Multimodal in situ x-ray experiments at the ALS revealed how copper–silver nanoparticle catalysts evolve during CO2 photoreduction. The findings, which demonstrate dynamic catalyst restructuring at the atomic level, provide crucial insights for enhancing the selectivity and efficiency of CO2 conversion into high-value chemicals. Read more »![]()
![]()
Multimetallic Systems Convey Cost-Effective Hydrogen Storage
A bimetallic material (Pd-Ni) produces hydrogen-active nanopockets that improve the efficiency and lower the cost of hydrogen storage systems. Mechanistic understanding of a Pd-Ni bimetallic system paves the way to design cost-effective hydrogen storage, opening new opportunities to develop reliable energy technologies necessary to advance the energy industry. Read more »![]()
![]()
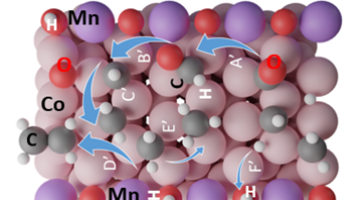
Understanding the Role of Manganese in Fuel Production Catalysts
Using specialized equipment at the Advanced Light Source (ALS), including a custom-built reaction cell, researchers uncovered the role of manganese in cobalt manganese oxide catalysts used for fuel production. Read more »![]()
![]()
HyMARC Aims to Hit Targets for Hydrogen Storage Using X-Ray Science
Understanding how materials absorb and release hydrogen is the focus of the Hydrogen Materials Advanced Research Consortium (HyMARC). At the ALS, the HyMARC Approved Program was recently renewed, underscoring the key role that soft x-ray techniques have played in addressing the challenges of hydrogen storage. Read more »
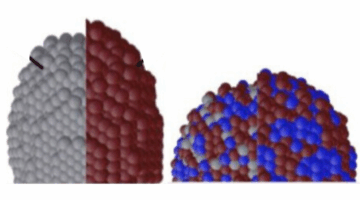
Watching Nanoparticle Chemistry and Structure Evolve
Using a multimodal approach, researchers learned how chemical properties correlate with structural changes during nanoparticle growth. The work will enable a greater understanding of the mechanisms affecting the durability of nanoparticles used to catalyze a broad range of chemical reactions, including clean-energy reactions. Read more »![]()
![]()
Nanoscale Confinement of Photo-Injected Electrons at Hybrid Interfaces
Picosecond time-resolved x-ray photoemission spectroscopy provides real-time electron distributions of donors and acceptors in a prototypical bipyridyl-ZnO hybrid light harvesting system. The measurements show that photo-injected electrons remain localized within the defect-rich surface region of the nanoporous ZnO substrate, revealing a challenge for the extraction of free charge carriers. Read more »
When Timing Isn’t Everything: Spontaneous Chemical Dynamics
Researchers combined aspects of x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) with correlation spectroscopy—a statistical method capable of detecting patterns in microscopic fluctuations across space and time. The new technique, called time-correlation XPS, allows researchers to monitor dynamics without the need for a timed trigger. Read more »
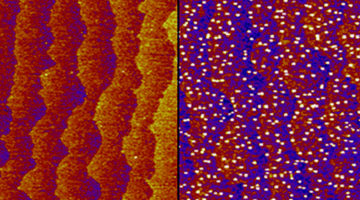
Tuning of One Atomic Layer Unlocks Catalytic Pathway
An atomically precise surface probe helped researchers discover that a catalyst can be activated by tuning the composition of just one atomic surface layer. The work sharpens our understanding of how surface changes can improve the production of hydrogen fuel from water using efficient catalysts made of inexpensive materials. Read more »![]()
![]()
Identifying Ionic and Electronic Charge Transfer at Oxide Heterointerfaces
Researchers identified how ion and electron transfer naturally balance at the LaAlO3/SrTiO3 oxide heterointerface, affecting the band alignment and magnetic signature of the interface. The results show that Sr ions are more mobile at the interface than in the bulk, implicating a high importance of ionic charge transfer in oxide heterostructures. Read more »
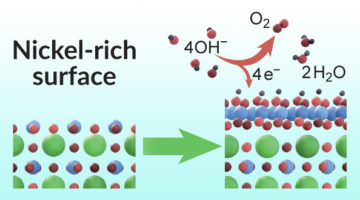
A 1-Atom-Deep Look at a Water-Splitting Catalyst
X-ray experiments revealed an unexpected transformation in a single atomic layer of a material that contributed to a doubling in the speed of a chemical reaction—the splitting of water into hydrogen and oxygen gases. This process is a first step in producing hydrogen fuel for applications such as electric vehicles powered by hydrogen fuel cells. Read more »