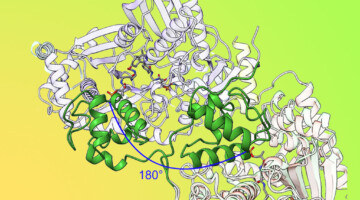
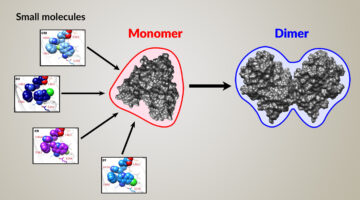
By locking down certain movable parts of a modular drug-building protein, researchers learned new details about how carrier proteins transfer the product protein between modules. The results offer insights that could enable scientists to design and create new and improved medicines, such as antibiotics, using synthetic biology. Read more »![]()
![]()
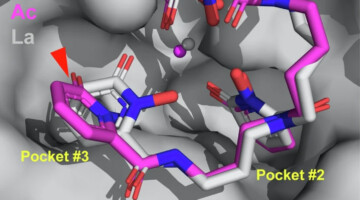
A Macromolecular Scaffold for Probing Actinium Chemistry
By encapsulating actinium atoms within a macromolecular complex for analysis using protein crystallography, researchers discovered that actinium has a unique solid-state bonding configuration. A better understanding of actinium behavior could help improve a promising cancer treatment known as targeted alpha therapy. Read more »![]()
![]()
Protein Pioneer: Enabling Scientists to Design Novel Proteins for the Future
The 2024 Nobel Prize in Chemistry was awarded to David Baker, Demis Hassabis, and John M. Jumper for the development of protein structure prediction and design. At the ALS, Baker leveraged high-throughput small-angle x-ray scattering (SAXS) and protein crystallography capabilities to design novel proteins and pave a new pathway for science, technology, and the environment. Read more »
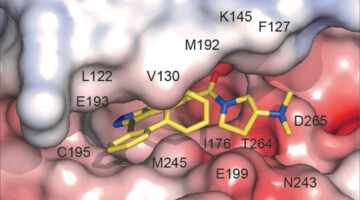
A Promising Compound for Reversible Male Contraception
Researchers found that a small-molecule protein inhibitor—screened from billions of compounds and analyzed using structural insights from protein crystallography—reversibly suppresses male fertility in mice. The work addresses the pressing need for more contraceptive options that enable all individuals to control their own fertility. Read more »![]()
![]()
Comparative Pore Structure and Dynamics for Bacterial Microcompartment Shell Protein Assemblies in Sheets or Shells
Bacterial microcompartment proteins can assemble into multiple structures, such as sheets, shells, and intermediates. While this is shown artistically in this figure, we study the differences in the pore dynamics within bacterial microcompartment assemblies to assess potential changes in permeability. Read more »
Caught in the Actinium
In this work, researchers demonstrated a macromolecular scaffold that combines an 8-coordinate synthetic ligand and a mammalian protein to characterize the solution and solid-state behavior of the longest-lived actinium isotope. The information could help design better cancer treatments. Read more »
Time-Resolved SAXS Screen of Small-Molecule Drug Candidates
Time-resolved, high-throughput, small-angle x-ray scattering improved the screening of small-molecule drug candidates, providing insight into how they stimulate structural transitions in protein targets. The work will speed the discovery of treatments designed to activate biomolecular dynamics associated with desired therapeutic outcomes. Read more »![]()
![]()
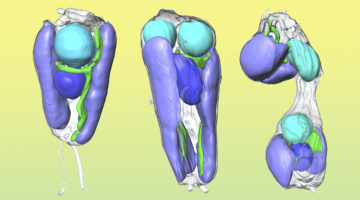
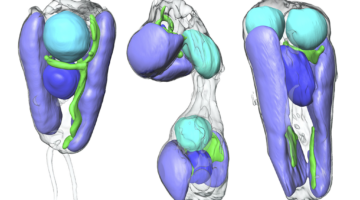
Symbiotic Nitrogen-Fixing Microbe Evolves into Organelle
Researchers found that a symbiont capable of fixing nitrogen (turning it into a biologically usable form) has evolved into an organelle—an intrinsic part of the algae cells that host it. The discovery is of great interest for understanding organelle genesis and for efforts to engineer agricultural plants with built-in nitrogen-fixing capabilities. Read more »![]()
![]()
Scientists Discover First Nitrogen-Fixing Organelle
In two recent papers, an international team of scientists describe the first known nitrogen-fixing organelle within a eukaryotic cell. The organelle is the fourth example in history of primary endosymbiosis—the process by which a prokaryotic cell is engulfed by a eukaryotic cell and evolves beyond symbiosis into an organelle. Read more »
Nitrogen-fixing organelle in a marine alga
A nitrogen-fixing organelle, or “nitroplast,” has been identified in a marine alga on the basis of intracellular imaging and proteomic evidence. This discovery sheds light on the evolutionary transition from endosymbiont to organelle. The image depicts the cell architecture and synchronized cell division of the alga Braarudosphaera bigelowii with nitroplast UCYN-A (large brown spheres). Read more »
- 1
- 2
- 3
- …
- 8
- Next Page »