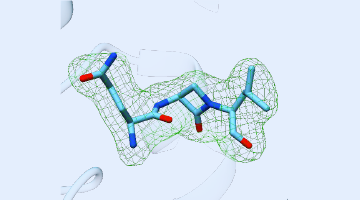
Using ALS beamlines, a new study revealed how CMX410 inhibits Pks13, a cell wall enzyme in Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the bacterium responsible for tuberculosis. CMX410 is effective against drug-sensitive and drug-resistant strains of the bacterium and has been proven safe in multiple animal models of infection. Read more »
Deep-Dive Inspection of a Molecular Assembly Line
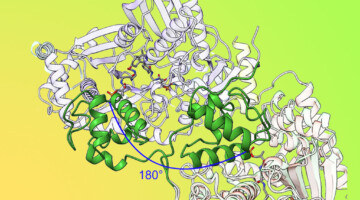
By locking down certain movable parts of a modular drug-building protein, researchers learned new details about how carrier proteins transfer the product protein between modules. The results offer insights that could enable scientists to design and create new and improved medicines, such as antibiotics, using synthetic biology. Read more »![]()
![]()
Mechanistic Insight into a Viral-Factory Component
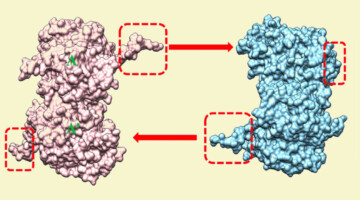
Recent protein-structure studies conducted at the ALS provided mechanistic insights into the function of a protein (σNS) involved in viral replication. Understanding these mechanisms will foster the development of therapeutic strategies against viruses that use σNS-like proteins to replicate. Read more »
Uncompetitive, adduct-forming SARM1 inhibitors are neuroprotective in preclinical models of nerve injury and disease
Researchers describe potent small-molecule inhibitors that are neuroprotective in preclinical models of nerve injury and disease. The cover depicts the destruction of an axon by the enzyme SARM1, shown disproportionately large to convey its catastrophic role in driving degeneration once it is activated upon injury. Read more »
Deep-Learning AI Program Accurately Predicts Key Rotavirus Protein Fold
Rotaviruses are the major causative agents of gastroenteritis worldwide. Attempts to design vaccines are complicated by the rotaviruses’ enormous genetic and immunological diversity. At the ALS, researchers validated the novel structure of a key rotavirus protein, predicted using AlphaFold2, a deep-learning artificial-intelligence program. Read more »
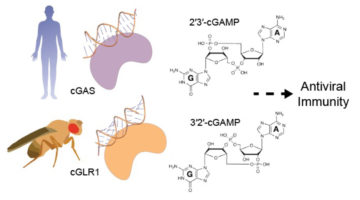
Sounding the Antiviral Alarm: A New Family of Immune-System Sensors
Comparison of enzyme structures from humans and insects revealed a new family of evolutionarily related immune-system sensors, triggered by viral RNA or DNA to produce tailored signals that initiate antiviral action. The results shed new light on the diversity and development of immune defenses in animals. Read more »
Structure of blood coagulation factor VIII in complex with an anti–C1 domain pathogenic antibody inhibitor
van der Waals sphere representation of the factor VIII C1 domain, highlighting surface‐exposed hemophilia A–associated mutations that cause impaired von Willebrand factor binding and overlap with a pathogenic anti‐C1 domain inhibitor epitope. Read more »
CC-90009, a novel cereblon E3 ligase modulator, targets acute myeloid leukemia blasts and leukemia stem cells
A number of clinically validated drugs have been developed by repurposing the CUL4-DDB1-CRBN-RBX1 (CRL4CRBN) E3 ubiquitin ligase complex with molecular glue degraders to eliminate disease-driving proteins. Here, we present the identification of a first-in-class GSPT1-selective cereblon E3 ligase modulator, CC-90009, that targets acute myeloid leukemia blasts and leukemia stem cells. Read more »
Experimental Drug Targets HIV in a Novel Way
Researchers from Gilead Sciences Inc. solved the structure of an experimental HIV drug bound to a novel target: the capsid protein that forms a shield around the viral RNA. The work could lead to a long-lasting HIV treatment that overcomes the problem of drug resistance and avoids the need for burdensome daily pill-taking. Read more »![]()
![]()
Providing New Technologies for Vaccine Development
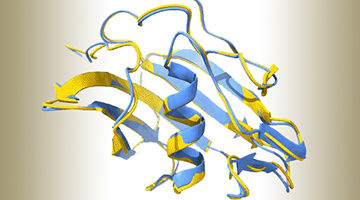
Antigens can sometimes be attached to a protein scaffold to mimic the shape of a virus and elicit a stronger immune response. Scientists developed a method to design such proteins, and ALS data helped to visualize the atomic structure and determine the dynamics of the designed scaffolds. Read more »