The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has approved a new antibiotic that, in combination with two existing antibiotics, can tackle one of the most formidable and deadly treatment-resistant forms of the bacterium that causes tuberculosis. Studies exploring the structure and function of the new drug benefited from x-ray experiments at the ALS. Read more »
A Bullfrog’s Powerful Defense Against Toxic Red Tides
Working as a “molecular sponge,” a bullfrog protein known as saxiphilin provides powerful, yet little understood, protection against deadly neurotoxins produced in red tides. Crystallography studies at the ALS have clarified saxiphilin’s function, potentially enabling better ways to monitor and combat toxins in our oceans and food supplies. Read more »![]()
How Light-Harvesting Bacteria Toggle Off and On
Researchers clarified the atomic-level mechanism that enables bacteria to switch light harvesting off and on in response to potentially damaging overexposure to light. The results could have long-range implications for artificial photosynthesis and optogenetics—the use of light to selectively activate biological processes. Read more »![]()
![]()
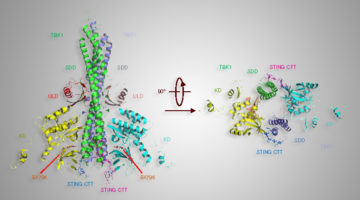
X-Ray Studies Key in Study Relating to Immune System-Signaling Protein
A grouping of amino acids—part of an important signaling protein, STING—plays an important role in activating the immune system. A study conducted through the Collaborative Crystallography program at the ALS confirmed how this part of the STING protein helps to bind a protein-modifying enzyme associated with autoimmune diseases and some cancers. Read more »
A Frog Worth Kissing: Natural Defense Against Red Tide Toxin Found in Bullfrogs
Researchers have discovered how a protein produced by bullfrogs binds to and inhibits the action of saxitoxin, a deadly neurotoxin that causes paralytic shellfish poisoning. The findings could lead to the first-ever antidote for the compound, which blocks nerve signaling in animal muscles, causing death by asphyxiation when consumed in sufficient quantities. Read more »
The Stomatopod Telson: Convergent Evolution in the Development of a Biological Shield
In this article, researchers identify multiscale structure‐mechanical property relationships within the shield-like exoskeletal telson structure of the mantis shrimp, used for defense and protection. Comparison of telsons from two evolutionarily divergent species reveal differences in macromorphology, cuticle thickness, and mineralization, imparting compressive stiffness as well as compliance for energy absorption. Read more »
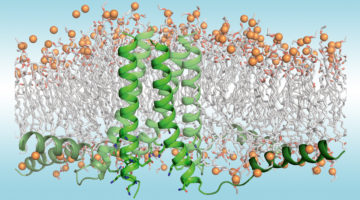
Breakthrough in Membrane-Protein Design Settles Long-Standing Debate
Scientists characterized designed membrane proteins to better understand the forces that stabilize these large, complex structures. The results necessitate a rethinking of membrane-protein biophysics and could lead to better therapies for related illnesses as well as functional membrane proteins for engineering applications. Read more »![]()
![]()
Self-Assembling 2D Arrays with de Novo Protein Building Blocks
Modular self-assembly of biomolecules in two dimensions (2D) is straightforward with DNA but has been difficult to realize with proteins, due to the lack of modular specificity similar to Watson–Crick base pairing. Here, researchers describe a general approach to designing 2D arrays using de novo designed pseudosymmetric protein building blocks. Read more »
Exploring the “minimal” structure of a functional ADAMTS13 by mutagenesis and small-angle X-ray scattering
Researchers used the SIBYLS beamline to gain insight into ADAMTS13, the only known protein to regulate the adhesive function of von Willebrand factor (VWF), a blood-clotting protein. When VWF is deficient or abnormal, it causes a common inherited bleeding disorder, von Willebrand disease. VWF is also implicated in arterial and deep-vein thrombosis, stroke, atherosclerosis, sickle cell crisis, and sepsis. Read more »
Design and Synthesis of Selective Phosphodiesterase 4D (PDE4D) Allosteric Inhibitors for the Treatment of Fragile X Syndrome and Other Brain Disorders
PDE4D enzymes are important for normal brain function. Mutations have been asssociated with an ultrarare neurodevelopmental disorder, and genetic variation in PDE4D contributes to biological variation in human cognitive ability. Here, researchers report on novel PDE4D inhibitors providing potent memory-enhancing effects in a mouse model, with improved tolerability and reduced vascular toxicity over earlier PDE4 inhibitors. Read more »
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- …
- 24
- Next Page »