Scientists have long sought to mimic the process by which plants make their own fuel using sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water through artificial photosynthesis devices, but exactly how catalysts work to generate renewable fuel remains a mystery. Now, a study has uncovered new insight into how to better control cobalt oxide, one of the most promising catalysts for artificial photosynthesis. Read more »
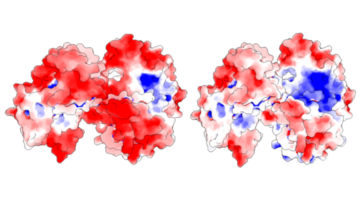
X-Ray Footprinting Solves Mystery of Metal-Breathing Protein
Scientists have discovered the details of an unconventional coupling between a bacterial protein and a mineral that allows the bacterium to breathe when oxygen is not available. The research could lead to innovations in linking proteins to other materials for bioelectronic devices such as sensors that can diagnose disease or detect contaminants. Read more »
NIH Grant Will Enhance Structural Biology Research Experience for ALS Users
A recently awarded National Institutes of Health (NIH) grant will help integrate existing structural biology resources at the ALS to better serve users. The funds will help establish a centralized collaborative mechanism, called ALS-ENABLE, that will guide users through the most appropriate routes for answering their biological questions. Read more »
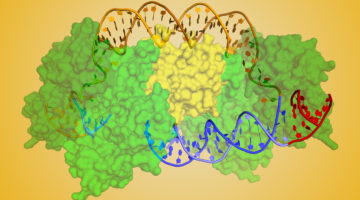
The CRISPR Target-Recognition Mechanism
CRISPR-associated (Cas) proteins have revolutionized gene editing by vastly simplifying the insertion of short snippets of new (“donor”) DNA into very specific locations of target DNA. Now, researchers have discovered how the Cas proteins are able to recognize the target locations with such great specificity. Read more »![]()
![]()
Carolyn Larabell to Receive Shirley Award at ALS User Meeting
Carolyn Larabell, Director of the National Center for X-Ray Tomography (NCXT), centered around ALS Beamline 2.1, has been selected by the ALS Users’ Executive Committee to receive the 2017 David A. Shirley Award for Outstanding Scientific Achievement at the ALS. Read more »
Global Blood Therapeutics Uses ALS to Tackle Sickle Cell Disease
Sickle cell disease (SCD), which affects millions of people worldwide, has traditionally been treated with a cytotoxic drug that has a range of negative side effects and variable patient response. Bay Area biopharmaceutical company Global Blood Therapeutics (GBT) is on a mission to develop a better treatment and is using the ALS to help. Read more »![]()
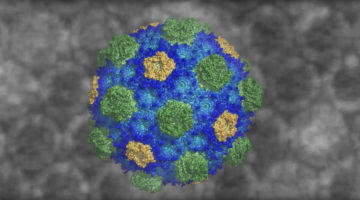
A Bacterial Jigsaw Puzzle Is Solved
Bacterial microcompartments (BMCs) are hollow protein shells that encapsulate enzymes involved in bacterial metabolism. Crystallography studies have provided atomic-resolution views of a fully assembled BMC, revealing basic principles of shell construction for fighting pathogens or bioengineering applications. Read more »![]()
![]()
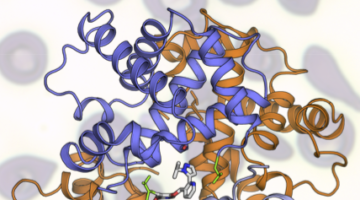
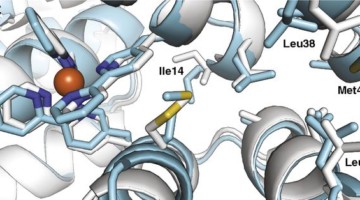
NCAA Drives Formation of Designed Proteins
A noncanonical amino-acid (NCAA) complex has been found to drive the self-assembly of a computationally designed protein. Bpy-ala, which is “noncanonical” because it’s not among the 20 amino acids that occur naturally, has useful properties that could be used to generate novel photoactive proteins. Read more »
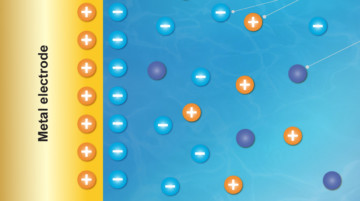
Tender X-Rays Map the Double-Layer Potential
In a first-of-its-kind experiment, ALS researchers demonstrated a new, direct way to study the inner workings of a phenomenon in chemistry known as an “electrochemical double layer” that forms where liquids meet solids—where battery fluid meets an electrode, for example. Read more »![]()
![]()
ALS Beamstop Device an R&D 100 Finalist
A beamstop device recently developed at the ALS has successfully combined two essential crystallographic functions–capturing the damaging portion of the beam while simultaneously monitoring its intensity–into a single miniaturized package. The technology has been licensed and launched commercially and is also a finalist for an R&D 100 Award. Read more »![]()
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- Next Page »