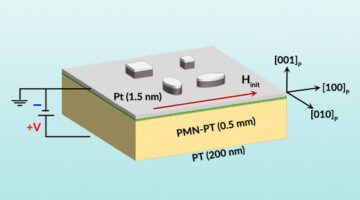
Researchers learned how the size, shape, and orientation of microstructures affect how they switch magnetization directions in response to an applied voltage. The work advances our understanding of strain-responsive composite materials for use in energy-efficient electronic applications such as memory devices, sensors, and actuators. Read more »![]()
![]()
ALS Work Using PEEM
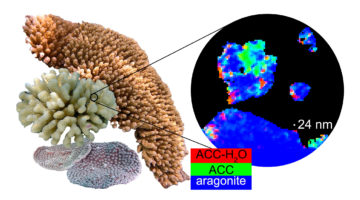
Surprise Mineral Precursor Found in Coral Skeletons and Mollusk Shells
Researchers studied samples from corals, mollusks, and sea urchins, at edges where mineral precursors start to form the new shell or skeleton. There, they found a surprise: corals and mollusks produced a mineral precursor that had never been observed before in living organisms or rocks, and had only recently been created synthetically. Read more »
Shedding Light on Sea Creatures’ Secrets
Exactly how does coral make its skeleton, a sea urchin grow a spine, or an abalone form the mother-of-pearl in its shell? A new study at the ALS revealed that this process of biomineralization, which sea creatures use to lock carbon away in their bodies, is more complex and diverse than previously thought. Read more »
A Molecular-Scale Understanding of Misorientation Toughening in Corals and Seashells
Researchers reveal that the toughness of polycrystalline seashells and coral skeletons is increased by small misorientation of adjacent crystals. The findings pave the way toward bioinspired materials with tunable toughness. Read more »
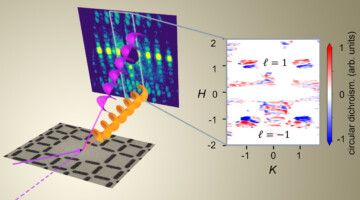
Spiraling Beams Differentiate Antiferromagnetic States
Using spiraling x-ray beams, researchers differentiated between energetically equivalent (“degenerate”) states in an antiferromagnetic lattice. The work shows the potential of these beams to probe properties that would otherwise be inaccessible, to better understand phenomena of fundamental interest and for applications such as spintronics. Read more »![]()
![]()
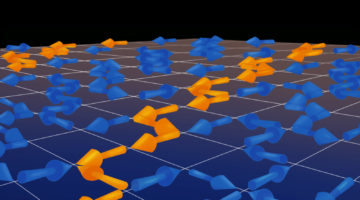
Disorder Drives Long-Range Order in “Tetris Ice” Nanomagnet Arrays
Long-range ordering is typically associated with a decrease in disorder, or entropy. Yet, it can also be driven by increasing entropy in certain special cases. In a recent DOE-funded study, researchers demonstrated that certain artificial spin-ice arrays—nanomagnets lithographically patterned to form Tetris-like shapes—can produce such entropy-driven order. Read more »
Key to Coral Resilience Is Faster Skeletal Crystallization
In a new study, researchers show that the crystallization rate of coral skeletons differs across species and is correlated with their resilience to ocean acidification. The results have implications for predicting coral reef survival and developing mitigation strategies against having their bony skeletons weakened by ocean acidification. Read more »
Biomineralization: Integrating mechanism and evolutionary history
In this review, Gilbert et al. develop a model for calcium carbonate biomineralization applicable to all phyla. Their model may help elucidate the key genetic components that drive biomineralization and offers insight into the consequences of global climate change on marine organisms. Read more »
Loss of biological control of enamel mineralization in amelogenin-phosphorylation-deficient mice
Amelogenin phosphorylation plays crucial roles in controlling structural, crystallographic, mechanical, and compositional characteristics of dental enamel. Thus, loss of amelogenin phosphorylation leads to a reduction in the biological control over the enamel mineralization process. Read more »
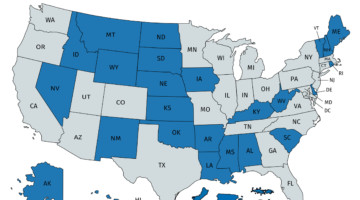
EPSCoR Collaboration Fosters New Research and New Careers
The DOE Established Program to Stimulate Competitive Research (DOE EPSCoR) encourages partnerships between national labs and researchers in qualifying states and territories. An EPSCoR collaboration with researchers from Kentucky has resulted in an ALS highlight, career advancement for young scientists, and a larger, center-scale proposal. Read more »
- 1
- 2
- 3
- …
- 5
- Next Page »