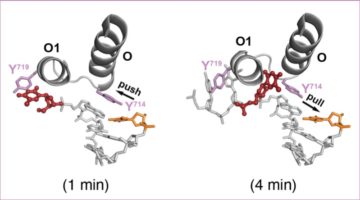
What if the current model for DNA synthesis were flipped on its head? Using time-resolved x-ray crystallography, researchers gained new insights into this essential biological process, revealing that two steps in the synthesis pathway are, in reality, reversed. Read more »
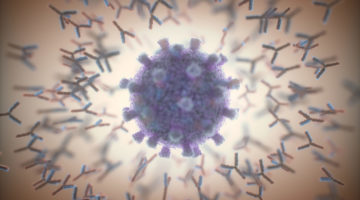
An Antibody That Broadly Neutralizes SARS-CoV-2
An antibody that appears to neutralize all known SARS-CoV-2 strains and closely related coronaviruses was discovered with the help of the ALS. The work highlights principles underlying antibody potency, breadth, and escapability that can guide the development of therapeutics against the current and potential future pandemics. Read more »![]()
![]()
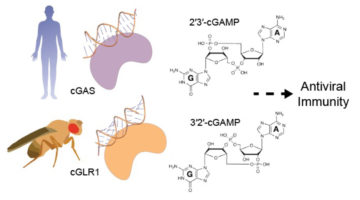
Sounding the Antiviral Alarm: A New Family of Immune-System Sensors
Comparison of enzyme structures from humans and insects revealed a new family of evolutionarily related immune-system sensors, triggered by viral RNA or DNA to produce tailored signals that initiate antiviral action. The results shed new light on the diversity and development of immune defenses in animals. Read more »
Cell ‘Fingerprinting’ Could Yield Long-Awaited Alzheimer’s Disease Diagnostic
A new application of infrared spectromicroscopy analyzes cells for signs of Alzheimer’s disease by measuring how the molecules in cells vibrate upon exposure to infrared light. The vibrational profile of each sample is so distinct and the difference between diseased and healthy cell samples is so visible that researchers liken the process to “cellular fingerprinting.” Read more »
Functional and structural characterization of AntR, an Sb(III) responsive transcriptional repressor
Antimony is considered a priority environmental pollutant by the EPA. The ant operon of the antimony-mining bacterium, C. testosterone, confers resistance to Sb(III). The operon is regulated by the product of the first gene in the operon, antR. This is the first report of the structure and binding properties of antR, with high selectivity for environmental antimony. Read more »
Sifting through Fragments for COVID-19 Treatments
COVID-19 vaccines are essential for preventing serious disease, but the identification of new drugs is still necessary for the treatment of patients who become sick as a result of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Here, scientists used computational docking and crystallography to screen large numbers of small molecules for potential use in drug compounds. Read more »
Scientist at Berkeley Lab Played a Hand in “Inescapable” COVID-19 Antibody Discovery
An antibody therapy that appears to neutralize all known SARS-CoV-2 strains—including newly emerged mutants that can now “escape” from previous antibody therapies—was developed with a little help from structural biologist Jay Nix. His work helped generate detailed structural maps of how antibodies bind to the spike protein, enabling the selection of promising contenders. Read more »
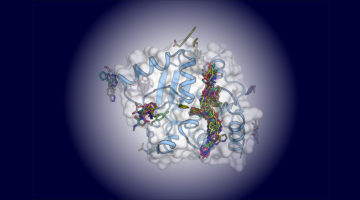
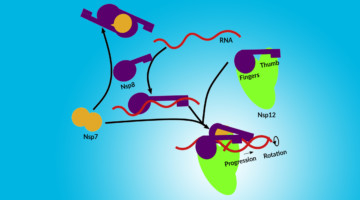
Assembly of the SARS-CoV-2 Replication Mechanism
Using a multimodal approach that included x-ray scattering at the ALS, researchers determined how components of the SARS-CoV-2 replication mechanism fit together. A better understanding of how this protein complex works provides insight into potential structural or functional weak spots to exploit for drug development. Read more »![]()
![]()
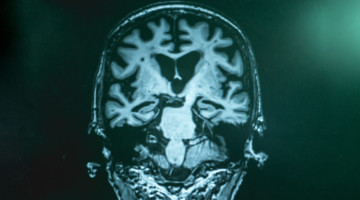
Nanoscale Metallic Particles Detected in Brain Tissue
Researchers detected nanoscale deposits of elemental copper and iron in brain tissues isolated from Alzheimer’s disease subjects. The discovery suggests new directions of study to determine the role that elemental metals might play in neurochemistry, neurobiology, and the development of neurodegenerative disease. Read more »![]()
![]()
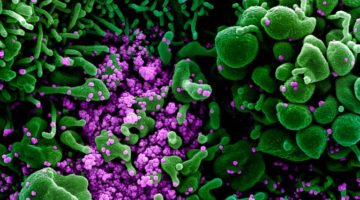
Deconstructing the Infectious Machinery of the SARS-CoV-2 Virus
Scientists collaborated to model the complex protein responsible for SARS-CoV-2 replication, revealing its potential weak spots for drug development. The investigation hinged on data collected from many advanced imaging techniques, including small-angle x-ray scattering (SAXS), crystallography, and small-angle neutron scattering (SANS). Read more »
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- …
- 24
- Next Page »