A technique newly available at the ALS has enabled the discovery of a surprising key event in photosynthetic systems. A protein shifting from an “orange” light-absorbing state to a “red” photoprotective state turns out to be an unanticipated molecular priming event in photoprotection. Read more »![]()
ALS Work Using Protein Crystallography
Protein crystallography is used for determining the molecular structure of proteins. Crystallized protein molecules cause a beam of incident x-rays to scatter in many directions, with constructive and destructive interference generating a diffraction pattern. By analyzing these patterns, a crystallographer can produce a three-dimensional picture of the density of electrons within the crystal and thus determine the protein's structure.
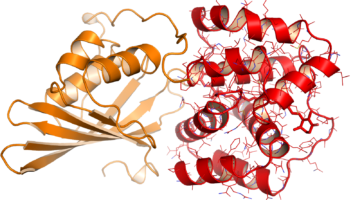
Ancient Proteins Help Unravel a Modern Cancer Drug’s Mechanism
The cancer drug Gleevec is extremely specific, binding and inhibiting only the cancer-causing tyrosine protein kinase Blc-Abl, while not targeting homologous protein kinases found in normal, healthy cells. Researchers at the ALS have uncovered exactly why that is the case, pointing to novel methods of drug discovery. Read more »![]()
![]()
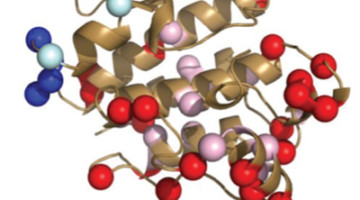
Takeda Advances Diabetes Drug Development at the ALS
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), characterized by abnormally high blood glucose levels, affects hundreds of millions of people worldwide. In the pursuit to better treat this disease, the human receptor protein GPR40 has been identified by pharmaceutical company Takeda as a potential new drug target.
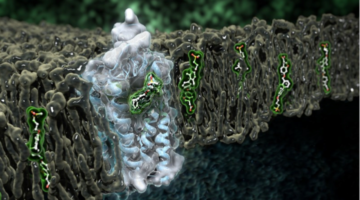
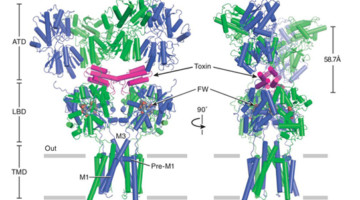
Brain Receptor Structures Key to Future Therapeutics
Neurotransmitter receptor proteins are critical to learning and memory. Mutations are associated with neurological and neuropsychiatric conditions including Alzheimer’s, epilepsy, and autism. Structures of two such receptors, solved by x-ray crystallography, provide a blueprint for the development of therapeutics. Read more »![]()
![]()
Designer Proteins Target Epstein-Barr-Virus-Associated Cancer
Researchers used new protein design approaches to develop a potential inhibitor of Epstein-Barr-Virus-associated cancer. The study shows not just how to help defeat the virus, but also opens up a whole new way to design proteins against viruses and ultimately, cancer. Read more »![]()
![]()
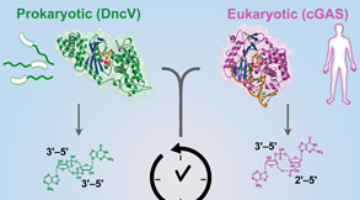
A New Link Between Human and Bacterial Signaling Machinery
Researchers showed that a bacterial signaling protein critical for pathogenesis in Vibrio cholerae is actually a homolog of the human enzyme, cGAS, which detects invading DNA. These results reveal a surprising evolutionary connection between bacterial signaling and human innate immunity. Read more »
Caribou Biosciences Has Roots at the ALS
When Rachel Haurwitz joined UC Berkeley biology professor Jennifer Doudna’s lab in 2007 as a graduate student, little did the two women know that the interesting bacterial immune system they were studying would be the subject of news headlines and the basis for a biotech startup just a few years later.
Validating Computer-Designed Proteins for Vaccines
Computationally designed proteins that accurately mimic key viral structures can help produce better vaccines. The resulting protein structures, validated at the ALS, encourage the further development of this strategy for a variety of vaccine targets, including HIV and influenza. Read more »![]()
![]()
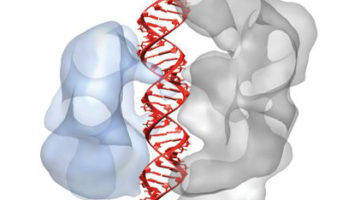
Intriguing DNA Editor Has a Structural Trigger
The molecular structures of two proteins from a family of genome-editing enzymes reveal how they target and cleave DNA. The results point the way to the rational design of new and improved versions of the enzymes for basic research and genetic engineering. Read more »![]()
![]()
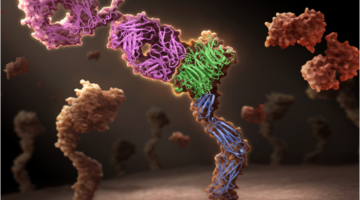
Genentech Uses ALS Crystallography for Therapeutic Antibody Research
Genentech has developed a unique one-armed antibody, onartuzumab, which is now in late-stage clinical trials in multiple cancer types. The company used crystal structures obtained at ALS Beamline 5.0.2 to demonstrate the mechanism of action of this unique potentially therapeutic antibody. Read more »![]()
![]()