Understanding how materials absorb and release hydrogen is the focus of the Hydrogen Materials Advanced Research Consortium (HyMARC). At the ALS, the HyMARC Approved Program was recently renewed, underscoring the key role that soft x-ray techniques have played in addressing the challenges of hydrogen storage. Read more »
ALS Work Using XAS
In x-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS), the incident x-ray energy is tuned over a range that will excite core-level electrons. Sharp increases in absorption occur at specific energies, characteristic of the absorbing element. The resulting spectra probe the elemental composition as well as the chemical and electronic structure of the material.
Case study evaluation of size-resolved molecular composition and phase state of carbonaceous particles in wildfire influenced smoke from the Pacific Northwest
Wildfires are significant sources of carbonaceous particles in the atmosphere. Given the dependence of atmospheric processes on particle physical and molecular properties, the interplay between particle size, phase state and chemical composition is investigated here for aerosols influenced by a 2021 Pacific Northwest wildfire event. Read more »
Electronic transport and polarization-dependent photoresponse in few-layered hafnium trisulfide (HfS3) nanoribbons
We report on the electrical and optoelectronic characterization of field-effect transistor (FET) devices based on few-layered HfS3 nanoribbons. The results support the contention that in the presence of light, the photocarriers include both electrons and holes, enhancing the photocurrent of devices. Read more »
Increasing the Energy Density of Hybrid Supercapacitor Electrodes
Hybrid supercapacitors (HSCs) integrate the merits of batteries with those of supercapacitors. However, the fraction of active material in HSC electrodes has remained too low for commercial requirements. Now, researchers have found a clever way to increase the active-mass ratio to achieve dramatic improvements in key measures. Read more »
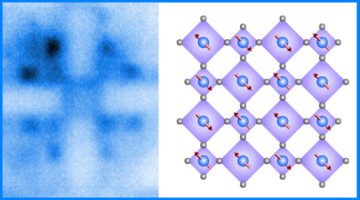
Doped Nickelate Enters a New Phase with Spintronics Potential
Rare-earth nickelates are known to undergo a metal-to-insulator phase transition as temperature decreases, the mechanism of which is not well understood. Here, researchers observed a new low-temperature phase that’s both metallic and antiferromagnetic—an unusual combination with potential value in spintronics. Read more »
Electric Vehicle Batteries Could Get Big Boost With New Polymer Coating
Scientists have developed a conductive polymer coating—called HOS-PFM—that conducts both electrons and ions at the same time. This ensures battery stability and high charge/discharge rates while enhancing battery life. The coating also shows promise as a battery adhesive that could extend the lifetime of a lithium-ion battery from an average of 10 years to about 15 years. Read more »
A Study on the Reaction Mechanism of a Model Organic Cathode in Magnesium-Ion Batteries
Battery and analytical studies of a model benzoquinone-type cathode reveal reversible structural transformations driven by a new precedence of a unique dissolution/precipitation mechanism and raise the question regarding its prevalence in other organic cathode batteries. Read more »
Enhanced low-temperature proton conductivity in hydrogen-intercalated brownmillerite oxide
Solid oxide materials typically need high temperatures to allow appreciable ion transport, limiting their flexibility as electrolytes for energy devices. Lu et al. now show unusually high proton conductivity in a hydrogenated oxide between 40 °C and 140 °C, which they attribute to ordered vacancy channels and high proton concentrations. Read more »
Multilayer Stack Opens Door to Low-Power Electronics
Researchers found that a multilayer stack of ultrathin materials exhibits a phenomenon called negative capacitance, which reduces the voltage required for transistor operation. The material is fully compatible with today’s silicon-based technology and is capable of reducing power consumption without sacrificing transistor size or performance. Read more »![]()
![]()
Jinghua Guo to Receive the 2022 Shirley Award
ALS senior scientist Jinghua Guo is the recipient of this year’s Shirley Award for Outstanding Scientific Achievement at the ALS. Guo is being recognized for pioneering the development of operando soft x-ray spectroscopy, work that’s enabled studies under realistic conditions, which is of great importance in environmental and energy research. Read more »
- « Previous Page
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- …
- 10
- Next Page »