A research team led by Berkeley Lab designed and fabricated catalysts by precisely tuning the co-localization of active metals—key catalytic centers for specific steps in reaction pathways—offering a new level of control over catalytic performance. Read more »
Catching “Hydrogen Spillover” onto a Catalytic Surface
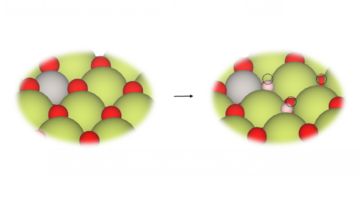
Researchers uncovered the precise mechanism of hydrogen spillover (H2 splitting and migration) onto a catalytic surface by watching it happen under various conditions. The research lays the foundation for designing more efficient catalysts and storage materials essential for next-generation hydrogen energy technologies. Read more »![]()
![]()
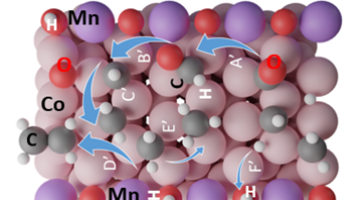
Understanding the Role of Manganese in Fuel Production Catalysts
Using specialized equipment at the Advanced Light Source (ALS), including a custom-built reaction cell, researchers uncovered the role of manganese in cobalt manganese oxide catalysts used for fuel production. Read more »![]()
![]()
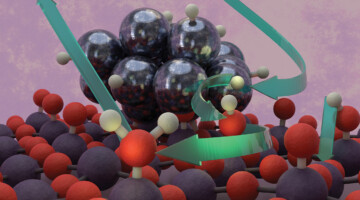
Operando Unveiling of Hydrogen Spillover Mechanisms on Tungsten Oxide Surfaces
An artistic depiction of hydrogen spillover on Pt/WO3, illustrating H2 activation and dissociation on Pt metal clusters, followed by hydrogen migration to WO3 for water formation. At elevated temperatures, water desorption and surface-to-bulk diffusion of hydrogen drive tungsten redox and oxygen vacancy formation on the surface of WO3. Read more »
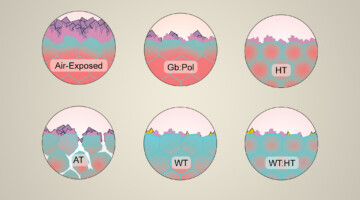
Studying Interfacial Effects in Solid-Electrolyte Batteries
An ambient-pressure probe of a solid electrolyte revealed how surface electrochemical mechanisms lead to poor electrolyte performance and battery failure. The results can help scientists engineer better coatings and interfaces, which are essential for building safer and better-performing batteries, particularly for use in vehicles. Read more »![]()
![]()
Unveiling Direct Electrochemical Oxidation of Methane at the Ceria/Gas Interface
Ceria-based oxides embedded in solid-oxide fuel cells are recognized for their critical role in managing hydrocarbon activation and carbon coking. However, even for the simplest hydrocarbon molecule, CH4, the mechanism of electrochemical oxidation at the ceria/gas interface is not well understood. This study presents a Sm-doped ceria thin-film model cell that selectively monitors CH4 direct-electro-oxidation on the ceria surface. Read more »
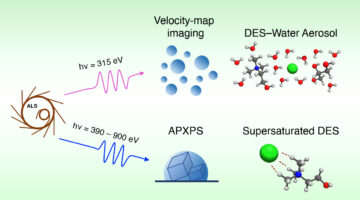
Probing the Liquid/Vapor Interface of a Tunable Solvent
Despite the ready tunability and industrial promise of deep eutectic solvents (DESs), there have been few x-ray spectroscopy studies at their liquid/vapor interfaces—which is relevant for their use in applications such as greenhouse-gas capture. Here, researchers probed the liquid/vapor interface of a benchmark DES using complementary spectroscopies. Read more »
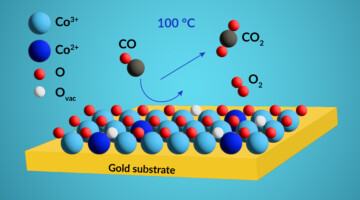
Probing Active-Site Chemical States in a Co-Based Catalyst
Researchers identified the dominant chemical state of active sites in a cobalt-based catalyst using resonant photoemission spectroscopy under realistic conditions. The work will help scientists develop more-efficient catalysts for removing noxious carbon monoxide gas from exhaust streams generated by the burning of fossil fuels. Read more »![]()
![]()
HyMARC Aims to Hit Targets for Hydrogen Storage Using X-Ray Science
Understanding how materials absorb and release hydrogen is the focus of the Hydrogen Materials Advanced Research Consortium (HyMARC). At the ALS, the HyMARC Approved Program was recently renewed, underscoring the key role that soft x-ray techniques have played in addressing the challenges of hydrogen storage. Read more »
Spectroscopic investigation of a Co(0001) model catalyst during exposure to H2 and CO at near-ambient pressures
We have performed near-ambient-pressure X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy on Co(0001) model catalysts during exposure to gases relevant to Fischer–Tropsch synthesis, i.e., CO and H2, at 0.25 mbar total pressure. At this pressure, CO seems to be more efficient at keeping the Co(0001) surface metallic than H2, which is the opposite behavior as reported in the literature for other pressure ranges. Read more »
- 1
- 2
- 3
- …
- 5
- Next Page »