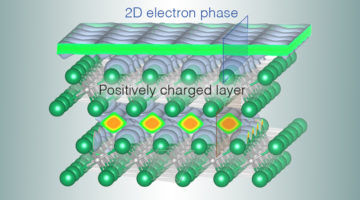
Researchers discovered a liquid-like layer of electrons that floats on the surface of an unusual crystal and appears to undergo a phase transition upon doping. The system is an ideal platform for studying exotic phenomena involving electrons (e.g. superconductivity) without complications arising from other types of interactions. Read more »![]()
![]()
ALS Work Using Spectroscopy
These techniques are used to study the energies of particles that are emitted or absorbed by samples that are exposed to the light-source beam and are commonly used to determine the characteristics of chemical bonding and electron motion.
Macromolecular organic matter in samples of the asteroid (162173) Ryugu
We investigated the macromolecular organic matter in samples of the asteroid Ryugu—brought to Earth by the Hayabusa2 spacecraft—measuring its elemental, isotopic, and functional group compositions along with its small-scale structures and morphologies. Analytical methods used included spectro-microscopies, electron microscopy, and isotopic microscopy. Read more »
A Study on the Reaction Mechanism of a Model Organic Cathode in Magnesium-Ion Batteries
Battery and analytical studies of a model benzoquinone-type cathode reveal reversible structural transformations driven by a new precedence of a unique dissolution/precipitation mechanism and raise the question regarding its prevalence in other organic cathode batteries. Read more »
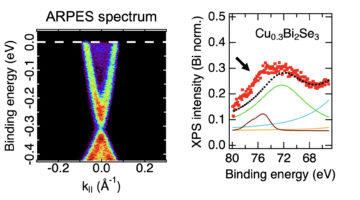
Copper Migrates to Surface of Topological Insulator in Air
An ambient-pressure study of a topological insulator doped with copper revealed that the copper atoms, inserted between the material’s layers, migrate to the surface when exposed to air. The work represents a novel way of modifying the material’s surface composition, which can confer it with new properties such as superconductivity. Read more »
Charge Density Wave Found in Magnetic Kagome Crystal
Researchers discovered a wave-like charge order in a magnetic material with a “kagome” geometric structure and obtained clues to the order’s origins in the material’s electronic structure. By helping to connect certain structures with emergent quantum properties, the work brings us a step closer to the goal of creating materials by design. Read more »![]()
![]()
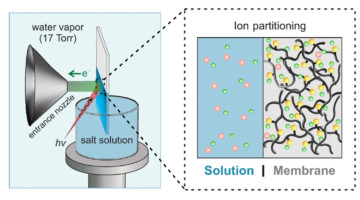
First Direct Measurement of Elusive Donnan Potential
Researchers performed the first direct measurement of the Donnan electrical potential, which arises from an imbalance of charges at membrane-solution interfaces. Considered unmeasurable for over a century, the Donnan potential is relevant to a wide range of fields, from cell biology to energy storage and water desalination. Read more »![]()
![]()
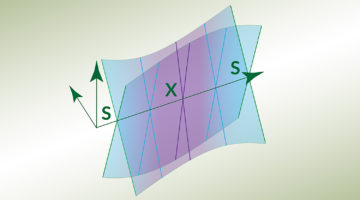
Dirac Nodal Line in Hourglass Semimetal Nb3SiTe6
Hourglass fermion in an electronic band structure is protected by the nonsymmorphic symmetry of a layered semimetal Nb3SiTe6. Angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy demonstrates the band features of an hourglass fermion in k-space, such as band crossings and nodal loops. Read more »
The Donnan Potential, Revealed at Last
Researchers at the ALS recently led the first direct measurement of the Donnan potential, an electric potential that arises from an imbalance of charges at the interface of a charged membrane and a liquid. The work could yield new insights in areas such as ion transport through cellular membranes, ion exchange membranes in energy storage strategies, and water purification technologies. Read more »
Enhanced low-temperature proton conductivity in hydrogen-intercalated brownmillerite oxide
Solid oxide materials typically need high temperatures to allow appreciable ion transport, limiting their flexibility as electrolytes for energy devices. Lu et al. now show unusually high proton conductivity in a hydrogenated oxide between 40 °C and 140 °C, which they attribute to ordered vacancy channels and high proton concentrations. Read more »
Crossing from One to Two Dimensions in a Single Material
Low-dimensional materials exhibit excellent properties for use in next-generation electronic devices. Now, researchers have discovered an ideal platform for tuning between 1D and 2D physics, expanding the possibilities for device engineering and offering a versatile platform for the exploration of intriguing low-dimensional physics. Read more »
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- …
- 31
- Next Page »