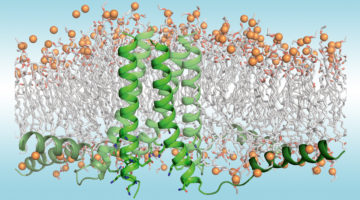
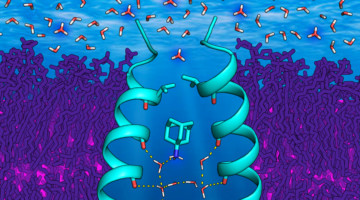
Scientists characterized designed membrane proteins to better understand the forces that stabilize these large, complex structures. The results necessitate a rethinking of membrane-protein biophysics and could lead to better therapies for related illnesses as well as functional membrane proteins for engineering applications. Read more »![]()
![]()
ALS Work Using Protein Crystallography
Protein crystallography is used for determining the molecular structure of proteins. Crystallized protein molecules cause a beam of incident x-rays to scatter in many directions, with constructive and destructive interference generating a diffraction pattern. By analyzing these patterns, a crystallographer can produce a three-dimensional picture of the density of electrons within the crystal and thus determine the protein's structure.
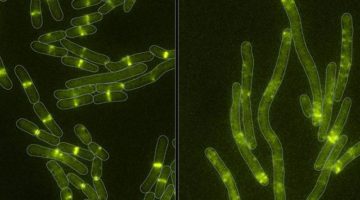
Self-Assembling 2D Arrays with de Novo Protein Building Blocks
Modular self-assembly of biomolecules in two dimensions (2D) is straightforward with DNA but has been difficult to realize with proteins, due to the lack of modular specificity similar to Watson–Crick base pairing. Here, researchers describe a general approach to designing 2D arrays using de novo designed pseudosymmetric protein building blocks. Read more »
Design and Synthesis of Selective Phosphodiesterase 4D (PDE4D) Allosteric Inhibitors for the Treatment of Fragile X Syndrome and Other Brain Disorders
PDE4D enzymes are important for normal brain function. Mutations have been asssociated with an ultrarare neurodevelopmental disorder, and genetic variation in PDE4D contributes to biological variation in human cognitive ability. Here, researchers report on novel PDE4D inhibitors providing potent memory-enhancing effects in a mouse model, with improved tolerability and reduced vascular toxicity over earlier PDE4 inhibitors. Read more »
Structural Characterization of a Synthetic Tandem-Domain Bacterial Microcompartment Shell Protein Capable of Forming Icosahedral Shell Assemblies
Bacterial microcompartments (BMCs) are subcellular compartments found in many prokaryotes, and they are of considerable interest for biotechnological applications. The BMC-H2 shell system constitutes a relatively simple generic building block that could be used to construct designed shells with a relatively highly tunable pore. Read more »
Antibody Uses Mimicry to Block SARS Coronavirus
Protein structures not only revealed how SARS and MERS antibodies inhibit the viruses from attaching to host cells, they also revealed an unprecedented example of receptor mimicry that triggers the cell-invasion machinery of the SARS virus. The results inform efforts to prevent and treat these serious, often deadly, respiratory diseases. Read more »![]()
![]()
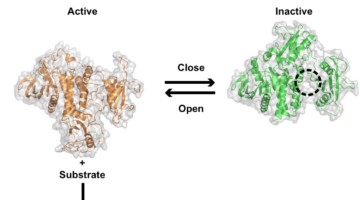
Locking Protein Structure to Close the Door on Cancer
While the SHP2 protein helps regulate cellular activity, mutations in its structure can lead to cancer. X-ray crystallography at the ALS and SSRL has revealed differences between normal and mutated SHP2, as well as how it binds to certain cancer drugs. These structural insights open the door to new types of cancer therapy. Read more »
A Two-Pronged Defense against Bacterial Self-Intoxication
Researchers solved the structure of a bacterial toxin bound to a neutralizing protein, revealing two distinct mechanisms for how the toxin-producing bacteria avoid poisoning themselves. The findings offer clues to the evolutionary origins of the potent toxins that enable bacterial pathogens to cause human diseases such as cholera and diphtheria. Read more »![]()
![]()
Toward a Blueprint for Anti-influenza Drugs
Researchers obtained high-resolution structures of several influenza antiviral drug molecules bound to their proton-channel targets in both open and closed conformations. The structures provide an atomic-level blueprint from which to design more effective anti-influenza drugs that can overcome growing drug resistance. Read more »![]()
![]()
Inhibitors of the M2 Proton Channel Engage and Disrupt Transmembrane Networks of Hydrogen-Bonded Waters
The influenza M2 proton channel can bind to drugs and inhibitors. The ammonium groups of these compounds form hydrogen bonds with networks of ordered waters within the channel, and the adamantyl groups sterically block the diffusion of hydronium into the channel pore. Read more »
Scientists Capture Photosynthesis in Unprecedented Detail
Scientists have captured a more detailed picture than ever of the steps in photosynthesis, the process by which plants use sunlight to split water and produce oxygen while making the carbohydrates that sustain life on Earth. The idea is eventually to have a continuous movie of how water is split into oxygen, and how plants do that using sunlight. Read more »
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- …
- 15
- Next Page »