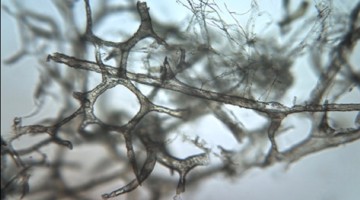
Researchers used several analytical techniques at the ALS to demonstrate how soft-tissue structures may be preserved in dinosaur bones, countering long-standing scientific dogma that protein-based body parts cannot survive more than one million years. Read more »
ALS Work Using Scattering/Diffraction
These techniques make use of the patterns of light produced when x-rays are deflected by the closely spaced lattice of atoms in solids and are commonly used to determine the structures of crystals and large molecules such as proteins.
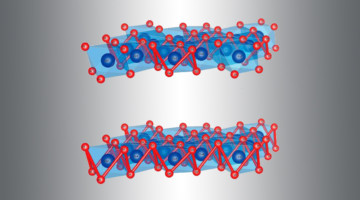
How a New Electrocatalyst Enables Ultrafast Reactions
With key data from the ALS, researchers discovered how a new, low-cost electrocatalyst enables an important oxygen reaction to proceed at an ultrafast rate. The work provides rational guidance for the development of better electrocatalysts for applications such as hydrogen-fuel production and long-range batteries for electric vehicles. Read more »![]()
![]()
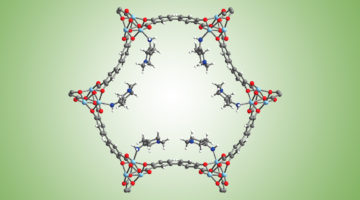
Blending Ionic and Coordinate Bonds in Hybrid Semiconductor Materials: A General Approach toward Robust and Solution-Processable Covalent/Coordinate Network Structures
Blending ionic and coordinate bonds in copper iodide based hybrid semiconductor materials with extended covalent/coordinate network structures leads to greatly enhanced solubility and solution processability, making it possible to form high-quality films for device fabrication. Read more »
X-ray Crystal Structures of the Influenza M2 Proton Channel Drug-Resistant V27A Mutant Bound to a Spiro-Adamantyl Amine Inhibitor Reveal the Mechanism of Adamantane Resistance
The M2 proton channel, shown with front and back monomer helices removed, is an anti-influenza drug target. Here, a bound inhibitor blocks the transport of protons through the V27A mutant channel. Read more »
Highly Permeable Perfluorinated Sulfonic Acid Ionomers for Improved Electrochemical Devices: Insights into Structure-Property Relationships
Perfluorinated sulfonic acid ionomers (PFSAs) induce significant mass-transport limitations in proton exchange membrane fuel cell catalyst layers due to their semicrystalline PTFE-based matrix. We present a novel PFSA with an amorphous perfluorinated matrix, which vastly improves gas permeability, reduces transport resistance, and improves catalyst utilization in functional catalyst layers. Read more »
Can Minerals in the Earth’s Lower Mantle Store Water?
Earth is considered a watery planet, simply by virtue of the fact that 71% of its surface is covered by oceans. But researchers have discovered that, in the massive volume of material in Earth’s interior, minerals can serve as an important water reservoir, providing a new perspective on our planet’s water budget. Read more »
Water Improves Material’s Ability to Capture CO2
With the help of the ALS, researchers from UC Berkeley and ExxonMobil fine-tuned a material to capture CO2 in the presence of water. The parties have applied for a patent on the material, which was developed for use on the relatively humid flue gases emitted by certain natural gas power plants, a cleaner-burning alternative to coal. Read more »![]()
![]()
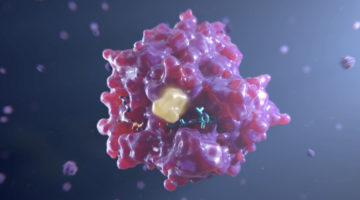
ALS Reveals Vulnerability in Cancer-Causing Protein
A promising anticancer drug, AMG 510, was developed by Amgen Inc. with the help of novel structural insights gained from protein structures solved at the ALS. AMG 510, which is currently in phase II clinical trials for efficacy, targets tumors caused by mutations in the KRAS protein, one of the most common causes of cancer. Read more »![]()
![]()
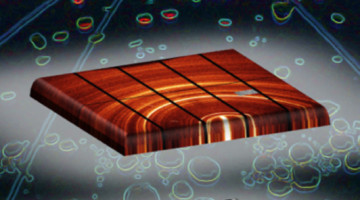
Probing the Evolution of Photovoltaic Films during the Spin-Coating Process
A new, in-beamline spin-coating platform enabled researchers to probe the structure of a promising photovoltaic material in the crucial early stages of processing. The results demonstrate the power of multimodal in situ techniques as promising tools for optimizing synthesis parameters and, thus, device performance. Read more »
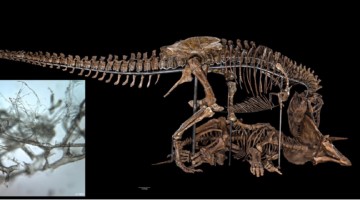
Berkeley Lab Helps Reveal How Dinosaur Blood Vessels Can Preserve Through the Ages
A team of scientists used infrared and x-ray imaging performed at the Advanced Light Source to determine the chemical mechanisms that allow soft tissue structures to persist in dinosaur bones—countering the long-standing scientific dogma that protein-based body parts can’t survive more than 1 million years. Read more »
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- …
- 39
- Next Page »