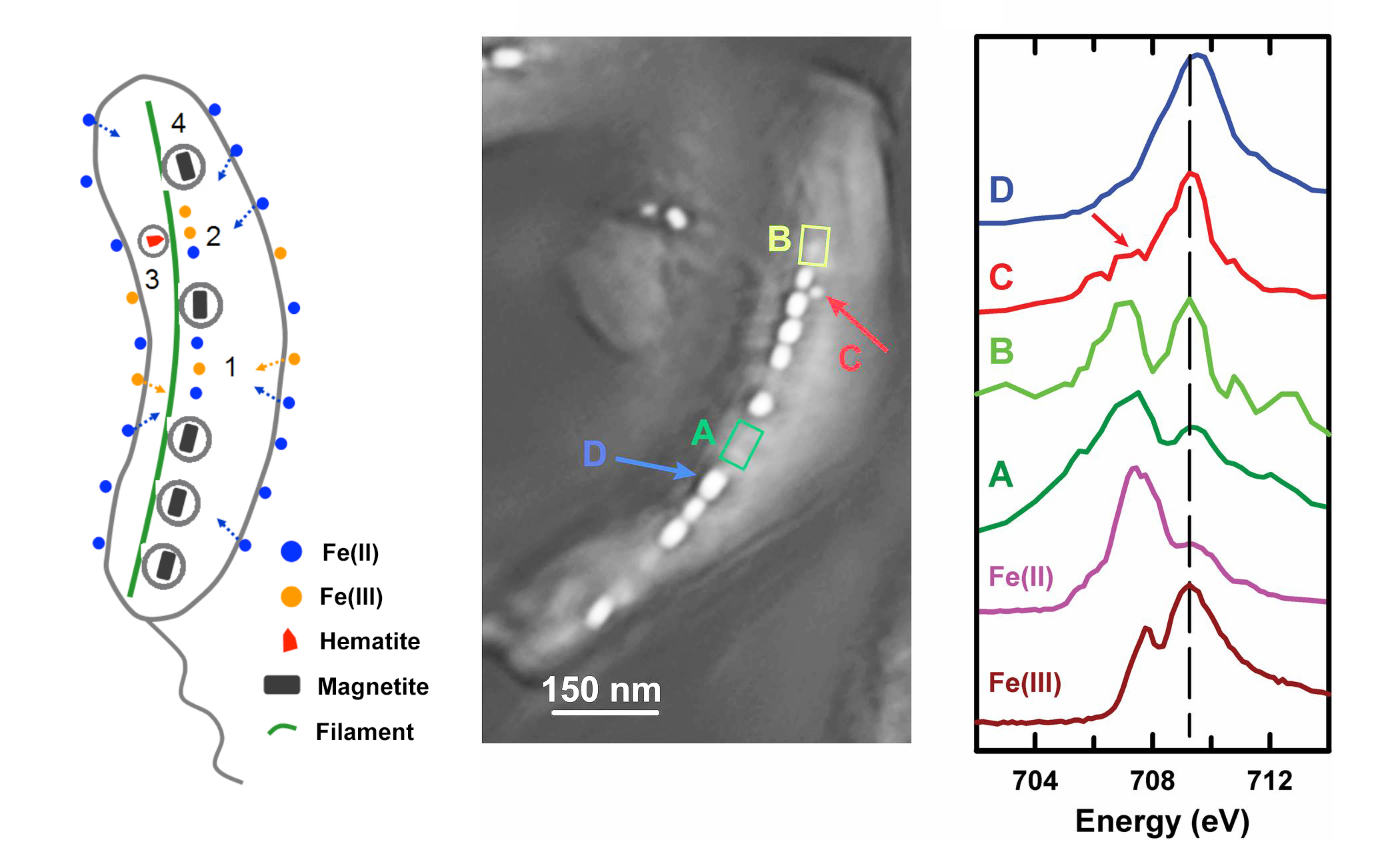
Magnetotactic bacteria (MTB) synthesize chains of magnetic nanocrystals (magnetosomes) that interact with the Earth’s magnetic field like an inner compass needle, simplifying their search for optimum environments. How do these magnetosomes form? Some studies suggest that hematite or amorphous ferrihydrite act as precursors, while others suggest that they are formed directly from solution-phase Fe(II) and Fe(III). Thus, identifying the chemical states of precursors would be a good way to differentiate among competing models.
Ptychography is a coherent diffractive imaging technique with high resolution (7 nm in this work) and excellent chemical-state sensitivity. At ALS Beamlines 5.3.2.1 and 11.0.2.2, researchers obtained ptychographic absorption and phase spectra of magnetosomes from a marine MTB (Magnetovibrio blakemorei strain MV-1). The data, obtained from mature magnetosomes, immature magnetosomes, precursor regions, and the gaps between magnetosome chains, indicated that different iron species can coexist in a single cell. Based on the results, the researchers proposed a model in which soluble Fe(II) is taken up from the environment, is partially oxidized to Fe(III), which in turn is then oxidized and transformed into hematite and ultimately into magnetite.
In addition, at Beamline 11.0.2.2, the researchers used ptychography to measure the x-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD) spectra of both extracellular and intracellular magnetosomes. XMCD probes the magnetism of a crystal in a site-specific manner. This part of the study showed that absorption and XMCD ptychography signals provide complementary information. These experiments demonstrate that ptychography, which combines high spatial resolution, high-sensitivity chemical speciation, and site-specific magnetic information, offers a powerful probe for biomineralization studies.
Work performed at ALS Beamlines 5.3.2.1 and 11.0.2.
X. Zhu, A.P. Hitchcock, D.A. Bazylinski, P. Denes, J. Joseph, U. Lins, S. Marchesini, H.-W. Shiu, T. Tyliszczak, and D.A. Shapiro, “Measuring spectroscopy and magnetism of extracted and intracellular magnetosomes using soft X-ray ptychography,” PNAS 113, E8219 (2016). doi: 10.1073/pnas.1610260114