LONP1 is an AAA+ protease that maintains mitochondrial homeostasis by removing damaged or misfolded proteins. Elevated activity and expression promotes cancer cell proliferation and resistance to apoptosis-inducing reagents. Herein, we report the development of selective boronic acid-based LONP1 inhibitors using structure-based drug design as well as the first structures of human LONP1 bound to various inhibitors. Read more »
Targeting KRAS Mutant Cancers via Combination Treatment: Discovery of a 5-Fluoro-4-(3H)-quinazolinone Aryl Urea pan-RAF Kinase Inhibitor
The cover feature shows a chessboard (representative of KRAS mutant cells) and how the concerted action of the MEK inhibitor cobimetinib (rook) and the new selective pan-RAF inhibitor GNE-0749 (queen) force the opposing king (phospho-ERK, the downstream signaling node of RAF and MEK) into checkmate. Read more »
Mystery Protein Helps COVID–19 Avoid Immunity
Using the Advanced Light Source (ALS), researchers solved the structure of ORF8, a protein specific to SARS-CoV-2. Understanding the structure of ORF8 opens the door to therapy studies targeting SARS-CoV-2, the virus responsible for causing COVID-19. Read more »![]()
![]()
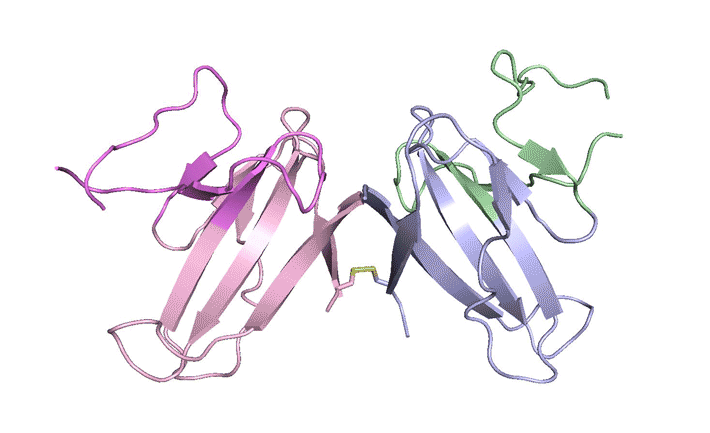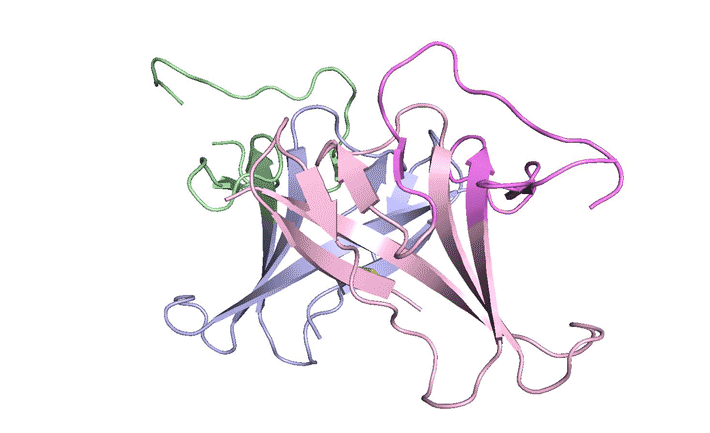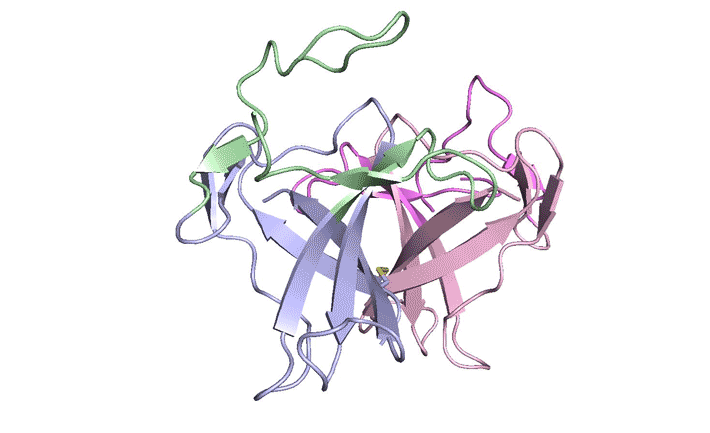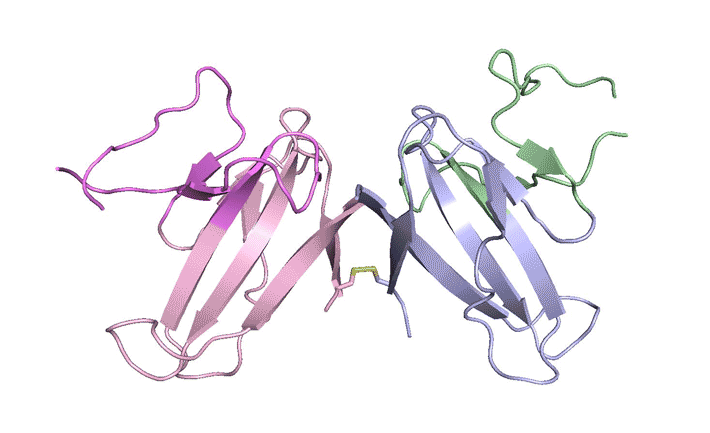
Construction, characterization and crystal structure of a fluorescent single-chain Fv chimera
In vitro display technologies based on phage and yeast have a successful history of selecting single-chain variable fragment (scFv) antibodies against various targets. However, single-chain antibodies are often unstable and poorly expressed. We explore the feasibility of converting scFv antibodies to an intrinsically fluorescent format by inserting a monomeric, stable fluorescent protein between the light- and heavy-chain variable regions. Read more »
CC-90009, a novel cereblon E3 ligase modulator, targets acute myeloid leukemia blasts and leukemia stem cells
A number of clinically validated drugs have been developed by repurposing the CUL4-DDB1-CRBN-RBX1 (CRL4CRBN) E3 ubiquitin ligase complex with molecular glue degraders to eliminate disease-driving proteins. Here, we present the identification of a first-in-class GSPT1-selective cereblon E3 ligase modulator, CC-90009, that targets acute myeloid leukemia blasts and leukemia stem cells. Read more »
