Organic semiconductor nanoparticles (OSNs) convert absorbed light into heat, and are commonly used in photothermal therapy and photoacoustic imaging. Here, the OAN, Y6, is shown to form strong intermolecular packing, manipulated by surface charge under restrained sizes, yielding new pi-pi stacking and fast exciton quenching. The temperature of the tumor area can rise to more than 70 degrees under NIR irradiation, which can effectively ablate a tumor. Read more »
ALS Work Using Scattering/Diffraction
These techniques make use of the patterns of light produced when x-rays are deflected by the closely spaced lattice of atoms in solids and are commonly used to determine the structures of crystals and large molecules such as proteins.
Uncompetitive, adduct-forming SARM1 inhibitors are neuroprotective in preclinical models of nerve injury and disease
Researchers describe potent small-molecule inhibitors that are neuroprotective in preclinical models of nerve injury and disease. The cover depicts the destruction of an axon by the enzyme SARM1, shown disproportionately large to convey its catastrophic role in driving degeneration once it is activated upon injury. Read more »
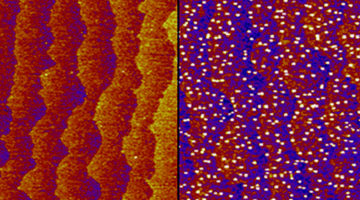
Watching Nanoparticle Chemistry and Structure Evolve
Using a multimodal approach, researchers learned how chemical properties correlate with structural changes during nanoparticle growth. The work will enable a greater understanding of the mechanisms affecting the durability of nanoparticles used to catalyze a broad range of chemical reactions, including clean-energy reactions. Read more »![]()
![]()
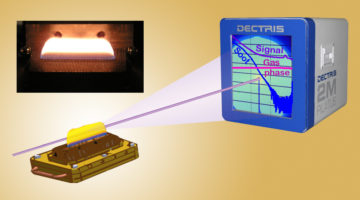
Distinguishing Nanoparticles from Gas-Phase Species in Reacting Flows
Researchers developed a strategy for distinguishing between gas-phase species and newly formed nanoparticles in mixed gas- and particle-phase reacting flows. The approach uses small-angle x-ray scattering to study particle formation as it occurs by explicitly accounting for temperature-dependent scattering from gases. Read more »![]()
Optical sensing of aqueous nitrate anion by a platinum(II) triimine salt based solid state material
Researchers present a new Pt(II) salt that enables the selective and quantitative measurement of aqueous nitrate anions without the need for pH adjustment. The method relies on the color change of the Pt(II) complex from yellow to red and an intense luminescence response, simplifying the detection process for on-site applications and expanding its applicability to broader matrices. Read more »
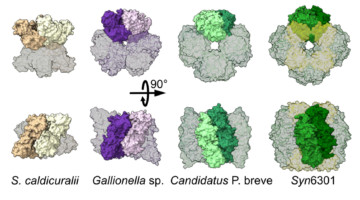
Protein Assemblies Show Surprising Variability
Protein-structure studies performed in part at the ALS helped researchers discover that the protein assemblies in a key carbon-cycling enzyme can rearrange with surprising ease. The findings raise the prospect of genetically tuning the protein in agricultural plant species to produce more productive and resource-efficient crops. Read more »![]()
![]()
Valence tautomerism in a cobalt-verdazyl coordination compound
Valence tautomerization in inorganic chemistry typically involves the distribution of electrons between a metal center and redox active ligand, with potential application as molecular switches or other molecular devices. Here we report an example of valence tautomerization and an unusual electronic structure in a cobalt verdazyl complex. Read more »
Chemical acylation of an acquired serine suppresses oncogenic signaling of K-Ras(G12S)
Small-molecule targeting of particular KRAS mutations offer promise for cancer therapy. The cover depicts a small-molecule ligand (red) inhibiting the oncogenic mutant protein K-Ras(G12S) (cyan) by forming a covalent ester adduct at the mutant serine. Read more »
Liquid Heterostructures: Generation of Liquid–Liquid Interfaces in Free-Flowing Liquid Sheets
Microscope image of a microfluidic nozzle producing a liquid heterostructure: a layered flat liquid sheet with outer toluene layers and an inner water layer. The colored bands arise from thin film interference, indicating the presence of buried liquid‒liquid interfaces and submicron layer thicknesses. Read more »
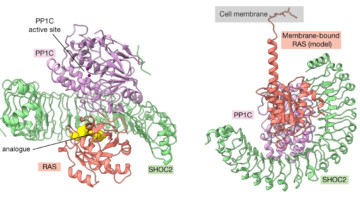
Structures Signal Fresh Targets for Anticancer Drugs
Researchers from Genentech used a suite of methods, including small-angle x-ray scattering, to learn how an assembly of three proteins works together to transmit signals for cell division. The work reveals new targets for the development of drugs that fight certain types of cancer, including lung, colorectal, and pancreatic cancer. Read more »![]()
![]()
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- …
- 39
- Next Page »