Early in the COVID-19 pandemic, it was quickly established that the receptor binding domain (RBD) of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein is a prime target for neutralizing antibodies. Now, scientists have found a second region of the spike protein that is targeted by dozens of antibodies, some of which exhibit ultrapotent neutralizing activity. Read more »
ALS Work Using Scattering/Diffraction
These techniques make use of the patterns of light produced when x-rays are deflected by the closely spaced lattice of atoms in solids and are commonly used to determine the structures of crystals and large molecules such as proteins.
Rapid In Situ Ligand-Exchange Process Used to Prepare 3D PbSe Nanocrystal Superlattice Infrared Photodetectors
A new strategy for retaining long-range order during ligand exchange of nanocrystal superlattices is used to construct PbSe infrared photodetectors. The ordered photodetectors have a 16× higher responsivity and 2× faster response time compared to disordered ones. Read more »
Label-Free Characterization of Organic Nanocarriers
A technique developed at the ALS enables accurate characterization of organic nanocarriers (molecules that encapsulate other molecules) without the need for disruptive labeling. The method will enable faster, more precise development of exciting new technologies, ranging from targeted drug delivery to oil-spill remediation. Read more »![]()
![]()
Conformational Dynamics in the Interaction of SARS-CoV-2 Papain-like Protease with Human Interferon-Stimulated Gene 15 Protein
The image depicts the complex formed between SARS-CoV-2 papain-like protease and human interferon-stimulated gene 15 protein. Small-angle scattering elucidated the structural details of this complex providing insight into its role in suppressing the innate immune response and also potential routes for development of therapeutics to combat COVID-19. Read more »
Understanding the Hydrothermal Formation of NaNbO3: Its Full Reaction Scheme and Kinetics
To understand and tune the properties of hydrothermally produced NaNbO3, the reaction was studied in situ with powder x-ray diffraction, small-angle scattering, and total scattering with pair-distribution function analysis. The full reaction scheme and kinetics were revealed, showing two different temperature-dependent growth mechanisms. Read more »
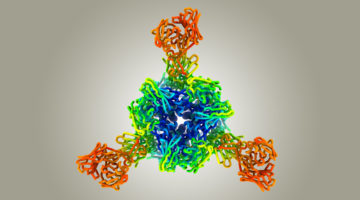
Structure of blood coagulation factor VIII in complex with an anti–C1 domain pathogenic antibody inhibitor
van der Waals sphere representation of the factor VIII C1 domain, highlighting surface‐exposed hemophilia A–associated mutations that cause impaired von Willebrand factor binding and overlap with a pathogenic anti‐C1 domain inhibitor epitope. Read more »
EPSCoR Collaboration Fosters New Research and New Careers
The DOE Established Program to Stimulate Competitive Research (DOE EPSCoR) encourages partnerships between national labs and researchers in qualifying states and territories. An EPSCoR collaboration with researchers from Kentucky has resulted in an ALS highlight, career advancement for young scientists, and a larger, center-scale proposal. Read more »
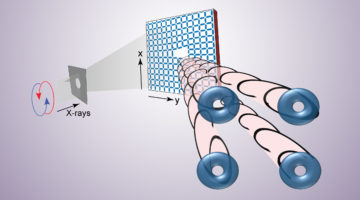
Artificial Spin Ice Toggles Twist in X-Ray Beams on Demand
ALS studies helped scientists understand how a nanoscale magnetic lattice (an artificial spin ice) acts as a toggle switch for x-ray beams with spiral character. The findings represent an important step toward the development of a versatile new tool for probing or controlling exotic phenomena in electronic and magnetic systems. Read more »![]()
![]()
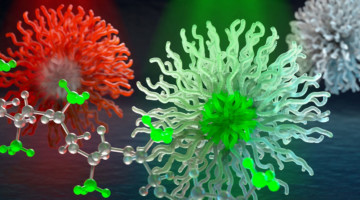
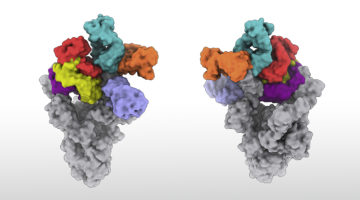
Guiding Target Selection for COVID-19 Antibody Therapeutics
Protein-structure studies helped demonstrate that the primary target of antibody-based COVID-19 immunity is the part of the virus’s spike protein that can most easily mutate. The work anticipated the rise of SARS-CoV-2 variants and guides the selection of antibody therapeutics that are likely to be more resistant to immune escape. Read more »![]()
![]()
How X-Rays Could Make Reliable, Rapid COVID-19 Tests a Reality
A highly sensitive lateral flow assay—the same type of device used in home pregnancy tests—could be developed using pairs of rigid antibodies that bind to the SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein. SAXS data showed that a particular pair of monoclonal antibodies bound to the nucleocapsid protein very strongly and stably, in part due to the antibodies’ rigidity. Read more »
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- …
- 39
- Next Page »