The Odd Structure of ORF8: Scientists Map the Coronavirus Protein Linked to Immune Evasion and Disease Severity
Researchers determined the atomic structure of a coronavirus protein thought to help the pathogen evade and dampen response from human immune cells. Researchers determined the atomic structure of a coronavirus protein thought to help the pathogen evade and dampen response from human immune cells. Read more »
Experimental Drug Targets HIV in a Novel Way
Researchers from Gilead Sciences Inc. solved the structure of an experimental HIV drug bound to a novel target: the capsid protein that forms a shield around the viral RNA. The work could lead to a long-lasting HIV treatment that overcomes the problem of drug resistance and avoids the need for burdensome daily pill-taking. Read more »![]()
![]()
Jennifer Doudna and the Nobel Prize: The Advanced Light Source Perspective
The 2020 Nobel Prize in Chemistry was awarded to Jennifer Doudna and Emmanuelle Charpentier for the development of a world-changing gene-editing technology. At the ALS, Doudna’s work on CRISPR-Cas9 was enabled by many visionary people with innovative ideas, implemented in support of a world-class structural biology program. Read more »![]()
Study Finds ‘Missing Link’ in the Evolutionary History of Carbon-Fixing Protein Rubisco
Scientists discovered an ancient form of rubisco, the most abundant enzyme on Earth and critical to life as we know it. Found in previously unknown environmental microbes, the newly identified rubisco provides insight into the evolution of the photosynthetic organisms that underlie the planet’s food chains. Read more »
Targeting the trypanosome kinetochore with CLK1 protein kinase inhibitors
Saldivia et al. identify CLK1 as the target for the amidobenzimidazoles series of compounds. Inhibition of this protein kinase impairs inner kinetochore recruitment, causing cell-cycle arrest and cell death in trypanosomal pathogens such as Trypanosoma brucei. Read more »
- « Previous Page
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- …
- 10
- Next Page »