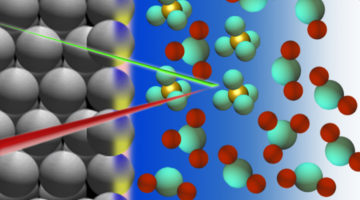
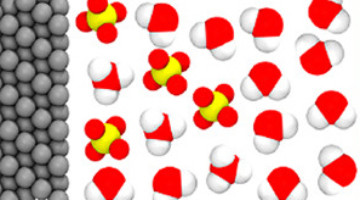
Aided by x-ray absorption spectroscopy at the ALS, researchers from Toyota and the University of Akron have uncovered a new catalysis mechanism to improve oxidation-reduction reactions in certain fuel cells by 40%. This enhancement, based on tin oxide, will support efforts to increase fuel efficiency in electric vehicles. Read more »![]()
ALS Work Using XAS
In x-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS), the incident x-ray energy is tuned over a range that will excite core-level electrons. Sharp increases in absorption occur at specific energies, characteristic of the absorbing element. The resulting spectra probe the elemental composition as well as the chemical and electronic structure of the material.
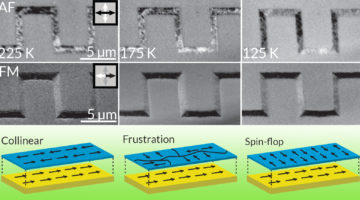
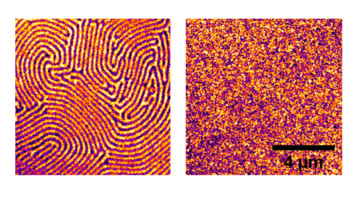
Controlling Spin in Antiferromagnetic Nanostructures
Researchers discovered that the spin configuration of a nanostructured antiferromagnetic material can be affected by the dimensions of features imprinted onto the material. The results suggest that nanoscale patterning can be a viable tool for engineering spin configurations in future antiferromagnetic spintronic devices. Read more »![]()
![]()
Chemical and Morphological Origins of Improved Ion Conductivity in Perfluoro Ionene Chain Extended Ionomers
Resonant x-ray scattering and x-ray absorption spectroscopy with elemental sensitivity unravel structural features tied to water–ion domains and discern sulfur-containing groups in sulfonated ionomers, which help delineate chemical factors controlling their phase-separated morphology and governing ion transport. Read more »
Molecular Framework Imparts Stability to Reactive Catalyst
Researchers have shown that a rigid metal–organic framework (MOF) can be used to stabilize core regions of a reactive catalyst that has potential for use in artificial photosynthesis. The framework immobilizes and preserves key reactive intermediates and affords a clearer view of how the catalyst’s structure correlates with function. Read more »
Catalyst Improves Cycling Life of Magnesium/Sulfur Batteries
Magnesium/sulfur batteries hold promise as a safer, energy-dense advancement, but previous iterations have suffered from extremely limited recharging capabilities. Studies at the ALS provided electrochemical insights into battery polarization and revealed how a titanium catalyst activates magnesium/sulfur compounds to improve battery performance. Read more »
Here Comes the Sun: A New Framework for Artificial Photosynthesis
Scientists have long sought to mimic the process by which plants make their own fuel using sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water through artificial photosynthesis devices, but exactly how catalysts work to generate renewable fuel remains a mystery. Now, a study has uncovered new insight into how to better control cobalt oxide, one of the most promising catalysts for artificial photosynthesis. Read more »
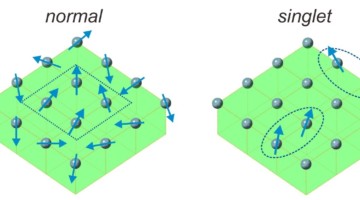
Evidence of a Long-Predicted Magnet
Half a century ago, theorists proposed a novel way for materials to produce a magnetic field. Now, scientists have discovered a uranium compound that bears out that long-ago theory—a new type of magnet that holds promise for enhancing the performance of data storage technologies. Read more »
Plumbing the Depths of Interfaces and Finding Buried Treasure
Understanding the interfaces where solids and liquids meet is key to controlling a wide range of energy-relevant processes, from how batteries store energy to how metals corrode, and more. Now researchers have explored such interfaces and found what they describe as a treasure trove of unexpected results that expands our understanding of working interfaces and how to probe them. Read more »
Getting to the Bottom of a Metal/Acid Interface
Researchers identified the molecules that collect at the interface between a platinum electrode and an acidic electrolyte under an applied voltage. Knowledge of the structure and composition of such nanometer-thin interface regions is key to understanding topics such as corrosion, geochemistry, electrocatalysis, and energy storage. Read more »![]()
![]()
Tunable Ferromagnetism in a 2D Material at Room Temperature
Researchers combined soft x-ray spectroscopy and microscopy to demonstrate the tunable ferromagnetic characteristics of a two-dimensional layered material at room temperature. The results open up exciting opportunities for the use of such materials in low-power spintronics, high-density magnetic storage, and flexible electronics. Read more »
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- …
- 10
- Next Page »