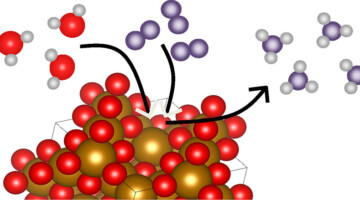
Ammonia is a critical ingredient in many important industrial and agricultural applications. The Haber–Bosch process is the primary process for large-scale ammonia production. A new study uses an experimental–theoretical approach to uncover how interfacial chemistry at the magnetite–water interface drives ammonia synthesis under ambient temperature and pressure. Read more »![]()
![]()
ALS Work Using Spectroscopy
These techniques are used to study the energies of particles that are emitted or absorbed by samples that are exposed to the light-source beam and are commonly used to determine the characteristics of chemical bonding and electron motion.
Separating an Electron into Waves of Spin and Charge
Researchers are exploring how a thin film can host a Tomonaga–Luttinger liquid, which separates an electron’s charge and spin. The research findings could contribute to the development of ultra-compact and energy-efficient technologies. Read more »
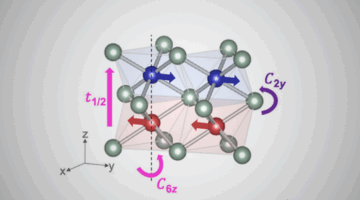
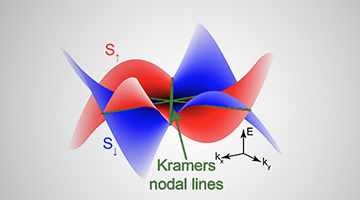
The Quest for an Altermagnet
Researchers determine the unique electronic structure of altermagnets, which offers numerous benefits in creating energy-efficient devices based on spin-polarized electron currents. Understanding how altermagnetism works could contribute to the development of next-generation memory, logic, or sensing devices that are faster and consume less power. Read more »
Designing Quantum Materials for Future Electronics
Researchers bring theory into practice and confirm a new material’s characteristics at the ALS. The study opens new opportunities to design a substance that renders extra “handles” on the electron—not just its charge, but its spin and valley—so we can build computers that are faster, cooler, and more energy-efficient compared to traditional electronics. Read more »
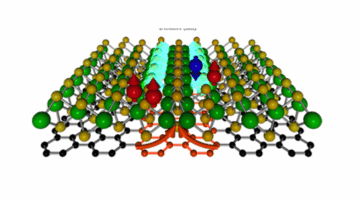
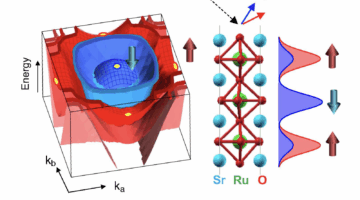
Pinpointing Magnetic Mysteries and Mechanisms in a Layered Perovskite
The strontium ruthenate family has a perovskite-like structure that can assemble into different configurations, offering an ideal way to study how the physics change as the material goes from 3D to 2D. In this study, researchers revealed how electrons with different spins behave in distinct layers of a three-layer magnetic material. The results deepen the field’s understanding of how magnetism emerges in layered materials, an important concept for future magnetic technologies and quantum electronic devices. Read more »![]()
![]()
Dehydration Key Element in Soil Microbe Evolution
A new study illustrates how microbes respond, in real time, to environmental stress, improving the research community’s knowledge of the hidden microbial engines that keep our planet running. Read more »
Operando probing dynamic migration of copper carbonyl during electrocatalytic CO2 reduction
In their work, Peidong Yang and colleagues reveal the dynamic evolution from faceted Cu nanocatalysts into metallic nanograins during CO2 reduction driven by the surface migration of electrogenerated copper carbonyl. Read more »
Multimetallic Systems Convey Cost-Effective Hydrogen Storage
A bimetallic material (Pd-Ni) produces hydrogen-active nanopockets that improve the efficiency and lower the cost of hydrogen storage systems. Mechanistic understanding of a Pd-Ni bimetallic system paves the way to design cost-effective hydrogen storage, opening new opportunities to develop reliable energy technologies necessary to advance the energy industry. Read more »![]()
![]()
Efficient Upcycling of Plastic Waste into Useful Liquid Fuels
Researchers found a way to turn single-use plastics (e.g., grocery bags and packaging) into useful liquid fuels, like components of gasoline or diesel, without needing high heat, rare metals, or added chemicals. The work presents a promising pathway to address the global plastic waste crisis, with both environmental and economic advantages. Read more »
A New Twist for Superconductivity in Bilayer Graphene
In a study of twisted bilayer graphene (TBG) systems, researchers found intriguing spectroscopic features in a superconducting “magic-angle” TBG—features that are absent in non-superconducting TBG. The results provide crucial information on superconductivity in magic-angle TBG for next-gen electronics and advanced energy technologies. Read more »![]()
![]()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- …
- 30
- Next Page »