Researchers found a way to turn single-use plastics (e.g., grocery bags and packaging) into useful liquid fuels, like components of gasoline or diesel, without needing high heat, rare metals, or added chemicals. The work presents a promising pathway to address the global plastic waste crisis, with both environmental and economic advantages. Read more »
Science Briefs
ALS Captures Structure of Engineered Protein, Opening New Options to Treat IBD
Researchers use the ALS to confirm the structure of an engineered immune protein that could open new opportunities to treat inflammatory bowel disease. Read more »
A Deeper Look into Emergent Magnetism at Interfaces
Researchers shed new light on interfacial ferromagnetism in superlattices of alternating magnetic layers. By advancing our understanding of atomic-level interactions at magnetic interfaces, this work expands the scope of traditional interface studies and lays the groundwork for future innovations in magnetic storage and spintronics. Read more »
Building a Gated-Access Fast Lane for Ions
In organic conductors where charge is carried by both electrons and ions, scientists have discovered a way to make the ions move more than ten times faster than in comparable ion-transport methods. The results could apply to a host of areas, including improved battery charging, biosensing, soft robotics, and neuromorphic computing. Read more »
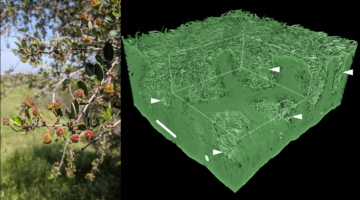
The Secret to Drought Tolerance Lies in a Lilac Crypt
Many species of California lilac grow throughout the state, north to Humboldt and south to San Diego. Some species have developed an adaptation for arid climates: the stomatal crypt. This extremely rare anatomy intrigued a group of researchers, who characterized species with these crypts at the ALS. Their microtomography characterization revealed how the stomatal crypt helps plants survive drought. Read more »
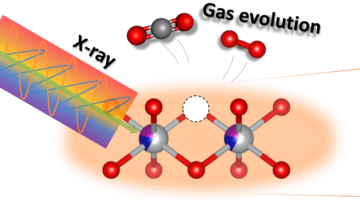
Energy-Saving, Acid-Free, Hard-Rock Lithium Extraction
Researchers used in situ x-ray diffraction to develop a direct, more energy-efficient, and cheaper way to extract lithium from its source mineral, spodumene. The approach not only promises to reduce energy consumption and processing costs but also supports the sustainable scaling of lithium production to meet growing market needs. Read more »![]()
Reaction Mechanism of Commercial Lithium-Ion Battery Cathodes
Researchers used soft x-ray resonant inelastic x-ray scattering at the ALS to understand the role of aluminum doping in improving the stability of commercially used cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries. Read more »
Mind-Blowing Materials: Mimicking Neurons for Faster Computing
Researchers used x-ray absorption spectroscopy and resonant inelastic x-ray scattering at the ALS to uncover the atomic-level mechanism of conductance switching for a neuromorphic material that has the potential for energy-efficient computing. Read more »
Autonomous Beamlines: Harnessing Bayesian Optimization to Revolutionize Accelerator Science
Scientists at the Advanced Light Source are developing automated beam optimization systems, collaborating with other light sources to deploy common controls across facilities. Using machine learning, they demonstrated automated beamline alignment that optimizes beam size and flux at the push of a button. Read more »
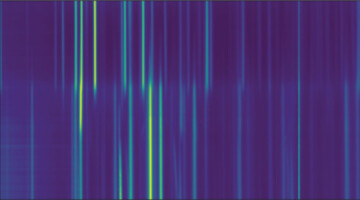
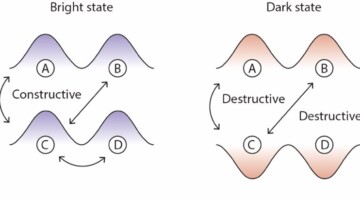
Hide-and-Seek with Sneaky Electrons in Solids
Researchers used angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy (ARPES) at the Advanced Light Source (ALS) to demonstrate the existence of dark—state electrons in solids for the first time, providing insights into complex phenomena in physics, such as high-temperature superconductivity and optoelectronics.
Read more »
- « Previous Page
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- …
- 23
- Next Page »