Using microtomography and other techniques, researchers identified the exoskeletal toughening mechanisms that explain the crush resistance of the aptly named diabolical ironclad beetle. The observations could be applied in developing tough, impact- and crush-resistant materials for joining dissimilar materials. Read more »![]()
![]()
Evidence of a magnetic transition in atomically thin Cr2TiC2Tx MXene
2D magnetic materials have recently attracted significant interest as model systems to understand low-dimensional magnetism and for potential spintronic applications. Here, we report on synthesis of Cr2TiC2Tx MXene and a detailed study of its magnetic as well as electronic properties. Read more »
Domain-Swap Dimerization of Acanthamoeba castellanii CYP51 and a Unique Mechanism of Inactivation by Isavuconazole
We investigated the mechanism of action of antifungal drugs in the human pathogen Acanthamoeba castellanii. We discovered that the enzyme target formed a dimer via an N-termini swap, whereas drug-bound AcCYP51 was monomeric. Cover image shows a molecular model of the AcCYP51 dimer in a phospholipid bilayer. Read more »
Scientists Design New Framework for Clean Water
A promising solution to water pollution from abandoned copper mines relies on materials that adsorb copper ions from wastewater, but commercially available products lack the required chemical specificity and load capacity. A team of scientists has designed a new crystalline material that targets and traps copper ions from wastewater with unprecedented precision and speed. Read more »
Balanced Charge Transport Optimizes Industry‐Relevant Ternary Polymer Solar Cells
In this article, Szymanski et al. develop novel, cost‐effective ternary polymer solar cells printed in semi‐industrial conditions from a relatively benign ink, which do not require any further processing. These solar cells show good stability and efficiency due to balanced charge-carrier mobilities achieved by optimizing the composition and morphology. Read more »
Rational Design of a Uranyl Metal–Organic Framework for the Capture and Colorimetric Detection of Organic Dyes
Diffraction data for a new uranyl-containing metal–organic framework reveals a structure of interpenetrating 3D nets with large pores. The material is stable in aqueous media and due to the large void space (constituting 76% of the unit cell by volume) can sequester organic dyes, the uptake of which induces a visible change to the color of the material. Read more »
X-Rays Reveal Architectural Clues to the Crush-Resistance of Diabolical Ironclad Beetles
The appropriately named diabolical ironclad beetle has an incredibly crush-resistant exoskeleton, which could serve as a blueprint for tougher materials. To see, in microscopic detail, what makes the beetle so uniquely ironclad, researchers used the ALS to explore a protective covering known as the “elytra,” its abdomen, and other parts. Read more »
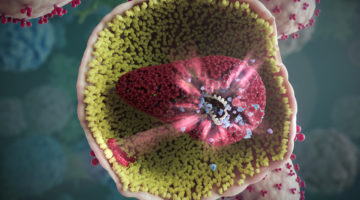
Experimental Drug Targets HIV in a Novel Way
Researchers from Gilead Sciences Inc. solved the structure of an experimental HIV drug bound to a novel target: the capsid protein that forms a shield around the viral RNA. The work could lead to a long-lasting HIV treatment that overcomes the problem of drug resistance and avoids the need for burdensome daily pill-taking. Read more »![]()
![]()
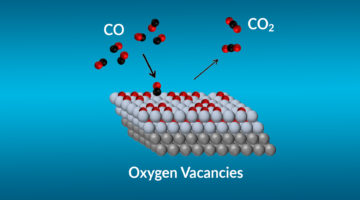
Increasing the Efficiency of CO Catalytic Conversion
Using a combination of tools at the ALS and other facilities, researchers probed specific mechanisms affecting the efficiency of catalysts for CO-to-CO2 conversion. The work brings us closer to the rational design of more effective catalysts for cleaning up toxic CO exhaust and advances our understanding of fundamental catalytic reactions. Read more »![]()
![]()
ALS in the News (October 2020)
-
-
- X-rays reveal architectural clues to the crush-resistance of diabolical ironclad beetles
- Chasing their tails but getting somewhere: Reimagining the shape of noise leads to improved molecular models
- 2020 Nobel Prize victories confirm the necessity of Energy Department’s public and private partnerships
- Berkeley Lab names Noël Bakhtian to lead new Energy Storage Center
- Focusing in on aquatic microbes: Berkeley Lab scientists receive grant for new microscopy approach
-
- Coming down the pike: Long-haul trucks powered by hydrogen fuel cells
- First day in a Nobel life: Jennifer Doudna
- Jennifer Doudna wins 2020 Nobel Prize in Chemistry
- Study finds ‘missing link’ in the evolutionary history of carbon-fixing protein rubisco
- Providing new technologies for vaccine development
-
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- …
- 83
- Next Page »