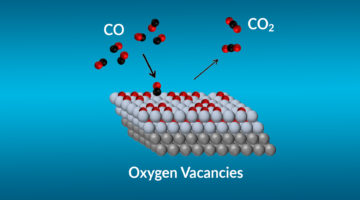
Using a combination of tools at the ALS and other facilities, researchers probed specific mechanisms affecting the efficiency of catalysts for CO-to-CO2 conversion. The work brings us closer to the rational design of more effective catalysts for cleaning up toxic CO exhaust and advances our understanding of fundamental catalytic reactions. Read more »![]()
![]()
Site-dependent selectivity in oxidation reactions on single Pt nanoparticles
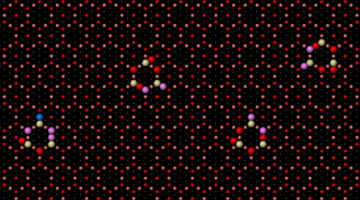
Heterogeneous catalysis is a surface-controlled phenomenon in which different surface sites often show variations in reactivity, posing a major complication for the chemical industry. Here, site-dependent selectivity in oxidation reactions on Pt nanoparticles was identified by conducting IR nanospectroscopy measurements while using allyl-functionalized N-heterocyclic carbenes (allyl-NHCs) as probe molecules. Read more »
How Water Promotes Catalysis of Methane to Methanol
Researchers unraveled how water helps catalyze the conversion of methane, the main component of natural gas, into methanol, a liquid fuel. The work supports the efficient production of methanol and other useful chemicals and could help reduce the amount of greenhouse gases released by the flaring and venting of methane. Read more »![]()
![]()
Time‐Dependent Cytotoxic Properties of Terpyridine‐Based Copper Complexes
The cover feature picture shows the progressive activation of terpyridine‐based copper(II) compounds that are not cytotoxic against various cell lines after 24 h of incubation but become highly efficient after 72 h of incubation, with IC50 values in the low‐micromolar to nanomolar range. Read more »
Divergent Adsorption-Dependent Luminescence of Amino-Functionalized Lanthanide Metal–Organic Frameworks for Highly Sensitive NO2 Sensors
A novel gas-sensing mechanism exploiting lanthanide luminescence modulation upon NO2 adsorption is demonstrated. Two isostructural lanthanide MOFs are used, including an amino group as the recognition center for NO2. Energy transfer from the ligands to Ln is strongly dependent on the presence of NO2, resulting in an unprecedented photoluminescent sensing scheme. Read more »
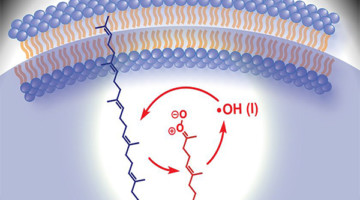
Criegee Intermediates Play Unexpected Role in Cell Chemistry
Researchers employed mass spectrometry to illuminate lipid nanodroplets under ultraviolet light. The results unexpectedly showed that hydroxyl radicals cause damage to cells via the formation of Criegee intermediates: molecules first proposed in 1975 to explain how pollutants react with the ozone layer in our atmosphere. Read more »
Blending Ionic and Coordinate Bonds in Hybrid Semiconductor Materials: A General Approach toward Robust and Solution-Processable Covalent/Coordinate Network Structures
Blending ionic and coordinate bonds in copper iodide based hybrid semiconductor materials with extended covalent/coordinate network structures leads to greatly enhanced solubility and solution processability, making it possible to form high-quality films for device fabrication. Read more »
Scientists Discover New Clue Behind Age-Related Diseases and Food Spoilage
Scientists at Berkeley Lab have made a surprising discovery that could help explain our risk for developing chronic diseases or cancers as we get older, and how our food decomposes over time. The findings point to an unexpected link between the ozone chemistry in our atmosphere and our cells’ hardwired ability to ward off disease. Read more »
Highly Permeable Perfluorinated Sulfonic Acid Ionomers for Improved Electrochemical Devices: Insights into Structure-Property Relationships
Perfluorinated sulfonic acid ionomers (PFSAs) induce significant mass-transport limitations in proton exchange membrane fuel cell catalyst layers due to their semicrystalline PTFE-based matrix. We present a novel PFSA with an amorphous perfluorinated matrix, which vastly improves gas permeability, reduces transport resistance, and improves catalyst utilization in functional catalyst layers. Read more »
Probing the Evolution of Photovoltaic Films during the Spin-Coating Process
A new, in-beamline spin-coating platform enabled researchers to probe the structure of a promising photovoltaic material in the crucial early stages of processing. The results demonstrate the power of multimodal in situ techniques as promising tools for optimizing synthesis parameters and, thus, device performance. Read more »
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- …
- 13
- Next Page »