High-energy Li-ion batteries can provide both high capacity and high voltage, both of which are important in electric vehicles for greater range and faster acceleration. Here, researchers untangled the contributions of nickel and cobalt in high-energy Li-rich battery cathodes, pointing the way to optimizing them via a compositional approach. Read more »
ALS Work Using RIXS
Resonant inelastic x-ray scattering (RIXS) is a photon-in/photon-out spectroscopy where both the energy and momentum of the scattered photons could be measured. A full-energy-range mapping of RIXS (mRIXS) is collected by sweeping the incident x-ray photon energy across the absorption edge of interest, and the inelastically scattered photon energy is detected by a spectrometer. Critical RIXS features often correspond to various low-energy charge, spin, orbital, and lattice excitations. At the ALS, an iRIXS endstation has been developed for high-efficiency mRIXS experiments.
Surface Engineering Boosts Water-Splitting Efficiency
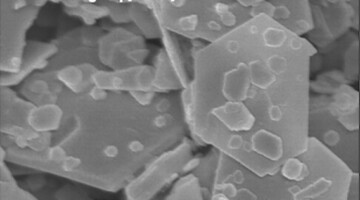
Researchers modified the surface of an electrocatalyst to maximize its efficiency at splitting water. The optimized material is approximately 40 times more efficient than similar commercial electrocatalysts and could help make the production of clean hydrogen fuel more sustainable and economical. Read more »![]()
![]()
Jinghua Guo to Receive the 2022 Shirley Award
ALS senior scientist Jinghua Guo is the recipient of this year’s Shirley Award for Outstanding Scientific Achievement at the ALS. Guo is being recognized for pioneering the development of operando soft x-ray spectroscopy, work that’s enabled studies under realistic conditions, which is of great importance in environmental and energy research. Read more »
Copper Doping Improves Sodium-Ion Battery Performance
A big plus for batteries based on sodium over lithium is that sodium is more earth-abundant, which lowers costs and eases environmental and supply-chain concerns. Research to improve the performance of sodium-ion batteries includes this effort to use copper doping of the cathode to enhance oxygen redox reversibility. Read more »
How Iron Remediates Arsenic in Groundwater
Though iron has been demonstrated as an effective means to remediate arsenic contamination in groundwater, the mechanism was not well understood until now. For the first time, researchers have untangled the detailed steps of the interaction, informing more robust strategies for cleanup. Read more »
Trace Key Mechanistic Features of the Arsenite Sequestration Reaction with Nanoscale Zerovalent Iron
The advancing in situ XAS technique made it possible to uncover the As-nZVI reaction pathway, especially capturing transient reaction process at subsecond scale. Combining the in situ XAS experimental data with computational chemistry enabled the reaction steps to be verified, clarifying the unambiguous identification of the transit reactive intermediates. Read more »
Coulombically-stabilized oxygen hole polarons enable fully reversible oxygen redox
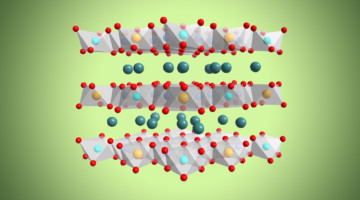
We investigate oxygen redox in layered Na2−xMn3O7, a positive electrode material with ordered Mn vacancies. Our results establish a complete picture of redox energetics by highlighting the role of coulombic interactions across several atomic distances and suggest avenues to stabilize highly oxidized oxygen for applications in energy storage and beyond. Read more »
X-Ray Study Recasts Role of Battery Material from Cathode to Catalyst
Researchers used the ALS to learn about a lithium-rich battery material that has been the subject of much study for its potential to extend the range of electric vehicles and the operation of electronic devices. Through a fundamental spectroscopic study, they not only clarified the reaction mechanism of this material, but also found a conceptually different use of it as a catalyst. Read more »
Study Shines New Light on Li-Battery Cathode Materials
Researchers clarified key reaction mechanisms in a Li-battery cathode material, revealing its surprising utility as a catalyst for next-gen batteries. The work refutes widely held ideas about reversible reactions in a highly debated material for Li-based batteries and expands the range of materials suitable for use in high-power batteries and fuel cells. Read more »![]()
![]()
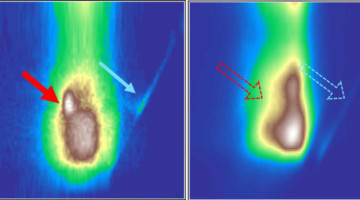
Redirecting dynamic surface restructuring of a layered transition metal oxide catalyst for superior water oxidation
Electrocatalysts, particularly those for water oxidation, often experience substantial or at least partial reconstruction. Here, Wang et al. are able to control surface reconstruction using a cationic redox-tuning method on layered LiCoO2–xClx catalysts for the oxygen evolution reaction. The resulting optimized catalyst exhibits excellent electrocatalytic performance in alkaline electrolyte. Read more »