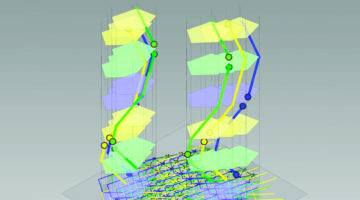
Researchers demonstrated that coupled electronic and magnetic properties in a material can be repeatably tuned using laser light. The results suggest the possibility of creating microelectronic devices that use a laser beam to erase and rewrite bits of information in materials engineered for random-access memory and data storage. Read more »![]()
![]()
Science Highlights
How Light-Harvesting Bacteria Toggle Off and On
Researchers clarified the atomic-level mechanism that enables bacteria to switch light harvesting off and on in response to potentially damaging overexposure to light. The results could have long-range implications for artificial photosynthesis and optogenetics—the use of light to selectively activate biological processes. Read more »![]()
![]()
Linking Structure to Behavior in Twisted Liquid Crystals
Researchers untangled connections between structure and behavior in a class of liquid crystals consisting of flexible, chain-like molecules that self-organize into twisting patterns. The study opens up new possibilities for designing novel liquid-crystal molecules that allow greater control of nanoscale behavior for technological applications. Read more »![]()
![]()
Electric Dipoles Form Chiral Skyrmions
Researchers demonstrated that polar skyrmions—cousins of magnetic skyrmions but comprising swirls of electric dipoles instead of spins—exhibit chirality in a material with electrically switchable properties. Control of such phenomena could one day lead to low-power, nonvolatile data storage as well as to high-performance computers. Read more »![]()
![]()
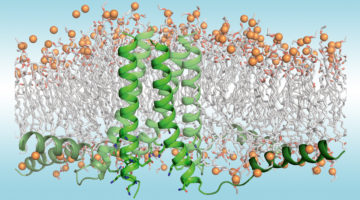
Breakthrough in Membrane-Protein Design Settles Long-Standing Debate
Scientists characterized designed membrane proteins to better understand the forces that stabilize these large, complex structures. The results necessitate a rethinking of membrane-protein biophysics and could lead to better therapies for related illnesses as well as functional membrane proteins for engineering applications. Read more »![]()
![]()
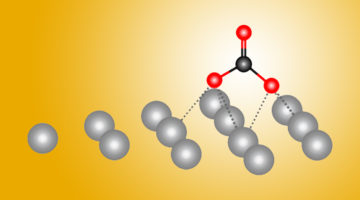
A New Path to Carbon Dioxide Transformation
Combining ALS experiments with quantum-mechanical calculations, scientists found dramatic differences in how carbon dioxide (CO2) reactions begin on silver as opposed to copper. Both metals help transform CO2—a greenhouse gas—into more useful forms, and this new atomic-level data could help make the process more efficient. Read more »![]()
![]()
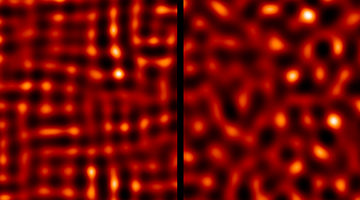
Superconductor Exhibits “Glassy” Electronic Phase
Researchers discovered that electrons in a high-temperature superconductor can exhibit a new type of collective behavior that is more “glassy” (disordered) than expected. The study provides valuable insight into the nature of collective electron behaviors and how they relate to high-temperature superconductivity. Read more »![]()
![]()
Antibody Uses Mimicry to Block SARS Coronavirus
Protein structures not only revealed how SARS and MERS antibodies inhibit the viruses from attaching to host cells, they also revealed an unprecedented example of receptor mimicry that triggers the cell-invasion machinery of the SARS virus. The results inform efforts to prevent and treat these serious, often deadly, respiratory diseases. Read more »![]()
![]()
Absorber Captures Excess Chemotherapy Drugs
Researchers have designed a biomedical device for absorbing excess chemotherapy drugs during cancer treatment, characterizing the active surface layer using x-ray microtomography. The work opens up a new route to fighting cancer that minimizes drug toxicity and enables personalized, targeted, high-dose chemotherapy. Read more »![]()
![]()
Reversible Lattice-Oxygen Reactions in Batteries
Researchers quantified a strong, beneficial, and reversible (over hundreds of cycles) chemical reaction involving oxygen ions in the crystal lattice of battery electrode materials. The results open up new ways to explore how to pack more energy into batteries with electrodes made out of low-cost, common materials. Read more »![]()
![]()
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- …
- 27
- Next Page »