The cover image shows the triphenylene molecule as a potential precursor to two‐dimensional graphite nanosheets in the interstellar medium. The barrier‐less, exoergic nature of the reaction reveals a versatile reaction mechanism that may drive molecular mass growth processes in cold environments in deep space. Read more »
Conductive triethylene glycol monomethyl ether substituted polythiophenes with high stability in the doped state
Researchers synthesized and characterized two iodine-doped polymers with high conductivity and stability. The doping increases the transparency of thin films of the polymer, which are resistant to common organic solvents. All these properties indicate great potential for the polymers to be used in applications such as organic field effect transistors, organic photovoltaic devices, and sensors. Read more »
Plumbing the Depths of Interfaces and Finding Buried Treasure
Understanding the interfaces where solids and liquids meet is key to controlling a wide range of energy-relevant processes, from how batteries store energy to how metals corrode, and more. Now researchers have explored such interfaces and found what they describe as a treasure trove of unexpected results that expands our understanding of working interfaces and how to probe them. Read more »
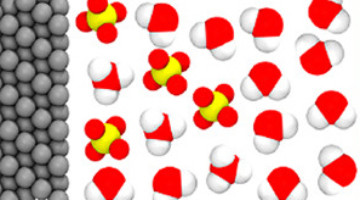
Getting to the Bottom of a Metal/Acid Interface
Researchers identified the molecules that collect at the interface between a platinum electrode and an acidic electrolyte under an applied voltage. Knowledge of the structure and composition of such nanometer-thin interface regions is key to understanding topics such as corrosion, geochemistry, electrocatalysis, and energy storage. Read more »![]()
![]()
Palladium and Zirconium Convert Greenhouse Gases into Fuel
Greenhouse gases cause the rising global temperatures associated with climate change. At the ALS, researchers have determined that palladium/zirconium catalysts can reduce greenhouse gases like methane and carbon dioxide by converting them into useful fuel. Read more »![]()
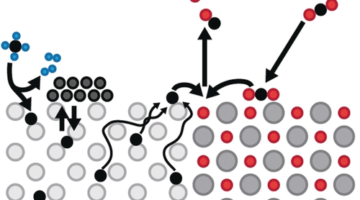
The Smoking Gun of Soot Formation
Scientists identified a mechanism for the formation of soot involving a series rapid chemical reactions rather than the typical condensation of particles from gas. The results are critical to developing methods for controlling emissions responsible for millions of deaths annually, severe degradation of air quality, and enhanced global warming. Read more »![]()
![]()
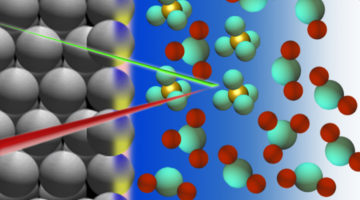
Scientists Present New Clues to Cut Through the Mystery of Titan’s Atmospheric Haze
Saturn’s largest moon, Titan, has a nitrogen-rich atmosphere, the formation of which has been the source of some scientific debate. Researchers have zeroed in on a low-temperature chemical mechanism that may have driven the formation of multiple-ringed molecules—the precursors to more complex chemistry now found in the moon’s brown-orange haze layer. Read more »
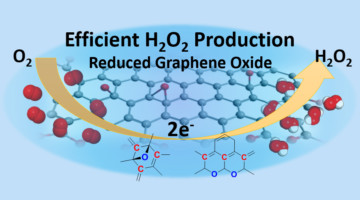
Graphene-Based Catalyst Improves Peroxide Production
Scientists characterized a graphene-based electrocatalyst that potentially makes the production of hydrogen peroxide more selective, efficient, and cost effective. Hydrogen peroxide is an important commodity chemical with growing demand in many areas, including the electronics industry, wastewater treatment, and paper recycling. Read more »![]()
![]()
Reversible Fe(II) uptake/release by magnetite nanoparticles
The coexistence of magnetite and aqueous Fe2+ is common in anoxic subsurface environments and can have a great influence on important biogeochemical redox processes. This study demonstrates that the flow direction of electron equivalents in the form of Fe(II) across the magnetite–solution interface changes in a predictable fashion by altering solution pH, background Fe2+(aq) concentration, and magnetite loading. Read more »
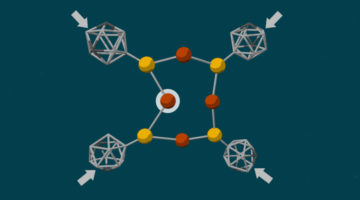
Molecular Anvils Trigger Chemical Reactions
“Molecular anvils” (diamondoids) were used to trigger chemical reactions using pressure, yielding products that differ from those produced in conventionally driven reactions with the same reactants. The discovery opens up new possibilities for the high-specificity synthesis of valuable but challenging molecules in an environmentally friendly process. Read more »![]()
![]()
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- …
- 13
- Next Page »