Scientists have captured a more detailed picture than ever of the steps in photosynthesis, the process by which plants use sunlight to split water and produce oxygen while making the carbohydrates that sustain life on Earth. The idea is eventually to have a continuous movie of how water is split into oxygen, and how plants do that using sunlight. Read more »
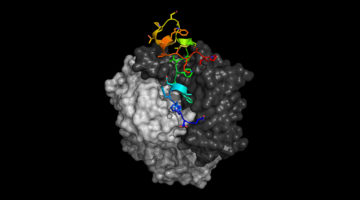
Respiratory Virus Study Points to Likely Vaccine Target
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) causes serious respiratory disease in infants and older adults, but no vaccine is yet available. Researchers have now determined the molecular structures of human antibodies bound to an RSV surface protein, providing a promising route for designing a vaccine effective against a broad range of RSV strains. Read more »![]()
![]()
NIH Grant Will Enhance Structural Biology Research Experience for ALS Users
A recently awarded National Institutes of Health (NIH) grant will help integrate existing structural biology resources at the ALS to better serve users. The funds will help establish a centralized collaborative mechanism, called ALS-ENABLE, that will guide users through the most appropriate routes for answering their biological questions. Read more »
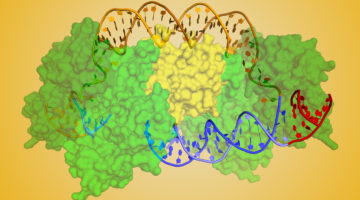
The CRISPR Target-Recognition Mechanism
CRISPR-associated (Cas) proteins have revolutionized gene editing by vastly simplifying the insertion of short snippets of new (“donor”) DNA into very specific locations of target DNA. Now, researchers have discovered how the Cas proteins are able to recognize the target locations with such great specificity. Read more »![]()
![]()
Global Blood Therapeutics Uses ALS to Tackle Sickle Cell Disease
Sickle cell disease (SCD), which affects millions of people worldwide, has traditionally been treated with a cytotoxic drug that has a range of negative side effects and variable patient response. Bay Area biopharmaceutical company Global Blood Therapeutics (GBT) is on a mission to develop a better treatment and is using the ALS to help. Read more »![]()
Molecular Switch Triggers Bacterial Pathogenicity
Using an array of high-powered x-ray imaging techniques at the ALS, scientists have revealed for the first time the molecular steps that turn on bacteria’s pathogenic genes. The study could open up new avenues in the development of drugs to prevent or treat bacterial infection. Read more »![]()
![]()
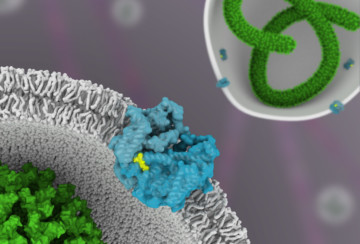
Shutting Out Ebola and Other Viruses
Researchers have used protein crystallography at the ALS to understand how a drug molecule that has shown some efficacy against Ebola in mice inactivates a membrane protein, called TPC1, used by viruses to infect host cells. Read more »![]()
![]()
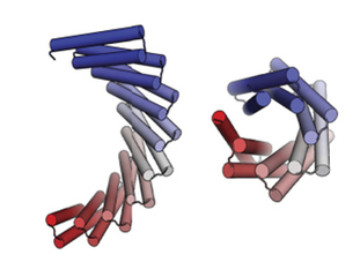
Exploring the Repeat-Protein Universe
Researchers have published a landmark study that used both crystallography and SAXS to validate computationally designed structures of novel proteins with repeated motifs. The results show that the protein-folding universe is far larger than realized, opening up a wide array of new possibilities for biomolecular engineering. Read more »![]()
![]()
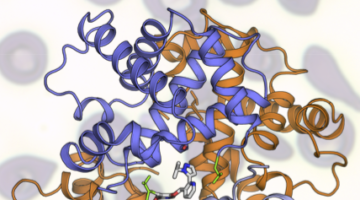
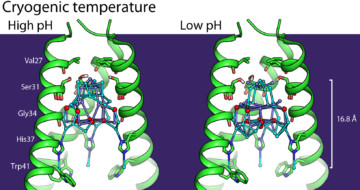
Improving Anti-Influenza Medications
Protein crystallography at ALS Beamline 8.3.1 helped scientists understand the M2 proton-channel structure from the influenza A virus, an understanding that is needed to design better anti-influenza medications. Read more »
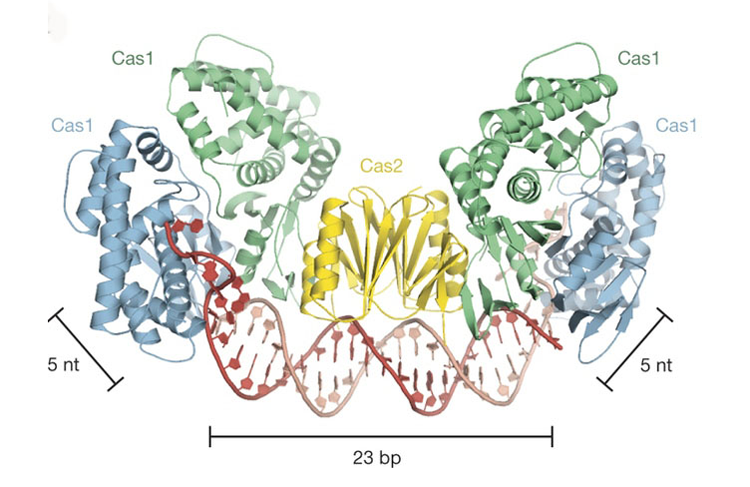
Foreign DNA Capture during CRISPR–Cas Adaptive Immunity
Using macromolecular crystallography at Beamline 8.3.1 at the ALS, Berkeley researchers discovered how CRISPR/Cas captures foreign DNA for the bacterial immune system. Read more »