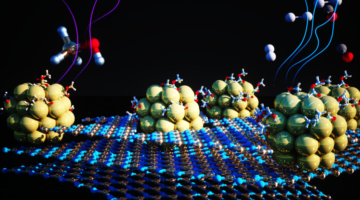
Researchers synthesized a material that speeds up one of the limiting steps in extracting hydrogen from alcohols. The catalyst cleanly and efficiently accelerates the removal of hydrogen atoms from a liquid chemical carrier. The material is robust, made from earth-abundant metals, and will help make hydrogen a viable energy source for a wide range of applications. Read more »
Super-Resolution Measurement of X-Ray Mirrors
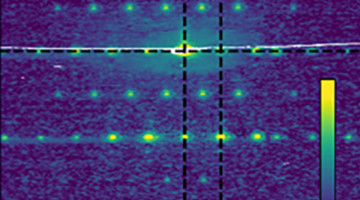
ALS researchers, in collaboration with software and nanofabrication small businesses, developed a way to improve the accuracy of instruments that measure the surfaces of x-ray mirrors. The work significantly improves the quality of the data needed for the fabrication and optimal performance of advanced x-ray beamlines and space telescopes. Read more »![]()
![]()
Scientists Design New Framework for Clean Water
A promising solution to water pollution from abandoned copper mines relies on materials that adsorb copper ions from wastewater, but commercially available products lack the required chemical specificity and load capacity. A team of scientists has designed a new crystalline material that targets and traps copper ions from wastewater with unprecedented precision and speed. Read more »
ALS and Molecular Foundry Funded to Lead the Development of New Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Tools
DOE recently awarded a combined $8.55 million to two Berkeley Lab-led teams to build new tools that harness the power of artificial intelligence and machine learning. Synchrotron and nanoscience users will benefit from Alex Hexemer’s MLExchange and Andrew Minor’s 4D Camera Distillery, both multidisciplinary projects involving multiple national labs. Read more »
Coming Down the Pike: Long-Haul Trucks Powered by Hydrogen Fuel Cells
DOE has announced several major investments to take hydrogen fuel cells to the next level, and Berkeley Lab is set to play a leading role. Ten DOE national labs have been selected to participate in two new consortia and a third continuing one to improve the durability, lifetime, and efficiency of fuel cells. Read more »
A Closer Look at Water-Splitting’s Solar Fuel Potential
Although bismuth vanadate (BiVO4) is a theoretically attractive material for electrodes in photoelectric chemical cells (PECs) used for artificial photosynthesis, it hasn’t lived up to its potential. Researchers used a multimodal approach to gain new insight into what might be happening at the nanoscale to hold BiVO4 back. Read more »
Artificial Antiferromagnets Facilitate Studies of Domain-Wall Motion
Researchers fabricated artificial spin lattices that undergo a paramagnetic-to-antiferromagnetic phase transition. These artificial antiferromagnets enable studies of dynamical properties that are critical to understanding, and ultimately implementing, real-world applications such as advanced computing and data-storage technologies. Read more »
Battery Breakthrough Gives Boost to Electric Flight and Long-Range Electric Cars
While lithium metal extends an EV’s driving range, it also shortens the battery’s useful life due to lithium dendrites that can cause short circuits. Researchers report a new class of soft, solid electrolytes—made from both polymers and ceramics—that suppress dendrites, before they can propagate and cause the battery to fail. Read more »
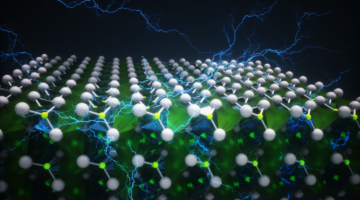
Unexpected Rise in Ferroelectricity as Material Thins
Researchers showed that hafnium oxide surprisingly exhibits enhanced ferroelectricity (reversible electric polarization) as it gets thinner. The work shifts the focus of ferroelectric studies from more complex, problematic compounds to a simpler class of materials and opens the door to novel ultrasmall, energy-efficient electronics. Read more »![]()
![]()
A Graphene Innovation That Is Music to Your Ears
A California-based company called GraphAudio is moving toward commercializing graphene-based audio technology developed by researchers at Berkeley Lab and UC Berkeley. The technology could transform a variety of devices, including speakers, earbuds and headphones, microphones, autonomous vehicle sensors, and ultrasonic and echolocation systems. Read more »
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- …
- 10
- Next Page »