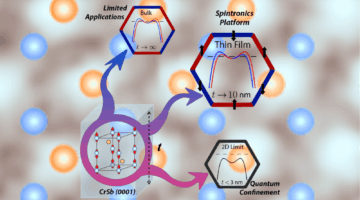
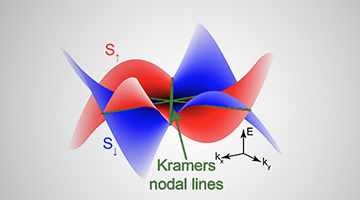
Altermagnets are an emerging class of magnetic materials that offer the potential for energy-efficient, high-density memory chips. Researchers at Penn State, UC Santa Barbara, and the ALS demonstrated that characteristic altermagnetic band splitting in chromium antimonide is evident in thin films relevant for real-world device application. Read more »
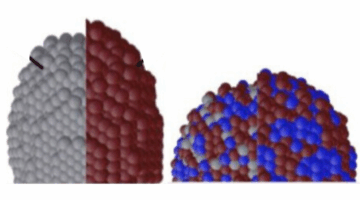
Dynamic Surface Restructuring in Ag–Cu Boosts CO2 Conversion
Multimodal in situ x-ray experiments at the ALS revealed how copper–silver nanoparticle catalysts evolve during CO2 photoreduction. The findings, which demonstrate dynamic catalyst restructuring at the atomic level, provide crucial insights for enhancing the selectivity and efficiency of CO2 conversion into high-value chemicals. Read more »![]()
![]()
Robotics Project Pushes Toward Self-Driving Materials Optimization
A new multi-disciplinary team aims to automate complex sample handling at Beamline 7.3.3, leveraging AI and robotics to speed up material optimization and discovery. Read more »
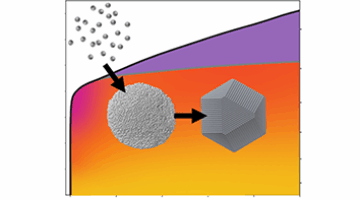
Building Materials from the Nanocrystal Up
Researchers used the Advanced Light Source to clarify how an unusual intermediate state accelerates the transformation of nanocrystals into a superlattice during a two-step process with fewer defects than a one-step process. Read more »![]()
![]()
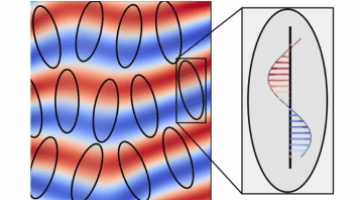
Nematic Magnetic Helices Fluctuate at Different Tempos
During a series of experiments at the ALS, researchers identified helical magnetic spins that fluctuate at different time scales during a phase transition as a function of temperature in a nematic iron germanium thin film. The results provide a framework for characterizing exotic phases, which may have interesting optical and transport properties for microelectronics and spintronics. Read more »![]()
![]()
Separating an Electron into Waves of Spin and Charge
Researchers are exploring how a thin film can host a Tomonaga–Luttinger liquid, which separates an electron’s charge and spin. The research findings could contribute to the development of ultra-compact and energy-efficient technologies. Read more »
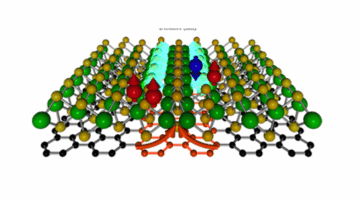
The Quest for an Altermagnet
Researchers determine the unique electronic structure of altermagnets, which offers numerous benefits in creating energy-efficient devices based on spin-polarized electron currents. Understanding how altermagnetism works could contribute to the development of next-generation memory, logic, or sensing devices that are faster and consume less power. Read more »
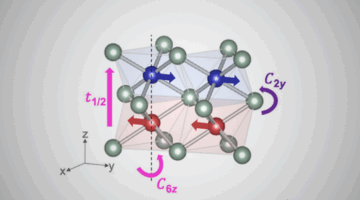
Designing Quantum Materials for Future Electronics
Researchers bring theory into practice and confirm a new material’s characteristics at the ALS. The study opens new opportunities to design a substance that renders extra “handles” on the electron—not just its charge, but its spin and valley—so we can build computers that are faster, cooler, and more energy-efficient compared to traditional electronics. Read more »
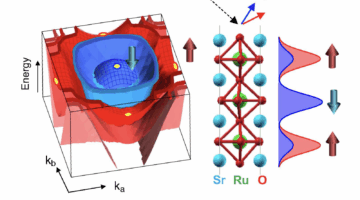
Pinpointing Magnetic Mysteries and Mechanisms in a Layered Perovskite
The strontium ruthenate family has a perovskite-like structure that can assemble into different configurations, offering an ideal way to study how the physics change as the material goes from 3D to 2D. In this study, researchers revealed how electrons with different spins behave in distinct layers of a three-layer magnetic material. The results deepen the field’s understanding of how magnetism emerges in layered materials, an important concept for future magnetic technologies and quantum electronic devices. Read more »![]()
![]()
A New Twist for Superconductivity in Bilayer Graphene
In a study of twisted bilayer graphene (TBG) systems, researchers found intriguing spectroscopic features in a superconducting “magic-angle” TBG—features that are absent in non-superconducting TBG. The results provide crucial information on superconductivity in magic-angle TBG for next-gen electronics and advanced energy technologies. Read more »![]()
![]()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- …
- 27
- Next Page »