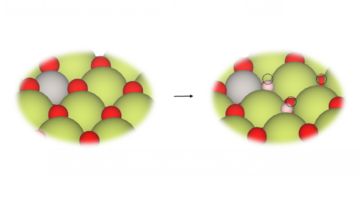
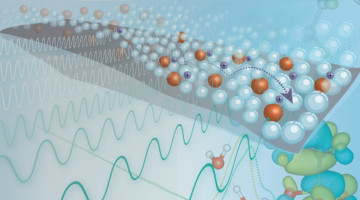
A research team led by Berkeley Lab designed and fabricated catalysts by precisely tuning the co-localization of active metals—key catalytic centers for specific steps in reaction pathways—offering a new level of control over catalytic performance. Read more »
Manganese Cathodes Could Boost Lithium-ion Batteries
Rechargeable lithium-ion batteries are used in mobile devices, electric vehicles, and energy storage systems. But supplies of nickel and cobalt, commonly used in the cathodes of these batteries, are limited. New research opens up a potential low-cost, safe alternative in manganese, the fifth most abundant metal in the Earth’s crust. Read more »
HyMARC Aims to Hit Targets for Hydrogen Storage Using X-Ray Science
Understanding how materials absorb and release hydrogen is the focus of the Hydrogen Materials Advanced Research Consortium (HyMARC). At the ALS, the HyMARC Approved Program was recently renewed, underscoring the key role that soft x-ray techniques have played in addressing the challenges of hydrogen storage. Read more »
Looking Inside a Battery with Infrared Light
Researchers have developed a new infrared methodology with unparalleled spatial and chemical imaging capabilities that helps to characterize processes at the interfaces between electrodes and electrolytes, with an eye toward bringing increased safety, lifetime, and energy density to the next-generation solid-state battery market. Read more »
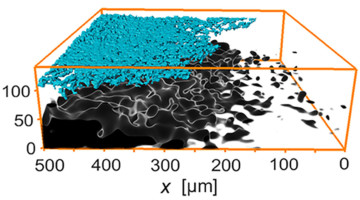
3D View Reveals Shadow Effect after Rapid Battery Charging
Using 3D x-ray microtomography, researchers measured the lithiation levels of particles in Li-ion battery electrodes during charging. At faster charging rates, lithium metal accumulated on the electrode surface and created a “shadow effect,” a region of poor lithiation in the electrode at some distance away from the lithium plating. Read more »
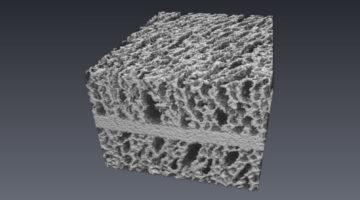
Porous Electrolyte Frameworks for All-Solid-State Batteries
With the help of microtomography at the ALS, researchers developed a method to produce a porous electrolyte framework that they used to construct a working all-solid-state battery. Such batteries potentially offer a higher energy density, longer cycle life, and better inherent safety than state-of-the-art lithium-ion batteries. Read more »
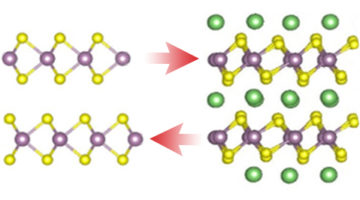
Multimodal Study of Ion-Conducting Membranes
Using multiple x-ray characterization tools, researchers showed how chemical and structural changes improve the performance of a novel ion-conducting polymer (ionomer) membrane from 3M Company. The work provides insight into factors impacting the proton conductivity of ionomers used for fuel cells and the production of hydrogen fuel. Read more »![]()
![]()
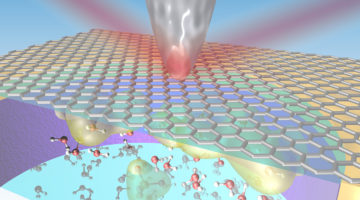
Infrared Nanospectroscopy at Graphene–Liquid Interfaces
Researchers developed a new infrared approach to probing the first few molecular layers of a liquid in contact with a graphene electrode under operating conditions. The work offers a new way to study the interfaces that are key to understanding batteries, corrosion, and other bio- and electrochemical phenomena. Read more »![]()
![]()
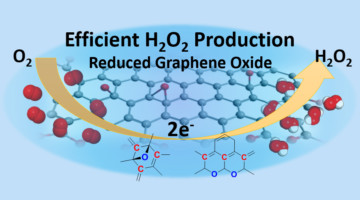
Graphene-Based Catalyst Improves Peroxide Production
Scientists characterized a graphene-based electrocatalyst that potentially makes the production of hydrogen peroxide more selective, efficient, and cost effective. Hydrogen peroxide is an important commodity chemical with growing demand in many areas, including the electronics industry, wastewater treatment, and paper recycling. Read more »![]()
![]()
Clarifying the Working Principle of a High-Capacity Battery Electrode
Operando x-ray absorption spectroscopy experiments revealed the electrochemical reaction mechanism of molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) electrodes in lithium-ion battery cells. The work unambiguously clarifies that the MoS2 conversion reaction is not reversible and that the Li2S formed is converted to sulfur in the first charge process. Read more »