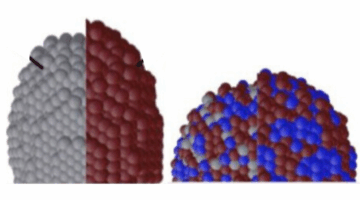
Multimodal in situ x-ray experiments at the ALS revealed how copper–silver nanoparticle catalysts evolve during CO2 photoreduction. The findings, which demonstrate dynamic catalyst restructuring at the atomic level, provide crucial insights for enhancing the selectivity and efficiency of CO2 conversion into high-value chemicals. Read more »![]()
![]()
ALS Work Using Scattering/Diffraction
These techniques make use of the patterns of light produced when x-rays are deflected by the closely spaced lattice of atoms in solids and are commonly used to determine the structures of crystals and large molecules such as proteins.
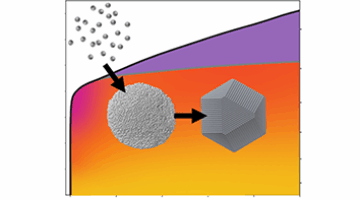
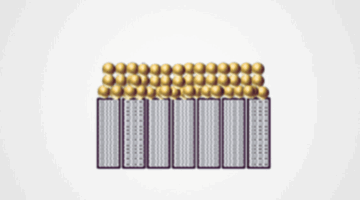
Building Materials from the Nanocrystal Up
Researchers used the Advanced Light Source to clarify how an unusual intermediate state accelerates the transformation of nanocrystals into a superlattice during a two-step process with fewer defects than a one-step process. Read more »![]()
![]()
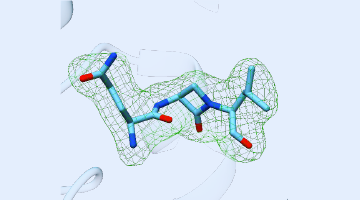
X-Rays Shed Light on Possible New Treatments for TB
Using ALS beamlines, a new study revealed how CMX410 inhibits Pks13, a cell wall enzyme in Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the bacterium responsible for tuberculosis. CMX410 is effective against drug-sensitive and drug-resistant strains of the bacterium and has been proven safe in multiple animal models of infection. Read more »![]()
![]()
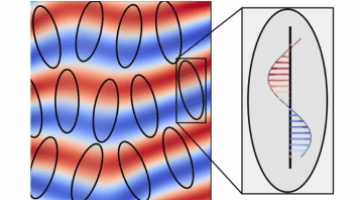
Nematic Magnetic Helices Fluctuate at Different Tempos
During a series of experiments at the ALS, researchers identified helical magnetic spins that fluctuate at different time scales during a phase transition as a function of temperature in a nematic iron germanium thin film. The results provide a framework for characterizing exotic phases, which may have interesting optical and transport properties for microelectronics and spintronics. Read more »![]()
![]()
Characterizing Membrane Fouling with Operando Experiments
Membrane filtration offers a cost-effective, energy-efficient approach to purify and desalinate water, but fouling limits the performance of these devices. A new study explored the new experimental design that allows one to study the dynamic fouling process in real time to improve the field’s understanding of how materials deposit, accumulate, and/or crystallize on the membrane’s surface. Read more »![]()
![]()
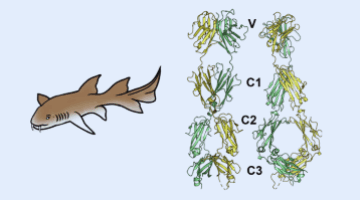
Sharks Shed Light on Origins of Adaptive Immune System
A team of researchers identified the three-dimensional structure of a protein expressed by a gene of a modern nurse shark that is proposed to be a close homologue to a gene that, more than 500 million years ago, gave rise to the adaptive immune system shared by all vertebrates. By understanding the emergence and evolution of the immune system, researchers may advance work in immunology, genetics, and biotechnology.
Read more »![]()
![]()
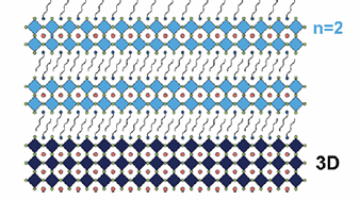
Stable 2D Interlayer Prolongs Perovskite Devices
Layered 2D/3D perovskite bilayer heterostructures have the potential to boost the performance and durability of many types of electronic and photonic devices, but maintaining this performance depends on the stability of the cell’s 2D interlayer. In this study, researchers optimized time-resolved, spontaneous thin-film deposition of 2D perovskites using a mixed solvent approach to produce phase pure, stable thin films with high crystallinity. Read more »![]()
![]()
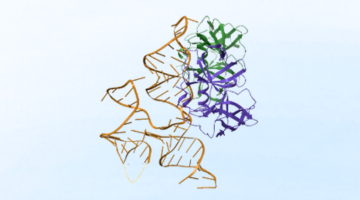
Researchers Identify Viral Swiss Army Knife, Clarifying How Replication Occurs
Viruses are ingenious, infectious agents, capable of replicating inside the living cells of a host organism. Enterovirus, a common viral pathogen, is responsible for a range of diseases from mild colds to severe conditions, including viral meningitis, myocarditis, and paralysis. A new study sheds light on how enteroviruses use structured RNA elements and multifunctional proteins to coordinate viral replication efficiently using minimal genetic material. Read more »
Operando probing dynamic migration of copper carbonyl during electrocatalytic CO2 reduction
In their work, Peidong Yang and colleagues reveal the dynamic evolution from faceted Cu nanocatalysts into metallic nanograins during CO2 reduction driven by the surface migration of electrogenerated copper carbonyl. Read more »
ALS Captures Structure of Engineered Protein, Opening New Options to Treat IBD
Researchers use the ALS to confirm the structure of an engineered immune protein that could open new opportunities to treat inflammatory bowel disease. Read more »
- 1
- 2
- 3
- …
- 39
- Next Page »