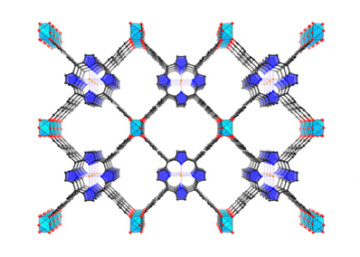
Researchers have made significant headway in the quest to convert CO2 into valuable chemical products such as fuels, pharmaceuticals, and plastics. Recent work at the ALS has shown MOFs and COFs as a valuable new class of CO2 reduction catalysts. Read more »![]()
![]()
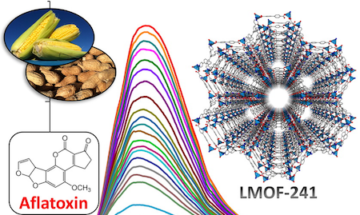
Luminescent MOFs for Mycotoxin Detection
Crystal diffractometry at ALS Beamline 11.3.1 helped scientists develop and understand a new, highly sensitive luminescent metal–organic framework for mycotoxin detection. Read more »
A New Pathway for Radionuclide Uptake
Scientists have reported a major advance in understanding the biological chemistry of radioactive metals, opening up new avenues of research into strategies for remedial action in the event of possible human exposure to nuclear contaminants. Read more »![]()
![]()
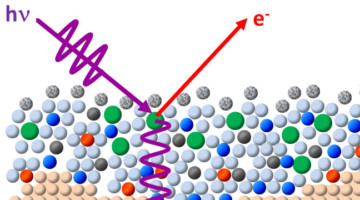
ALS X-Rays Shine a New Light on Catalysis
Recently a team of Stanford and Berkeley Lab researchers used x-rays at the ALS in a novel way to observe the behavior of electrons during technologically important chemical reactions in metal oxide electrocatalysts. What they learned has upended long-held scientific understanding of how these catalysts work. Read more »![]()
![]()
A Fullerene that Breaks the Rules
Scientists used small-molecule x-ray crystallography to verify and characterize the first non-functionalized fullerene with a heptagonal ring in the cage. This new molecule changes the definition of a classical fullerene and expands the range of structural possibilities for endohedral fullerenes. Read more »![]()
![]()
New Technique Gives a Deeper Look into the Chemistry of Interfaces
A new technique developed at the ALS offers sub-nanometer depth resolution of every chemical element to be found at heterogeneous interfaces, such as those in batteries and fuel cells. The technique has relevance to energy research, heterogeneous catalysis, electrochemistry, and atmospheric and environmental science. Read more »![]()
![]()
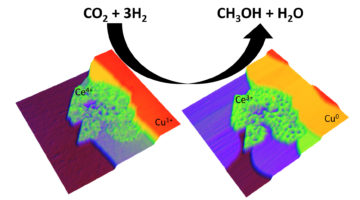
From CO2 to Methanol via Novel Nanocatalysts
Researchers have found novel nanocatalysts that lower the barrier to converting carbon dioxide—an abundant greenhouse gas—into methanol—a key commodity used to produce numerous industrial chemicals and fuels. In one case, it worked almost 90 times faster than catalysts commonly used for this reaction today. Read more »![]()
![]()
ALS Evidence Confirms Combustion Theory
Researchers recently uncovered the first step in the process that transforms gas-phase molecules into solid particles like soot and other carbon-based compounds. It’s a discovery that could help combustion chemists make more efficient, less polluting fuels and help materials scientists fine-tune their carbon nanotubes and graphene sheets for faster, smaller electronics. Read more »![]()
![]()
Infrared Mapping Helps Optimize Catalytic Reactions
A pathway to more effective and efficient synthesis of pharmaceuticals and other flow-reactor chemical products has been opened by a study in which, for the first time, the catalytic reactivity inside a microreactor was mapped in high resolution from start to finish. Read more »![]()
![]()
ALS Gives Chevron Scientists New Insights into Corrosion Resistance
In the chemical environments common in energy production plants, steel pipes and equipment can accumulate layers of iron sulfide, some of which are corrosion resistant and provide protection to the steel surface. Understanding how operating conditions affect steel surface layers can improve corrosion rate estimates, decreasing building and maintenance costs, and increasing the safety and reliability of operating plants. Chevron Energy Technology Company (Chevron ETC) is currently studying the link between operating conditions and corrosion properties at ALS to determine which corrosion layers form and in what order.