A collaboration between Berkeley Lab and Genentech, a member of the Roche Group, is working to break through some of the drug delivery bottlenecks by designing the most effective lipid nanoparticles (LNPs)—tiny spherical pouches made of fatty molecules that encapsulate therapeutic agents until they dock with cell membranes and release their contents. Read more »
ALS Work Using Scattering/Diffraction
These techniques make use of the patterns of light produced when x-rays are deflected by the closely spaced lattice of atoms in solids and are commonly used to determine the structures of crystals and large molecules such as proteins.
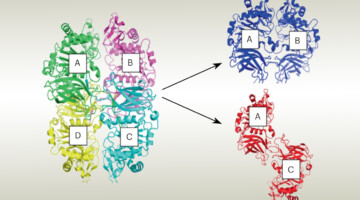
Allosteric Tuning of Caspase-7: Establishing the Nexus of Structure and Catalytic Power
How can allosteric sites be more effectively targeted by small-molecule drugs? Using an integrated in vitro/in silico experimental workflow; we discovered novel allosteric inhibitors of caspase-7 and revealed new connections between the active site and the remote allosteric site (i. e., allosteric structure–activity relationships, ASARs) for this valuable disease target. Read more »
Plant Enzyme Builds Polymers That Fortify Cell Walls
With data obtained at the ALS, researchers gained insight into how an enzyme orchestrates the synthesis of a pectin polymer that imparts strength and flexibility to plant cell walls. The work could lead to improved biofuel production and guide the design of polymers with tailored functionalities for industrial or biomedical applications. Read more »![]()
![]()
Impact of Thermal Stress on Device Physics and Morphology in Organic Photodetectors
Implementing organic photodetectors (OPDs) into Si-based manufacturing process requires high thermal resistance. This work showcases a comprehensive picture of the impact of high thermal stress (at 200 °C, up to 2 hours) on photosensing performance, bulk and interfacial morphologies, and device physics. Read more »
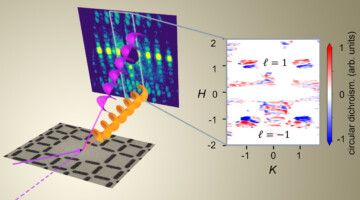
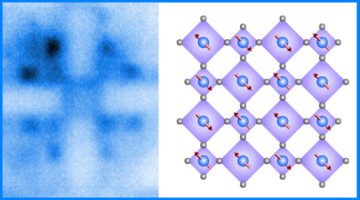
Spiraling Beams Differentiate Antiferromagnetic States
Using spiraling x-ray beams, researchers differentiated between energetically equivalent (“degenerate”) states in an antiferromagnetic lattice. The work shows the potential of these beams to probe properties that would otherwise be inaccessible, to better understand phenomena of fundamental interest and for applications such as spintronics. Read more »![]()
![]()
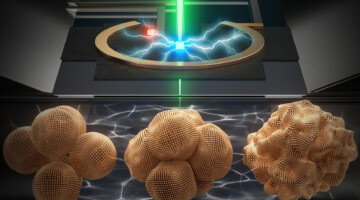
Extreme Closeup of Copper Electrocatalysts in Action
Researchers at Berkeley Lab have made real-time movies of copper nanoparticles as they evolve to convert carbon dioxide and water into renewable fuels and chemicals. Their new insights could help advance the next generation of solar fuels. Read more »
Gemini Beamline 2.0.1 Banks Its First Protein Structure
A protein structure obtained from ALS Beamline 2.0.1 (“Gemini”) has recently been published in the literature and deposited into the Protein Data Bank (PDB)—two significant firsts for this beamline. The structure helped provide new insights into the molecular mechanisms involved in triggering certain inflammatory diseases. Read more »
Doped Nickelate Enters a New Phase with Spintronics Potential
Rare-earth nickelates are known to undergo a metal-to-insulator phase transition as temperature decreases, the mechanism of which is not well understood. Here, researchers observed a new low-temperature phase that’s both metallic and antiferromagnetic—an unusual combination with potential value in spintronics. Read more »
In Situ and Operando Characterizations of Metal Halide Perovskite and Solar Cells: Insights from Lab-Sized Devices to Upscaling Processes
The performance and stability of metal halide perovskite solar cells strongly depend on precursor materials and deposition methods adopted during the perovskite layer preparation. This review presents an update of studies conducted in situ using a wide range of structural, imaging, and spectroscopic techniques, involving the formation/degradation of halide perovskites. Read more »
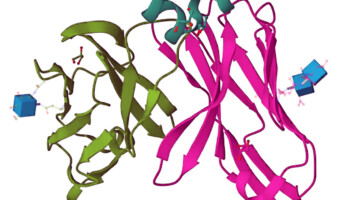
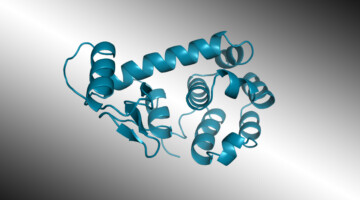
Chatbot-Style AI Designs Novel Functional Protein
Researchers used an artificial intelligence (AI) algorithm, similar to those used in natural-language (“chatbot”) models, to design a functional protein that was then structurally validated at the ALS. The work could speed the development of novel proteins for almost anything from therapeutics to degrading plastic. Read more »![]()
![]()
- « Previous Page
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- …
- 34
- Next Page »