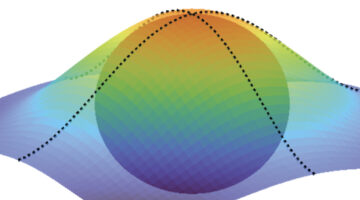
Researchers found a way to reconstruct quantum geometric tensors (QGTs)—mathematical entities that encode how an electron’s wave function is shaped by its quantum environment. The mapping of QGTs enables the discovery and control of novel quantum phenomena such as superconductivity and unconventional electronic phases. Read more »![]()
![]()
Energy-Saving, Acid-Free, Hard-Rock Lithium Extraction
Researchers used in situ x-ray diffraction to develop a direct, more energy-efficient, and cheaper way to extract lithium from its source mineral, spodumene. The approach not only promises to reduce energy consumption and processing costs but also supports the sustainable scaling of lithium production to meet growing market needs. Read more »![]()
ALS in the News (March 2025)
A New Way to Engineer Composite Materials
A new study led by researchers at Berkeley Lab outlines a way to engineer pseudo-bonds in materials. Instead of forming chemical bonds, which is what makes epoxies and other composites so tough, the chains of molecules entangle in a way that is fully reversible. Read more »
A Clearer Look at Lithium-Ion Traffic Jams in Batteries
By directly visualizing the uneven insertion of lithium ions into electrodes with well-defined crystal orientations, researchers learned why fast charging decreases battery lifespan and performance. The work could provide insights into better battery utilization and help investigations of the surface insertion reaction during fast charging. Read more »![]()
![]()
Bennu’s Ancient Brine Sheds Light on Recipe for Life
Researchers traced the evolution of minerals (“salts”) in an ancient brine, as recorded in samples from the asteroid Bennu, returned to Earth by NASA’s OSIRIS-REx mission. The results support the idea that asteroids like Bennu may have delivered water and essential chemical building blocks of life to Earth in the distant past. Read more »![]()
![]()
ALS in the News (February 2025)
Berkeley Lab Helps Explore Mysteries of Asteroid Bennu
The Advanced Light Source and Molecular Foundry provided powerful tools to study asteroid samples returned by NASA’s OSIRIS-REx mission to the asteroid Bennu. Researchers found a telltale set of salts formed by evaporation that illuminate Bennu’s watery past. Read more »
ALS in the News (January 2025)
-
- Berkeley Lab helps explore mysteries of Asteroid Bennu
- Unlocking algae biomolecule production at Berkeley’s synchrotron
- Intellectual Property Office announces Berkeley Lab Inventors and Developers of the Year for FY2024
- Scientists used a ‘forbidden fried egg’ to measure quantum geometry
- Three Berkeley Lab scientists receive PECASE Award
- Berkeley Lab’s Jennifer Doudna awarded National Medal of Technology and Innovation
- Former Berkeley Lab Director Paul Alivisatos receives the Enrico Fermi Presidential Award
- Berkeley Lab’s big science stories of 2024
- Leemann to deliver course at U.S. Particle Accelerator School
- World’s most powerful x-ray laser gets major energy boost
- Native American interns explore engineering opportunities at the Lab
- New ion speed record holds potential for faster battery charging, biosensing
Native American Interns Explore Engineering Opportunities at the Lab
This last summer, Berkeley Lab hosted three students from Navajo Technical University in a DOE-funded initiative that partners national labs with learning institutions whose populations are historically underrepresented in science. The goal is to increase enrollment of Native American students in Navajo Tech engineering programs. Read more »
- « Previous Page
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- …
- 83
- Next Page »