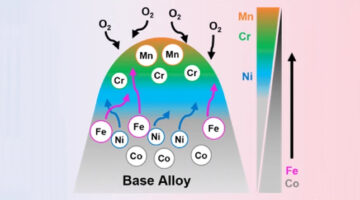
For extreme applications such as nuclear fusion reactors and high-temperature jet engines, scientists are experimenting with “high-entropy” alloys that consist of many metals mixed together in equal proportions. In this work, researchers begin to unravel how these materials degrade under high-temperature oxidative environments. Read more »![]()
ALS Work Using XANES
X-ray absorption near-edge structure (XANES) spectroscopy is form of x-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) that reveals the structures of molecules bonded to surfaces. It focuses on prominent features in the "near-edge" region of a spectrum (about 30 eV above the K-shell absorption edge). This "fine structure" can be correlated with specific molecular bond types, lengths, and orientations. XANES, also known as near-edge x-ray absorption fine-structure (NEXAFS) spectroscopy, is often performed as part of a STXM experiment.
Surface Engineering Boosts Water-Splitting Efficiency
Researchers modified the surface of an electrocatalyst to maximize its efficiency at splitting water. The optimized material is approximately 40 times more efficient than similar commercial electrocatalysts and could help make the production of clean hydrogen fuel more sustainable and economical. Read more »![]()
![]()
Vestiges of the Early Solar System in Ryugu Asteroid
Samples returned to Earth from the asteroid Ryugu revealed that the building blocks of life formed 4.6 billion years ago in the extreme cold of space, followed by reaction with water. The dark, coal-like organic matter in the carbonaceous asteroid could have contributed to the formation of habitable planetary environments. Read more »![]()
![]()
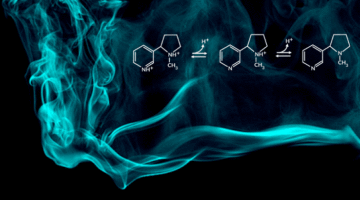
Nicotine Protonation in Simulated Vaping Aerosols
To better understand how e-cigarette additives alter nicotine chemistry and users’ perceptions of vaping, researchers used x-ray spectroscopy technology at the Advanced Light Source to analyze the acid-base equilibria of additive-enhanced nicotine in simulated vaping aerosols. Read more »
Sub-4 nm mapping of donor–acceptor organic semiconductor nanoparticle composition
We report, for the first time, sub-4 nm mapping of donor : acceptor nanoparticle composition in eco-friendly colloidal dispersions for organic electronics. This technology shows great promise for the optimization of organic semiconductor blends for organic electronics and photocatalysis and has further applications in organic core–shell nanomedicines. Read more »
Macromolecular organic matter in samples of the asteroid (162173) Ryugu
We investigated the macromolecular organic matter in samples of the asteroid Ryugu—brought to Earth by the Hayabusa2 spacecraft—measuring its elemental, isotopic, and functional group compositions along with its small-scale structures and morphologies. Analytical methods used included spectro-microscopies, electron microscopy, and isotopic microscopy. Read more »
Visualizing the Nanoscale Oxygen and Cation Transport Mechanisms during the Early Stages of Oxidation of Fe–Cr–Ni Alloy Using In Situ Atom Probe Tomography
Understanding the early stages of interactions between oxygen and material surfaces is beneficial for fields ranging from materials degradation to forensics and catalysis. In situ atom probe tomography (APT) is demonstrated to track the diffusion of oxygen and metal ions at nanoscale spatial resolution during the early stages of oxidation of a model Fe–Cr–Ni alloy. Read more »
New Insight into Titan’s Hazy Atmospheric Chemistry
Researchers simulated the complex chemistry that may be occurring in the hazy atmosphere of Saturn’s largest moon, Titan, and analyzed the reaction products at the ALS. The work provided new insights into what future Titan probes may encounter upon arrival and what the atmosphere of Earth may have been like eons ago. Read more »
Decoupling the metal–insulator transition temperature and hysteresis of VO2 using Ge alloying and oxygen vacancies
The VO2 metal–insulator transition underpins applications in thermochromics, neuromorphic computing, and infrared vision. Ge alloying is shown to expand the stability of the monoclinic phase to higher temperatures, and by suppressing the propensity for oxygen vacancy formation, renders the hysteresis of the transition exquisitely sensitive to oxygen stoichiometry. Read more »
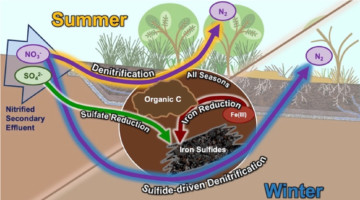
Removing Nitrogen from Wastewater using Horizontal Levees
Treated municipal wastewater often contains nitrogen, which has been linked to algal blooms that can devastate coastal ecosystems. In a recent study, researchers characterized the primary nitrogen-removal pathways in a horizontal levee, an engineered subsurface water-treatment system consisting of a gently sloping strip of land adjacent to storm-control levees. Read more »