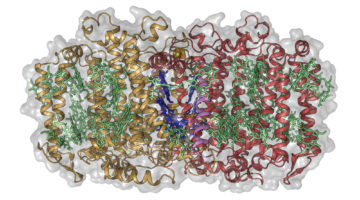
The bacterium, H. modesticaldum, is thought to have a photosynthetic reaction center resembling the earliest common ancestor of all photosynthesis complexes. Its molecular structure has now been solved, providing insight into the evolution of photosynthesis and how nature optimized light-driven energy collection. Read more »
ALS Work Using Scattering/Diffraction
These techniques make use of the patterns of light produced when x-rays are deflected by the closely spaced lattice of atoms in solids and are commonly used to determine the structures of crystals and large molecules such as proteins.
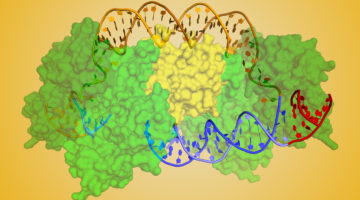
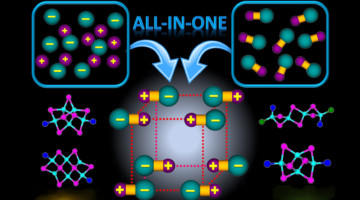
The CRISPR Target-Recognition Mechanism
CRISPR-associated (Cas) proteins have revolutionized gene editing by vastly simplifying the insertion of short snippets of new (“donor”) DNA into very specific locations of target DNA. Now, researchers have discovered how the Cas proteins are able to recognize the target locations with such great specificity. Read more »![]()
![]()
Structure of Nanoscale-Pitch Helical Phases: Blue Phase and Twist-Bend Nematic Phase Resolved by Resonant Soft X-Ray Scattering
Resonant soft x-ray scattering (RSoXS) at the carbon K-edge was used to probe periodic structures of phases with orientational molecular order but homogeneous electron density distribution. This approach can be applied to structures with periodicities below the optical wavelength, to which neither optical nor classical x-ray diffraction techniques are sensitive. Read more »
ALS Work Highlighted in DOE Top 40 Countdown
To celebrate DOE’s 40th anniversary (October 1, 2017), the Office of Science (SC) collected 40 scientific milestones from the previous 40 years, each one supported by SC. The ALS played a key role in two of the milestones: 2005 (ribosome) and 2009 (topological materials). Read more »
Global Blood Therapeutics Uses ALS to Tackle Sickle Cell Disease
Sickle cell disease (SCD), which affects millions of people worldwide, has traditionally been treated with a cytotoxic drug that has a range of negative side effects and variable patient response. Bay Area biopharmaceutical company Global Blood Therapeutics (GBT) is on a mission to develop a better treatment and is using the ALS to help. Read more »![]()
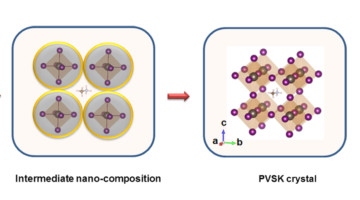
Formation of a Photovoltaic Material from Precursor to Crystal
Lead halide perovskites have emerged as high-performance photovoltaic materials, demonstrating remarkably rapid improvements in efficiency. In situ printing and time-resolved x-ray characterization have provided new insights into the relationship between device efficiency, perovskite crystallinity, and film morphology. Read more »
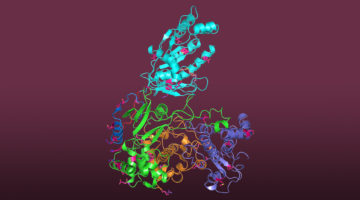
A Bacterial Jigsaw Puzzle Is Solved
Bacterial microcompartments (BMCs) are hollow protein shells that encapsulate enzymes involved in bacterial metabolism. Crystallography studies have provided atomic-resolution views of a fully assembled BMC, revealing basic principles of shell construction for fighting pathogens or bioengineering applications. Read more »![]()
![]()
Hybrid LED Phosphors Combine Performance and Durability
Light-emitting diodes (LEDs) last a long time and are very energy efficient. However, white LEDs currently rely on phosphor materials doped with rare-earth elements (REEs) that are increasingly costly and in short supply. A new class of hybrid phosphor materials shows promise as REE-free alternatives. Read more »
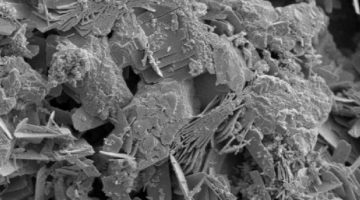
The Ancient Roman Secret to Concrete Resilience in Seawater
Researchers used x-ray microdiffraction to trace the complex sequences of crystal growth in concrete from ancient Roman pier and breakwater sites. The results indicate that minerals continue to form over millennia as seawater percolates through, reinforcing the cementing matrix in a kind of regenerative process. Read more »
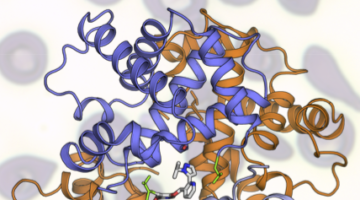
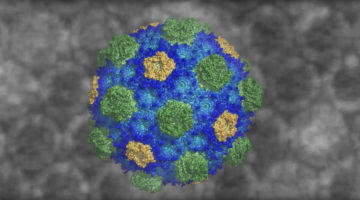
Structure of a Key Protein from the Zika Virus
The Zika virus (ZIKV) is a mosquito-borne pathogen recently linked to birth defects in infants. At the ALS, researchers have resolved the structure of a key ZIKV protein to 3.0 Å, an important step toward the rational design of drugs capable of disrupting viral functions and halting the spread of the disease. Read more »![]()
![]()
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- …
- 39
- Next Page »