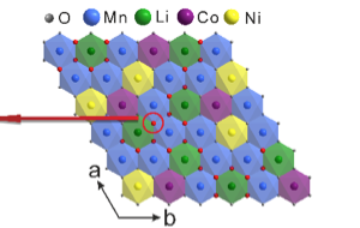
If you add more lithium to the positive electrode of a lithium-ion battery, it can store much more charge in the same amount of space, theoretically powering an electric car 30 to 50 percent farther between charges. But these lithium-rich cathodes quickly lose voltage, and years of research have not been able to pin down why—until now. Read more »![]()
X-Rays Provide Key Insights on Path to Lithium-Rich Battery Electrode
If you add more lithium to the positive electrode of a lithium-ion battery, it can store much more charge in the same amount of space, theoretically powering an electric car 30 to 50 percent farther between charges. But these lithium-rich cathodes quickly lose voltage, and years of research have not been able to pin down why—until now. Read more »
Elucidating the mechanism of MgB2 initial hydrogenation via a combined experimental–theoretical study
Magnesium borohydride Mg(BH4)2 is a promising solid-state hydrogen-storage material, releasing 14.9 wt% hydrogen upon conversion to MgB2. Although several dehydrogenation pathways have been proposed, the hydrogenation process is less well understood. This study elucidates the key atomistic mechanisms associated with the initial stages of hydrogen uptake within MgB2. Read more »
A Multifunctional Material with Electric-Field Control
Three distinct crystalline phases with different electronic, magnetic, and optical properties were reversibly induced in a material through the insertion and extraction of ions by an electric field at room temperature. Such multifunctional materials are desirable for many applications, from smart windows to spintronics. Read more »![]()
![]()
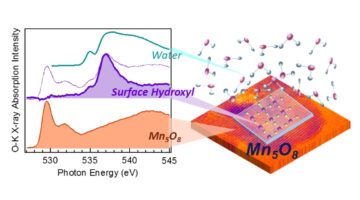
For Better Batteries, Open the Voltage Window
Electrochemical (battery) cells with aqueous electrolytes can be safe, inexpensive, and environmentally friendly, but they are limited by a narrow voltage window. X-ray absorption spectroscopy helps explain why an aqueous Na-ion system with Mn5O8 electrodes has a large voltage window and performs comparably to Li-ion batteries. Read more »
Exploring the Structure of Aqueous Solutions with SALSA
Researchers have published a series of papers that open up the possibility of probing hydrogen bonds in aqueous solutions by combining x-ray emission spectroscopy and resonant inelastic soft x-ray scattering, using the specialized Solid and Liquid Spectroscopic Analysis (SALSA) endstation at Beamline 8.0.1. Read more »
New Insights into Oxygen’s Role in Lithium Battery Capacity
Researchers working at the ALS have recently made new discoveries in understanding the nature of charge storage in lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries, opening up possibilities for new battery designs with significantly improved capacity. Looking at a popular Li-rich cathode material, the researchers used soft x-ray techniques to quantifiably explain oxygen’s role in Li-ion charge capacity. Read more »![]()
![]()
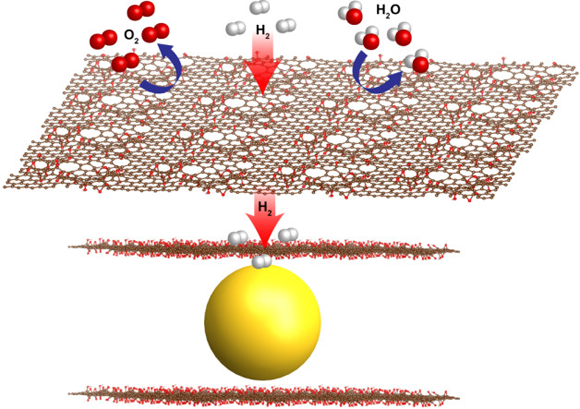
New Fuel Cell Design Powered by Graphene-Wrapped Nanoparticles
Hydrogen is the lightest and most plentiful element on Earth and could serve as a carbon-free, virtually limitless energy source. Recently, researchers working at the ALS and the Molecular Foundry developed a promising new materials recipe based on magnesium nanocrystals and graphene for a hydrogen fuel cell with improved performance in key areas. Read more »![]()
![]()
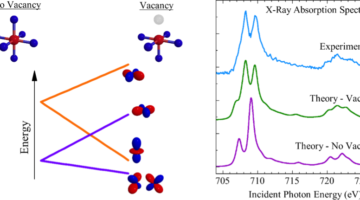
Missing Oxygen Atoms Are Key to Robust Spintronic Material
Researchers studied In2O3:Fe, a promising spintronic material, to determine what leads to its surprisingly robust magnetic properties, how to optimize it, and what to look for in other candidate spintronics materials. Read more »