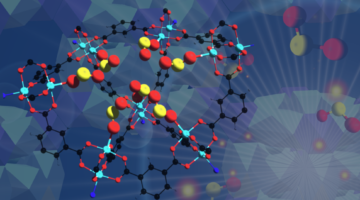
An international team has developed a robust material that can selectively take in toxic sulfur dioxide gas at record concentrations and preserve it for use in chemical production. The researchers verified its performance using a combination of techniques that included x-ray experiments at the ALS. Read more »
Renewed Prospects for Rechargeable Mg Batteries
Contrary to previous reports, it’s possible to create a rechargeable battery using magnesium ions if the electrode material is first conditioned at high temperature. With twice the charge of lithium ions, magnesium ions hold great promise as the basis for high-energy-density batteries suitable for use in electric vehicles. Read more »![]()
![]()
Peroxy self-reaction leading to the formation of furfural
Furan and its alkyl derivatives, such as methylfuran (2MF), have been identified as valid alternative biofuels. This study focuses on the self-reaction of the peroxy radical generated in the first oxidation step of 2MF. The mass spectrometry data reveal that furfural is the dominant product of 2MF oxidation. Various reaction mechanisms for furfural formation are proposed here. Read more »
Fingerprint Oxygen Redox Reactions in Batteries through High-Efficiency Mapping of Resonant Inelastic X-ray Scattering
We provide a comprehensive analysis and an explicit interpretation of the five evolving components of O-K mRIXS of the typical battery electrode that involves lattice oxygen redox reactions upon cycling. This work is the first benchmark for a complete assignment of all the important mRIXS features collected from battery materials, and thus delivers guidelines for future studies of oxygen redox reactions. Read more »
Reversible Lattice-Oxygen Reactions in Batteries
Researchers quantified a strong, beneficial, and reversible (over hundreds of cycles) chemical reaction involving oxygen ions in the crystal lattice of battery electrode materials. The results open up new ways to explore how to pack more energy into batteries with electrodes made out of low-cost, common materials. Read more »![]()
![]()
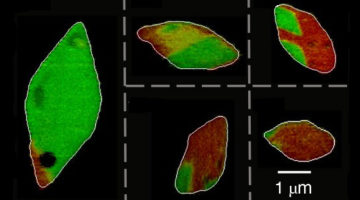
Hidden Flow of Lithium Ions Points Way to Better Batteries
Experiments revealed that lithium ions unexpectedly flow along the surfaces of electrode particles, boosting the growth of lithium “hot spots” that shorten battery life. The results correct decades’ worth of assumptions and will help improve battery design, potentially leading to a new generation of lithium-ion batteries. Read more »![]()
Miscibility–Function Relations in Organic Solar Cells: Significance of Optimal Miscibility in Relation to Percolation
In this article, Ye et al. present the determination of liquidus miscibility and its temperature dependence of organic films by scanning transmission x‐ray microscopy and outline an approach to convert liquidus miscibility to an effective Flory‐Huggins interaction parameter χ, which will pave a way to predict morphology and processing strategies of polymer solar cells. Read more »
New Manganese Materials Bolster Cathode Capacity
The most expensive component of a battery, the cathode, requires rare transition metals like cobalt. Previous attempts to replace cobalt with inexpensive and non-toxic manganese delivered insufficient performance. Now, researchers have optimized the composition of high-energy-density, high-capacity manganese-based cathodes. Read more »
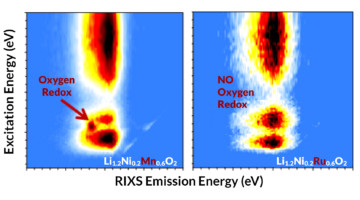
New Clues to Oxygen’s Role in Higher-Capacity Batteries
As battery electrodes, layered transition-metal (TM) oxides demonstrate storage capacities far beyond what’s explained solely by TM redox activity. In this work, measurements of the lattice oxygen redox activity in two lithium-rich layered oxides showed strong oxygen redox when manganese was the TM, but not with ruthenium. Read more »
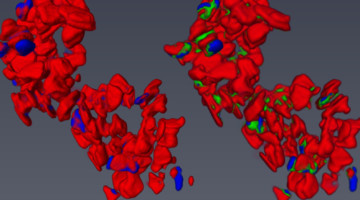
3D Localization of Nanoscale Battery Reactions
A new tool lets researchers pinpoint the locations of chemical reactions happening inside batteries in three dimensions at the nanoscale level. Combining ptychography, tomography, and spectroscopy, Nanosurveyor 1 is a multidimensional tool providing novel insight into the design of next-generation batteries and devices. Read more »
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- …
- 16
- Next Page »