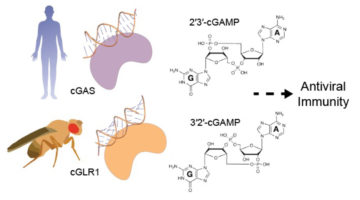
Comparison of enzyme structures from humans and insects revealed a new family of evolutionarily related immune-system sensors, triggered by viral RNA or DNA to produce tailored signals that initiate antiviral action. The results shed new light on the diversity and development of immune defenses in animals. Read more »
ALS Work Using Scattering/Diffraction
These techniques make use of the patterns of light produced when x-rays are deflected by the closely spaced lattice of atoms in solids and are commonly used to determine the structures of crystals and large molecules such as proteins.
New Technique Paves the Way for Perfect Perovskites
A new solar material, organic-inorganic halide perovskites, could one day help the U.S. achieve its solar ambitions and decarbonize the power grid. A recent study reports that manufacturing could be aided by a new instrument that uses invisible x-ray light and visible laser light to probe a perovskite material’s crystal structure and optical properties as it is synthesized. Read more »
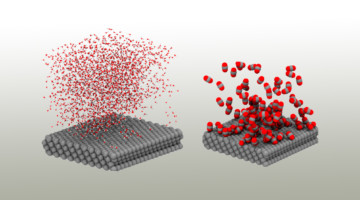
Exquisitely Selective CO2 Reduction on Silver
Researchers electrochemically reduced CO2 to CO with nearly perfect selectivity over other products by adding an organic compound to the surface of a silver electrode. With theoretical analyses and ALS data, the work revealed the key role of the microenvironment in promoting the conversion of CO2, a greenhouse gas, into useful products. Read more »![]()
![]()
Coulombically-stabilized oxygen hole polarons enable fully reversible oxygen redox
We investigate oxygen redox in layered Na2−xMn3O7, a positive electrode material with ordered Mn vacancies. Our results establish a complete picture of redox energetics by highlighting the role of coulombic interactions across several atomic distances and suggest avenues to stabilize highly oxidized oxygen for applications in energy storage and beyond. Read more »
Functional and structural characterization of AntR, an Sb(III) responsive transcriptional repressor
Antimony is considered a priority environmental pollutant by the EPA. The ant operon of the antimony-mining bacterium, C. testosterone, confers resistance to Sb(III). The operon is regulated by the product of the first gene in the operon, antR. This is the first report of the structure and binding properties of antR, with high selectivity for environmental antimony. Read more »
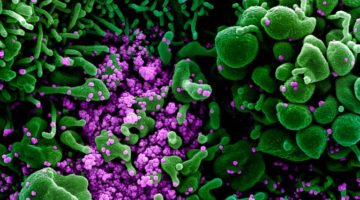
Sifting through Fragments for COVID-19 Treatments
COVID-19 vaccines are essential for preventing serious disease, but the identification of new drugs is still necessary for the treatment of patients who become sick as a result of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Here, scientists used computational docking and crystallography to screen large numbers of small molecules for potential use in drug compounds. Read more »
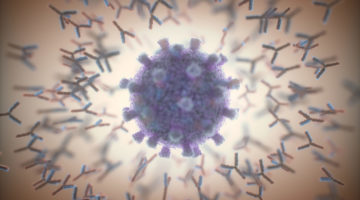
Scientist at Berkeley Lab Played a Hand in “Inescapable” COVID-19 Antibody Discovery
An antibody therapy that appears to neutralize all known SARS-CoV-2 strains—including newly emerged mutants that can now “escape” from previous antibody therapies—was developed with a little help from structural biologist Jay Nix. His work helped generate detailed structural maps of how antibodies bind to the spike protein, enabling the selection of promising contenders. Read more »
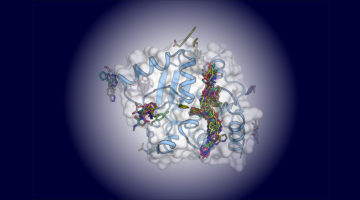
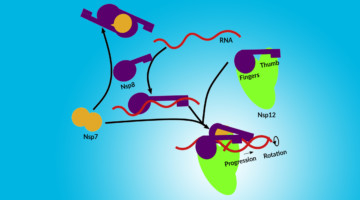
Assembly of the SARS-CoV-2 Replication Mechanism
Using a multimodal approach that included x-ray scattering at the ALS, researchers determined how components of the SARS-CoV-2 replication mechanism fit together. A better understanding of how this protein complex works provides insight into potential structural or functional weak spots to exploit for drug development. Read more »![]()
![]()
Deconstructing the Infectious Machinery of the SARS-CoV-2 Virus
Scientists collaborated to model the complex protein responsible for SARS-CoV-2 replication, revealing its potential weak spots for drug development. The investigation hinged on data collected from many advanced imaging techniques, including small-angle x-ray scattering (SAXS), crystallography, and small-angle neutron scattering (SANS). Read more »
Mineral Microstructures Shed Light on Planet-Scale Dynamics
To explore what happens to minerals under the extreme conditions in Earth’s mantle, researchers developed an x-ray technique that bridges the gap between methods that reveal bulk properties and those that focus on individual crystals. Use of the technique has shed light on the dynamics of tectonic-plate subduction in Earth’s lower mantle. Read more »
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- …
- 39
- Next Page »